
Identify the following structures which are present in the dioptrical region of the ommatidium of cockroaches.
A. Vitrellae, retinulea, rhabdome
B. Crystalline cone, retinulae, rhobdome
C. Lenticular cells, rhabdome, rhabdomeres
D. Lenticular cells, vitrellae, crystalline cone
Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint: Mechanoreceptors, chemoreceptors, thermoreceptors, and photoreceptors are the sense organs of a cockroach. Ocelli and compound eyes are photoreceptors. Compound eyes are black kidney-shaped and each eye consists of 2000 functional units called ommatidia.
Complete answer:
Each ommatidium is covered externally by a transparent hexagonal cuticular facet called the cornea. It is a biconvex, transparent, refractive part of the cuticle. The cornea is secreted by a pair of specialized epidermal cells called corneagen cells (or) lenticular cells. These cells later become withdrawn to the sides of the ommatidium as primary pigment cells that form an iris pigment sheath. Cornea converges light onto a crystalline cone. Four transparent more or less conical cells called vitrellae (or) cone cells lie below the corneagen cells. They surround and secrete a transparent conical structure called crystalline cones. It focuses the light on to the next part of the rhabdome. The part of the ommatidium from the cornea up to the extreme end of the crystalline cone forms the light focusing dioptrical region. Thus, a dioptrical region of the ommatidium of cockroach involves lenticular cells, vitrellae, and crystalline cones.
Figure 1: Vertical section of ommatidium of cockroach
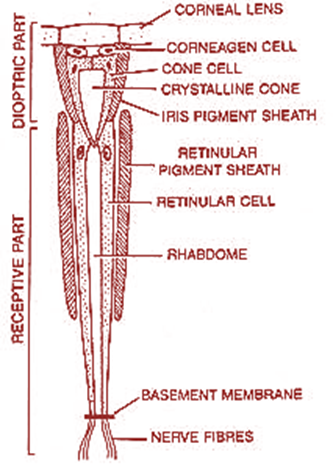
Additional Information: Inner ends of cone cells rest upon an elongated rod called rhabdome secreted surrounded by seven retinulae. The microvilli of each reticular cell collectively form a rhabdomere. The visual pigment is located within the microvilli. The rhabdomere fuse along the long axis of the ommatidium to form the rhabdome in the center.
So, The correct answer is Option A
Note: Inner ends of retinulae rest upon the basement membrane beyond which they are continuous with sensory nerve fibers of the optic nerve that extends up to the protocerebrum. Rhabdome and retinal cells constitute the region of the receptor of the eye. The retinulae are surrounded by seven secondary pigments cells that constitute the retinal pigment sheath.
Complete answer:
Each ommatidium is covered externally by a transparent hexagonal cuticular facet called the cornea. It is a biconvex, transparent, refractive part of the cuticle. The cornea is secreted by a pair of specialized epidermal cells called corneagen cells (or) lenticular cells. These cells later become withdrawn to the sides of the ommatidium as primary pigment cells that form an iris pigment sheath. Cornea converges light onto a crystalline cone. Four transparent more or less conical cells called vitrellae (or) cone cells lie below the corneagen cells. They surround and secrete a transparent conical structure called crystalline cones. It focuses the light on to the next part of the rhabdome. The part of the ommatidium from the cornea up to the extreme end of the crystalline cone forms the light focusing dioptrical region. Thus, a dioptrical region of the ommatidium of cockroach involves lenticular cells, vitrellae, and crystalline cones.
Figure 1: Vertical section of ommatidium of cockroach

Additional Information: Inner ends of cone cells rest upon an elongated rod called rhabdome secreted surrounded by seven retinulae. The microvilli of each reticular cell collectively form a rhabdomere. The visual pigment is located within the microvilli. The rhabdomere fuse along the long axis of the ommatidium to form the rhabdome in the center.
So, The correct answer is Option A
Note: Inner ends of retinulae rest upon the basement membrane beyond which they are continuous with sensory nerve fibers of the optic nerve that extends up to the protocerebrum. Rhabdome and retinal cells constitute the region of the receptor of the eye. The retinulae are surrounded by seven secondary pigments cells that constitute the retinal pigment sheath.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




