
(i) How a polaroid polarised and unpolarised light. Describe briefly, with the help of a diagram, the polarization of light by reflection form a transparent medium.
(ii) Two polaroid ‘A’ and ‘B’ are kept in crossed position. The intensity of polaroid light transmitted by polaroid B reduces to 1/8th of the intensity of unpolarized light incident of A. For this How should a third polaroid ‘C’ be placed between them?
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: Whenever the incident rays of intensity $I$ initially unpolarized pass through the polaroid, then the intensity will become $\dfrac{I}{2}$ and further this rays pass to another polaroid then intensity again become half of the initial ray that is it now become $\dfrac{I}{4}$.
We will also use Malus law which states that when an incident ray of intensity $\dfrac{I}{2}$ coming from polaroid 1 falls on the polaroid 2 which is inclined at an angle $\theta $ to polaroid 1 then the output intensity become ${I_o} = \dfrac{I}{2}{\cos ^2}\theta $.
Complete solution step by step:
(i) When an unpolarized light is passed through a polaroid or whenever unpolarised light is incident on the boundary between two transparent media, then the light wave gets polarized linearly with the electric field vector performing to and fro motion at an angle of ninety degree to the aligned molecules (pass-axis of polaroid). The reflected light gets partially or completely polarised. When reflected light is perpendicular to the refracted light, the reflected light is a completely polarised light.
The figure below shows you from a transparent medium polarisation by reflection. When light is reflected, it becomes linearly polarized with an electric field vector perpendicular to the plane of incidence.
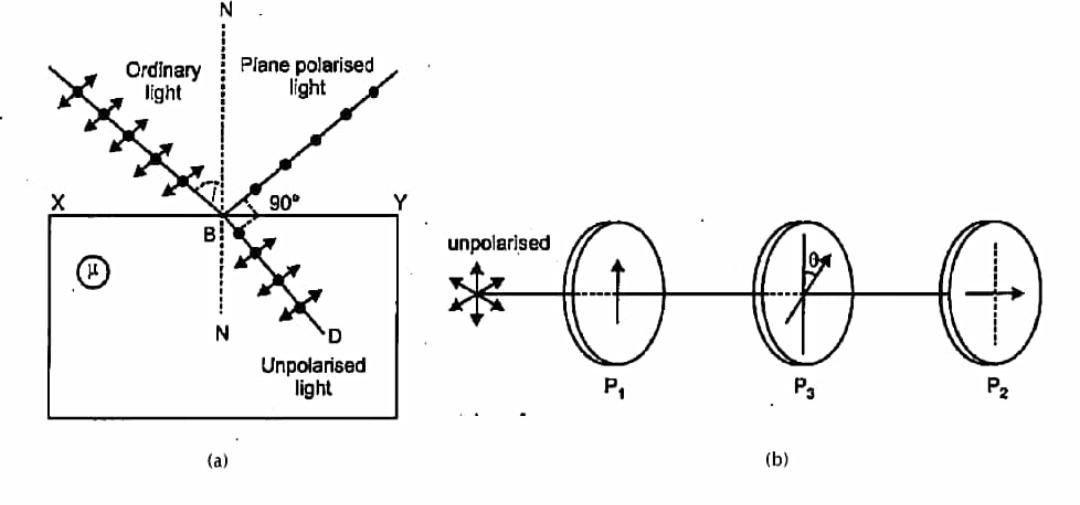
(ii) When the unpolarised light pass through polaroid A its intensity become $\dfrac{I}{2}$
Now polaroid C is placed at an angle $\theta $ with respect to polaroid A then applying Malus Law to polaroid C we get our output intensity as follows:
${I_2} = \dfrac{I}{2}{\cos ^2}\theta $
Now $\dfrac{\pi }{2} - \theta $ is the angle between polaroid B and polaroid, again applying Malus Law to polaroid B, ${I_3} = {I_2}{\cos ^2}\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2} - \theta } \right) = {I_2}{\sin ^2}\theta $
Putting the value of ${I_2}$ in the above equation we get
${I_3} = \dfrac{I}{2}{\cos ^2}\theta {\sin ^2}\theta $
Applying some trigonometry to reduce the expression we get
${I_3} = \dfrac{I}{8}{\sin ^2}2\theta $
Given that ${I_3} = \dfrac{I}{8}$
Putting the value of ${I_3}$
$
\dfrac{I}{8} = \dfrac{I}{8}{\sin ^2}2\theta \\
{\sin ^2}2\theta = 1 \\
2\theta = \dfrac{\pi }{2} \\
\theta = \dfrac{\pi }{4} \\
\\
$
Hence the value of $\theta $ is $\dfrac{\pi }{4}$.
Note: Polarized light which are also called light waves, here the vibrations occur in a single plane. There are a variety of methods of polarizing light. Some of these are Polarisation by transmission, Polarisation by reflection, Polarisation by refraction, Polarisation by scattering.
We will also use Malus law which states that when an incident ray of intensity $\dfrac{I}{2}$ coming from polaroid 1 falls on the polaroid 2 which is inclined at an angle $\theta $ to polaroid 1 then the output intensity become ${I_o} = \dfrac{I}{2}{\cos ^2}\theta $.
Complete solution step by step:
(i) When an unpolarized light is passed through a polaroid or whenever unpolarised light is incident on the boundary between two transparent media, then the light wave gets polarized linearly with the electric field vector performing to and fro motion at an angle of ninety degree to the aligned molecules (pass-axis of polaroid). The reflected light gets partially or completely polarised. When reflected light is perpendicular to the refracted light, the reflected light is a completely polarised light.
The figure below shows you from a transparent medium polarisation by reflection. When light is reflected, it becomes linearly polarized with an electric field vector perpendicular to the plane of incidence.

(ii) When the unpolarised light pass through polaroid A its intensity become $\dfrac{I}{2}$
Now polaroid C is placed at an angle $\theta $ with respect to polaroid A then applying Malus Law to polaroid C we get our output intensity as follows:
${I_2} = \dfrac{I}{2}{\cos ^2}\theta $
Now $\dfrac{\pi }{2} - \theta $ is the angle between polaroid B and polaroid, again applying Malus Law to polaroid B, ${I_3} = {I_2}{\cos ^2}\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2} - \theta } \right) = {I_2}{\sin ^2}\theta $
Putting the value of ${I_2}$ in the above equation we get
${I_3} = \dfrac{I}{2}{\cos ^2}\theta {\sin ^2}\theta $
Applying some trigonometry to reduce the expression we get
${I_3} = \dfrac{I}{8}{\sin ^2}2\theta $
Given that ${I_3} = \dfrac{I}{8}$
Putting the value of ${I_3}$
$
\dfrac{I}{8} = \dfrac{I}{8}{\sin ^2}2\theta \\
{\sin ^2}2\theta = 1 \\
2\theta = \dfrac{\pi }{2} \\
\theta = \dfrac{\pi }{4} \\
\\
$
Hence the value of $\theta $ is $\dfrac{\pi }{4}$.
Note: Polarized light which are also called light waves, here the vibrations occur in a single plane. There are a variety of methods of polarizing light. Some of these are Polarisation by transmission, Polarisation by reflection, Polarisation by refraction, Polarisation by scattering.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




