
(i) Write Hell-Volhard- Zelinsky reaction.
(ii) Write cross-aldol condensation
(iii) Ethanoic acid is a weaker acid than benzoic acid. Why?
Answer
580.5k+ views
Hint: (i) Hell-Volhard- Zelinsky reaction is alpha halogenation of carboxylic acids.
(ii) Aldol condensation reaction is given by aldehydes or ketones having alpha hydrogen atoms. In the presence of base, two molecules of carbonyl compound undergo condensation reaction.
(iii) When an electron withdrawing group is present, the acid strength increases.
Complete step by step answer:
(i) In the Hell-Volhard- Zelinsky reaction, carboxylic acids are brominated (or chlorinated) on the alpha position. Carboxylic acid reacts with bromine or chlorine in presence of a small amount of red phosphorus.
\[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{COOH }}\xrightarrow[{\text{P}}]{{{\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_2}}}{\text{ C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CHBrCOOH }}\xrightarrow[{\text{P}}]{{{\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_2}}}{\text{ C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CB}}{{\text{r}}_2}{\text{COOH }}\]
Since only two alpha hydrogen atoms are present, the reaction stops at dibromination stage.
(ii) When two different carbonyl compounds are used for aldol condensation, it is known as cross aldol condensation. If both carbonyl compounds have alpha hydrogen atoms, then crossed aldol condensation gives four different products. Given below are four different products obtained when ethanal and propanal undergo cross aldol condensation.
\[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CHO + C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CHO }}\xrightarrow[{\left( {ii} \right){\text{ heat}}}]{{\left( i \right){\text{ dil NaOH}}}}\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CH}} = {\text{CHCHO + C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CH = C}}\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right){\text{CHO}}} \\
{{\text{ + C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CH = C}}\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right){\text{CHO + C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CH = CHCHO}}}
\end{array}\]
Write the individual reaction for the formation of each of the products of the above crossed-aldol condensation reaction.
\[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CHO + C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CHO }}\xrightarrow[{(ii)heat}]{{(i)dilNaOH}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CH}} = {\text{CHCHO}} \\
{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CHO + C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CHO }}\xrightarrow[{(ii)heat}]{{(i)dilNaOH}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CH = C}}\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right){\text{CHO}} \\
{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CHO + C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CHO }}\xrightarrow[{(ii)heat}]{{(i)dilNaOH}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CH = C}}\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right){\text{CHO}} \\
{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CHO + C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CHO }}\xrightarrow[{(ii)heat}]{{(i)dilNaOH}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CH = CHCHO}} \\ \]
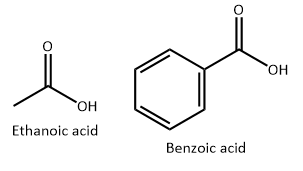
(iii) The strength of the acid depends on the ease with which it can lose a proton. Greater is the ease with which an acid loses a proton, greater is the acid strength. Benzoic acid loses a proton to form benzoate ions. The benzoate ion is stabilised by the electron withdrawing aryl group. However in the case of ethanoic acid, the electron withdrawing effect of the methyl group is not that significant. Hence, ethanoic acid is a weaker acid than benzoic acid.
Note: (i) If no alpha hydrogen atom is present, then carboxylic acids will not give Hell-Volhard- Zelinsky reaction.
(ii) If no alpha hydrogen atom is present, then carbonyl compounds will not give aldol condensation.
(iii) When electron releasing substituent is present, it decreases the acid strength of carboxylic acid.
(ii) Aldol condensation reaction is given by aldehydes or ketones having alpha hydrogen atoms. In the presence of base, two molecules of carbonyl compound undergo condensation reaction.
(iii) When an electron withdrawing group is present, the acid strength increases.
Complete step by step answer:
(i) In the Hell-Volhard- Zelinsky reaction, carboxylic acids are brominated (or chlorinated) on the alpha position. Carboxylic acid reacts with bromine or chlorine in presence of a small amount of red phosphorus.
\[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{COOH }}\xrightarrow[{\text{P}}]{{{\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_2}}}{\text{ C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CHBrCOOH }}\xrightarrow[{\text{P}}]{{{\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_2}}}{\text{ C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CB}}{{\text{r}}_2}{\text{COOH }}\]
Since only two alpha hydrogen atoms are present, the reaction stops at dibromination stage.
(ii) When two different carbonyl compounds are used for aldol condensation, it is known as cross aldol condensation. If both carbonyl compounds have alpha hydrogen atoms, then crossed aldol condensation gives four different products. Given below are four different products obtained when ethanal and propanal undergo cross aldol condensation.
\[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CHO + C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CHO }}\xrightarrow[{\left( {ii} \right){\text{ heat}}}]{{\left( i \right){\text{ dil NaOH}}}}\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CH}} = {\text{CHCHO + C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CH = C}}\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right){\text{CHO}}} \\
{{\text{ + C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CH = C}}\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right){\text{CHO + C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CH = CHCHO}}}
\end{array}\]
Write the individual reaction for the formation of each of the products of the above crossed-aldol condensation reaction.
\[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CHO + C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CHO }}\xrightarrow[{(ii)heat}]{{(i)dilNaOH}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CH}} = {\text{CHCHO}} \\
{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CHO + C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CHO }}\xrightarrow[{(ii)heat}]{{(i)dilNaOH}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CH = C}}\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right){\text{CHO}} \\
{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CHO + C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CHO }}\xrightarrow[{(ii)heat}]{{(i)dilNaOH}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CH = C}}\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right){\text{CHO}} \\
{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CHO + C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CHO }}\xrightarrow[{(ii)heat}]{{(i)dilNaOH}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CH = CHCHO}} \\ \]
(iii) The strength of the acid depends on the ease with which it can lose a proton. Greater is the ease with which an acid loses a proton, greater is the acid strength. Benzoic acid loses a proton to form benzoate ions. The benzoate ion is stabilised by the electron withdrawing aryl group. However in the case of ethanoic acid, the electron withdrawing effect of the methyl group is not that significant. Hence, ethanoic acid is a weaker acid than benzoic acid.

Note: (i) If no alpha hydrogen atom is present, then carboxylic acids will not give Hell-Volhard- Zelinsky reaction.
(ii) If no alpha hydrogen atom is present, then carbonyl compounds will not give aldol condensation.
(iii) When electron releasing substituent is present, it decreases the acid strength of carboxylic acid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




