
Identify the A and B in the following reaction:
$C{H_3} - CH = C{H_2}\xrightarrow{{HBr}}A\xrightarrow{{KOH{\text{ }}acl}}B$
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: Markovnikov rule states that in addition of protic acid $\left( {HX} \right)$ to an unsymmetrical alkene, acidic hydrogen gets attached to that carbon atom of double bond which has more hydrogen atoms and halide group gets attached to that carbon atom of double bond which is attached with more alkene groups.
Complete step by step answer:
Reaction given in this question is $C{H_3} - CH = C{H_2}\xrightarrow{{HBr}}A\xrightarrow{{KOH{\text{ }}acl}}B$ and we have to identify A and B in this reaction.
In the first part of the reaction, that is, $C{H_3} - CH = C{H_2}\xrightarrow{{HBr}}A$ anti markovnikov rule will be followed. Markonikov rule states that in addition of protic acid $\left( {HX} \right)$ to an unsymmetrical alkene, acidic hydrogen gets attached to that carbon atom of double bond which has more hydrogen atoms and halide group $\left( X \right)$ gets attached to that carbon atom of double bond which is attached with more alkene groups. In this reactant, the carbon atom of $C{H_2}$ has more hydrogen atoms as compared to $CH$. So, according to anti markovnikov rule hydrogen atom will be attached to $C{H_2}$ group and bromine atom will be attached to $CH$ group. So, the resulting compound that is A will be:
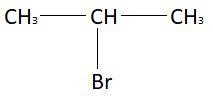
The chemical formula of this compound is ${C_3}{H_7}Br$.
So the first step of reaction is:
$C{H_3} - CH = C{H_2}\xrightarrow{{HBr}}C{H_3} - CHBr - C{H_3}$
Second step of reaction is:
$C{H_3} - CHBr - C{H_3}\xrightarrow{{KOH{\text{ }}acl}}B$
In this reaction halogen of the reactant will be replaced with $OH$ group of $KOH$ and $KBr$ will be released. So, B is ${C_3}{H_7}OH$ and the complete reaction is:
$C{H_3} - CH = C{H_2}\xrightarrow{{HBr}}C{H_3} - CHBr - C{H_3}\xrightarrow{{KOH{\text{ }}acl}}C{H_3} - CHOH - C{H_3}$
Hence A and B are ${C_3}{H_7}Br$ and ${C_3}{H_7}OH$ respectively.
Note:
Anti-markovnikov rule is opposite to the markovnikov rule. According to Anti-markovnikov rule hydrogen atom of $HX$ gets attached to that carbon atom of double bonded carbon which has less number of hydrogen atoms and halogen gets attached to that carbon atom of double bonded carbon atom which has more number of hydrogen atoms.
Complete step by step answer:
Reaction given in this question is $C{H_3} - CH = C{H_2}\xrightarrow{{HBr}}A\xrightarrow{{KOH{\text{ }}acl}}B$ and we have to identify A and B in this reaction.
In the first part of the reaction, that is, $C{H_3} - CH = C{H_2}\xrightarrow{{HBr}}A$ anti markovnikov rule will be followed. Markonikov rule states that in addition of protic acid $\left( {HX} \right)$ to an unsymmetrical alkene, acidic hydrogen gets attached to that carbon atom of double bond which has more hydrogen atoms and halide group $\left( X \right)$ gets attached to that carbon atom of double bond which is attached with more alkene groups. In this reactant, the carbon atom of $C{H_2}$ has more hydrogen atoms as compared to $CH$. So, according to anti markovnikov rule hydrogen atom will be attached to $C{H_2}$ group and bromine atom will be attached to $CH$ group. So, the resulting compound that is A will be:

The chemical formula of this compound is ${C_3}{H_7}Br$.
So the first step of reaction is:
$C{H_3} - CH = C{H_2}\xrightarrow{{HBr}}C{H_3} - CHBr - C{H_3}$
Second step of reaction is:
$C{H_3} - CHBr - C{H_3}\xrightarrow{{KOH{\text{ }}acl}}B$
In this reaction halogen of the reactant will be replaced with $OH$ group of $KOH$ and $KBr$ will be released. So, B is ${C_3}{H_7}OH$ and the complete reaction is:
$C{H_3} - CH = C{H_2}\xrightarrow{{HBr}}C{H_3} - CHBr - C{H_3}\xrightarrow{{KOH{\text{ }}acl}}C{H_3} - CHOH - C{H_3}$
Hence A and B are ${C_3}{H_7}Br$ and ${C_3}{H_7}OH$ respectively.
Note:
Anti-markovnikov rule is opposite to the markovnikov rule. According to Anti-markovnikov rule hydrogen atom of $HX$ gets attached to that carbon atom of double bonded carbon which has less number of hydrogen atoms and halogen gets attached to that carbon atom of double bonded carbon atom which has more number of hydrogen atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




