
Identify phenacetin from the following:
(A)
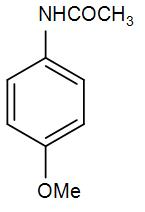
(B)
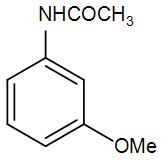
(C)
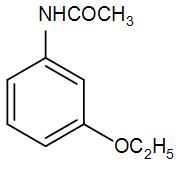
(D)
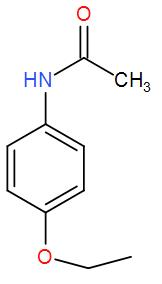




Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint: To answer this you should know that phenacetin belongs to the class of acetamide. It is prepared by Williamson’s ether synthesis and thus is a derivative of ether too. We can write its general formula as ${{C}_{10}}{{H}_{13}}N{{O}_{2}}$. You can use this to determine its structure.
Complete step by step solution:
To answer this, firstly let us discuss the structure of phenacetin.
Phenacetin is a derivative of acetamide and an ether. It can be derived from Williamson’s ether synthesis reaction. It can be derived from N-phenylacetamide, 4-ethoxyaniline and paracetamol.
It is used as an analgesic. It is a painkiller and it was the world's first synthetic pharmaceutical drug. Its effects are due to its actions on the sensory tract of the spinal cord.
Now, let us see its structure.
It is an organic compound and it belongs to the class of acetamide. An acetamide is an amide derivation of acetic acid. In phenacetin, one hydrogen atom of the group is substituted by a 4 – ethoxy phenyl group. We can draw its structure as-
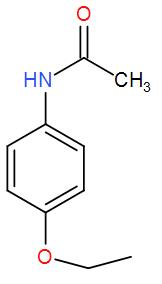
So, we can understand from the above discussion that the correct answer is option (D).
Note: In Williamson’s ether synthesis, an alkoxide anion undergoes substitution nucleophilic bimolecular reaction with an alkyl halide and forms ether. We generally carry out this reaction for the formation of unsymmetrical ethers. We will take an example to understand the mechanism of this reaction-
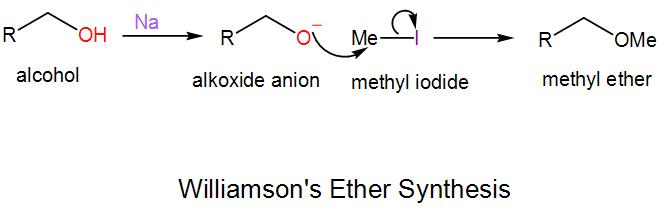
Here we have to use a strong base, $NaH$ to form the alkoxide anion as alcohols are a weak acid and methyl iodide is used here which is the electrophile.
Complete step by step solution:
To answer this, firstly let us discuss the structure of phenacetin.
Phenacetin is a derivative of acetamide and an ether. It can be derived from Williamson’s ether synthesis reaction. It can be derived from N-phenylacetamide, 4-ethoxyaniline and paracetamol.
It is used as an analgesic. It is a painkiller and it was the world's first synthetic pharmaceutical drug. Its effects are due to its actions on the sensory tract of the spinal cord.
Now, let us see its structure.
It is an organic compound and it belongs to the class of acetamide. An acetamide is an amide derivation of acetic acid. In phenacetin, one hydrogen atom of the group is substituted by a 4 – ethoxy phenyl group. We can draw its structure as-

So, we can understand from the above discussion that the correct answer is option (D).
Note: In Williamson’s ether synthesis, an alkoxide anion undergoes substitution nucleophilic bimolecular reaction with an alkyl halide and forms ether. We generally carry out this reaction for the formation of unsymmetrical ethers. We will take an example to understand the mechanism of this reaction-
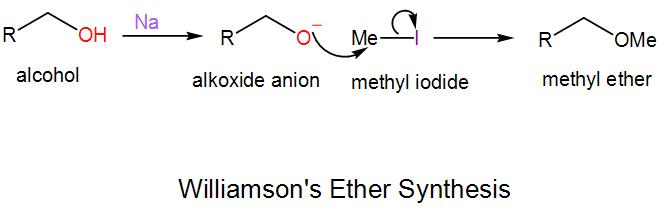
Here we have to use a strong base, $NaH$ to form the alkoxide anion as alcohols are a weak acid and methyl iodide is used here which is the electrophile.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




