
(i) What type of isomerism is shown by the complex $\left[ {{\text{Cr}}{{\left( {{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}} \right)}_{\text{6}}}} \right]{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$.
(ii) On the basis of crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration for ${\text{4d}}$ ion if ${\Delta _0} > {\text{P}}$
(iii) Write the hybridization and shape of ${\left[ {{\text{Co}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{6}}}} \right]^{3 - }}$(Atomic number of ${\text{Co = 27}}$).
Answer
581.1k+ views
Hint: The compounds having the same chemical formula but a different arrangement of atoms are known as isomers. CFT shows the splitting of metal orbitals. ${\Delta _0} > {\text{P}}$ means the pairing energy is low, so electrons will be paired. The orbitals of metal combine to form the hybrid orbitals. Ligand donates electron pairs in these hybrid orbitals.
Complete step by step answer:
(i) If the counter ion present in the complex can work as a ligand then the complex shows ionization isomerism. In this isomerism, the counter ion replaces the ligand so, the ligand becomes a counter ion, and the counter ion becomes a ligand.
If the ligand which has to be replaced is water then the isomerism is known as a solvent or hydrate isomerism.
The solvent isomerism in $\left[ {{\text{Cr}}{{\left( {{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}} \right)}_{\text{6}}}} \right]{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ complex is shown as follows:$\left[ {{\text{Cr}}{{\left( {{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}} \right)}_{\text{6}}}} \right]{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ or $\left[ {{\text{Cr}}{{\left( {{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}} \right)}_5}{\text{Cl}}} \right]{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_2}{\text{.}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$
So, $\left[ {{\text{Cr}}{{\left( {{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}} \right)}_{\text{6}}}} \right]{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ shows solvent isomerism.
(ii) Crystal field theory tells the splitting of metal orbitals in presence of ligand field. The d-orbitals of the metal remain degenerate in absence of ligand field and split in presence of ligand field.
The splitting of d-orbitals and filling of electrons is shown as follows:
The paring energy is low, so the electrons will pair.
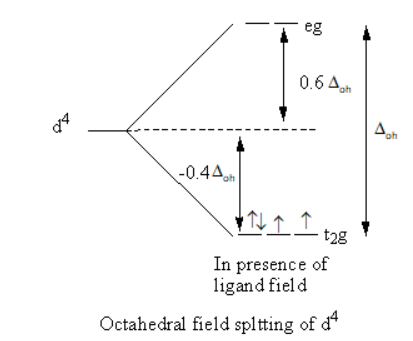
So, the electronic configuration of ${\text{4d}}$ is $t_{2g}^4e_g^0$ .
(iii) According to the valence bond theory, the orbitals of metals combine to form orbitals of the same energy. These orbitals are known as hybrid orbital. Each ligand donates an electron pair to a hybrid orbital.
Based on the number of electron pairs the hybridization and shape is determined.
The hybridization in${\left[ {{\text{Co}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{6}}}} \right]^{3 - }}$is as follows
Valence electronic configuration of ${\text{C}}{{\text{o}}^{3 + }} = 3{d^7}$.
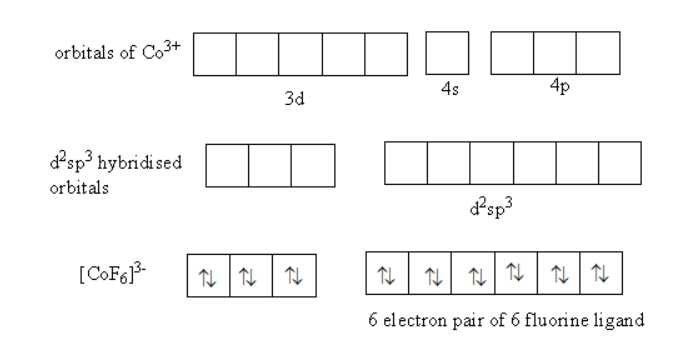
A total of six electron pairs are present in six hybridized orbitals so, the hybridization of the complex is ${{\text{d}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ and shape is octahedral.
Therefore, $\left[ {{\text{Cr}}{{\left( {{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}} \right)}_{\text{6}}}} \right]{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ complex shows solvent isomerism. The electronic configuration of ${\text{4d}}$ is $t_{2g}^4e_g^0$ . The hybridization of ${\left[ {{\text{Co}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{6}}}} \right]^{3 - }}$is ${{\text{d}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ and shape is octahedral.
Note:
Solvent isomerism is the same as ionization isomerism. ${\Delta _0} > {\text{P}}$means the energy gap is high, so electrons cannot go in the upper energy level. The number of hybrid orbitals also represents the type of hybridization.
Complete step by step answer:
(i) If the counter ion present in the complex can work as a ligand then the complex shows ionization isomerism. In this isomerism, the counter ion replaces the ligand so, the ligand becomes a counter ion, and the counter ion becomes a ligand.
If the ligand which has to be replaced is water then the isomerism is known as a solvent or hydrate isomerism.
The solvent isomerism in $\left[ {{\text{Cr}}{{\left( {{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}} \right)}_{\text{6}}}} \right]{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ complex is shown as follows:$\left[ {{\text{Cr}}{{\left( {{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}} \right)}_{\text{6}}}} \right]{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ or $\left[ {{\text{Cr}}{{\left( {{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}} \right)}_5}{\text{Cl}}} \right]{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_2}{\text{.}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$
So, $\left[ {{\text{Cr}}{{\left( {{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}} \right)}_{\text{6}}}} \right]{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ shows solvent isomerism.
(ii) Crystal field theory tells the splitting of metal orbitals in presence of ligand field. The d-orbitals of the metal remain degenerate in absence of ligand field and split in presence of ligand field.
The splitting of d-orbitals and filling of electrons is shown as follows:
The paring energy is low, so the electrons will pair.

So, the electronic configuration of ${\text{4d}}$ is $t_{2g}^4e_g^0$ .
(iii) According to the valence bond theory, the orbitals of metals combine to form orbitals of the same energy. These orbitals are known as hybrid orbital. Each ligand donates an electron pair to a hybrid orbital.
Based on the number of electron pairs the hybridization and shape is determined.
The hybridization in${\left[ {{\text{Co}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{6}}}} \right]^{3 - }}$is as follows
Valence electronic configuration of ${\text{C}}{{\text{o}}^{3 + }} = 3{d^7}$.

A total of six electron pairs are present in six hybridized orbitals so, the hybridization of the complex is ${{\text{d}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ and shape is octahedral.
Therefore, $\left[ {{\text{Cr}}{{\left( {{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}} \right)}_{\text{6}}}} \right]{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ complex shows solvent isomerism. The electronic configuration of ${\text{4d}}$ is $t_{2g}^4e_g^0$ . The hybridization of ${\left[ {{\text{Co}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{6}}}} \right]^{3 - }}$is ${{\text{d}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ and shape is octahedral.
Note:
Solvent isomerism is the same as ionization isomerism. ${\Delta _0} > {\text{P}}$means the energy gap is high, so electrons cannot go in the upper energy level. The number of hybrid orbitals also represents the type of hybridization.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




