
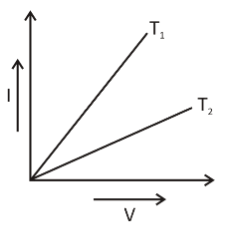
$I - V$ graph for a metallic wire at two different temperatures ${T_1}$ and ${T_2}$ is as shown in the figure. Which of the two temperatures is lower and why?

Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint:Here we have to apply the concepts of temperature dependence on resistance. In metal conductors, owing to the interaction of electrons between atoms, electrical current flows. Some collide with gases, other electrons or impurities, as electrons pass through a metal conductor. Such collisions cause resistance and heat generation. It allows atoms to vibrate further by heating the metal conductor, which in turn makes it more difficult for the electrons to flow, raising resistance.
Complete answer:
The resistance of all pure metals increases linearly over a small temperature range with increases in temperature. The ions are virtually stationary at a low temperature. The ions within the metal gain energy as the temperature increases and continue to oscillate across their mean locations. These vibrating ions collide with the electrons, but with elevated temperatures, resistance increases.
From the figure we can observe that the slope of ${T_1}$ is greater than ${T_2}$.
Since, it is a $V - I$ graph; its slope gives conductance i.e. $\dfrac{1}{R}$.
Hence,
$
\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} > \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} \\
\therefore{R_2} > {R_1} \\
$
Since, we know that resistance of metal increases with increase in temperature
Therefore, ${T_2} > {T_1}$
So, temperature ${T_1}$ is lower as the resistance is smaller.
Additional information:
Ohm's Law teaches us that the current passing through the conductor is directly proportional to the voltage through it while a conductor is at a steady temperature. The gradient of the straight-line graph is aligned with the conductor’s resistance as $V = I \times R$. Conductivity is a calculation of the capacity of the material to conduct electrical current, which is equal to the reciprocal resistance of the material.
Note:For the change in temperature, the electrical resistance alters. Not only does the resistance rise with the increase in temperature, but in certain situations, it also decreases. In fact, the amount of change in resistance due to temperature variations is different for the various types of materials.
Complete answer:
The resistance of all pure metals increases linearly over a small temperature range with increases in temperature. The ions are virtually stationary at a low temperature. The ions within the metal gain energy as the temperature increases and continue to oscillate across their mean locations. These vibrating ions collide with the electrons, but with elevated temperatures, resistance increases.
From the figure we can observe that the slope of ${T_1}$ is greater than ${T_2}$.
Since, it is a $V - I$ graph; its slope gives conductance i.e. $\dfrac{1}{R}$.
Hence,
$
\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} > \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} \\
\therefore{R_2} > {R_1} \\
$
Since, we know that resistance of metal increases with increase in temperature
Therefore, ${T_2} > {T_1}$
So, temperature ${T_1}$ is lower as the resistance is smaller.
Additional information:
Ohm's Law teaches us that the current passing through the conductor is directly proportional to the voltage through it while a conductor is at a steady temperature. The gradient of the straight-line graph is aligned with the conductor’s resistance as $V = I \times R$. Conductivity is a calculation of the capacity of the material to conduct electrical current, which is equal to the reciprocal resistance of the material.
Note:For the change in temperature, the electrical resistance alters. Not only does the resistance rise with the increase in temperature, but in certain situations, it also decreases. In fact, the amount of change in resistance due to temperature variations is different for the various types of materials.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




