
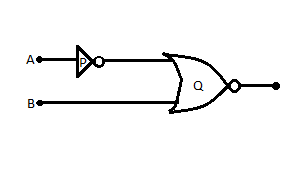
(i) Write the truth table for logic gates marked $P$ and $Q$ in the given circuit.
(ii) Write the truth table for the circuit.

Answer
578.7k+ views
Hint: The gate marked $P$ is a $NOT$ gate.
The gate marked $Q$ is a $NOR$ gate.
$A$ when passed through $NOT$ gate returns the inverted output.
When $B$ and the output of $A$ through $NOT$ gate are passed through $NOR$ gate, the output returned is high if and only if both the inputs are low.
Complete step by step solution:
(i) Gate marked $P$ is a $NOT$ GATE. It inverts the input and returns the value as output. Therefore, if the input is high, output is low and when input is low, output is high.
The logic equation of $NOT$ gate is as follows:
\[Y = \overline A \]
Where, $Y$ is the output and $A$ is the input.
Truth table of $NOT$ GATE IS:
The gate marked $Q$ is a $NOR$ gate. It gives a high output when both the inputs are low, and a low output when one or both the inputs are high.
The logic equation of $NOR$ gate is as follows:
\[Y = \overline {A + B} \]
Where, $Y$ is the output while $A$ and $B$ are the input.
Truth table of $NOR$ GATE IS:
(ii) The given circuit is a combinational circuit made out of basic logic gates:
The logic expression for the circuit is:
\[Y = \overline {\overline A + B} \]
Where, $Y$ is the output while both $A$ and $B$ are inputs.
Truth table for $NOR$ gate is:
Note: $NOT$ is a single input logic gate and is also known as the Inverter.
A $NOR$ gate can have two or more inputs and is the result of negation of $OR$ gate.
Remember that the final circuit takes inverted value of input $A$ as its own input.
The gate marked $Q$ is a $NOR$ gate.
$A$ when passed through $NOT$ gate returns the inverted output.
When $B$ and the output of $A$ through $NOT$ gate are passed through $NOR$ gate, the output returned is high if and only if both the inputs are low.
Complete step by step solution:
(i) Gate marked $P$ is a $NOT$ GATE. It inverts the input and returns the value as output. Therefore, if the input is high, output is low and when input is low, output is high.
The logic equation of $NOT$ gate is as follows:
\[Y = \overline A \]
Where, $Y$ is the output and $A$ is the input.
Truth table of $NOT$ GATE IS:
| INPUT( $A$ ) | OUTPUT( $Y$ ) |
| $1$ | $0$ |
| $0$ | $1$ |
The gate marked $Q$ is a $NOR$ gate. It gives a high output when both the inputs are low, and a low output when one or both the inputs are high.
The logic equation of $NOR$ gate is as follows:
\[Y = \overline {A + B} \]
Where, $Y$ is the output while $A$ and $B$ are the input.
Truth table of $NOR$ GATE IS:
| Input 1 ( $A$ ) | Input 2 ( $B$ ) | \[Y = \overline {A + B} \] |
| $0$ | $0$ | $1$ |
| $0$ | $1$ | $0$ |
| $1$ | $0$ | $0$ |
| $1$ | $1$ | $0$ |
(ii) The given circuit is a combinational circuit made out of basic logic gates:
The logic expression for the circuit is:
\[Y = \overline {\overline A + B} \]
Where, $Y$ is the output while both $A$ and $B$ are inputs.
Truth table for $NOR$ gate is:
| INPUT FOR P ( $A$ ) | INPUT1 ( $\overline A $ ) | INPUT2 ( $B$ ) | OUTPUT \[Y = \overline {\overline A + B} \] |
| $0$ | $1$ | $0$ | $0$ |
| $0$ | $1$ | $1$ | $0$ |
| $1$ | $0$ | $0$ | $1$ |
| $1$ | $0$ | $1$ | $0$ |
Note: $NOT$ is a single input logic gate and is also known as the Inverter.
A $NOR$ gate can have two or more inputs and is the result of negation of $OR$ gate.
Remember that the final circuit takes inverted value of input $A$ as its own input.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




