
Why is hyperconjugation called no bond resonance?
Answer
506.4k+ views
Hint: Hyperconjugation is a special case of resonance which involves the delocalization of sigma electrons of the \[C - H\] bond of any alkyl group. To answer the above question one must understand the term first.
Complete answer:
Resonance is the delocalisation of electrons in a molecule from bond pairs to lone pair or vice-versa.
The delocalisation of \[\sigma \] -electrons or lone pairs of electrons into adjacent \[\pi \] -orbital or p-orbital is called hyperconjugation. It occurs due to overlapping of \[\sigma \] -bonding orbital or the orbital containing a lone pair with adjacent \[\pi \] -orbital or p-orbital. The displacement of \[\sigma \] –electrons towards the multiple bond occurs when there are \[hydrogens\] on the \[\alpha - carbon\] which is adjacent to the multiple bond. This results in polarisation of the multiple bond.
For a hyperconjugation there requires a condition which is, there must be an \[\alpha - CH\] group or a lone pair on atom adjacent to \[s{p^2}\] hybrid \[\;carbon\] or atoms like \[nitrogen\]
Let's understand why hyperconjugation is called no bond resonance with the help of \[propene\]
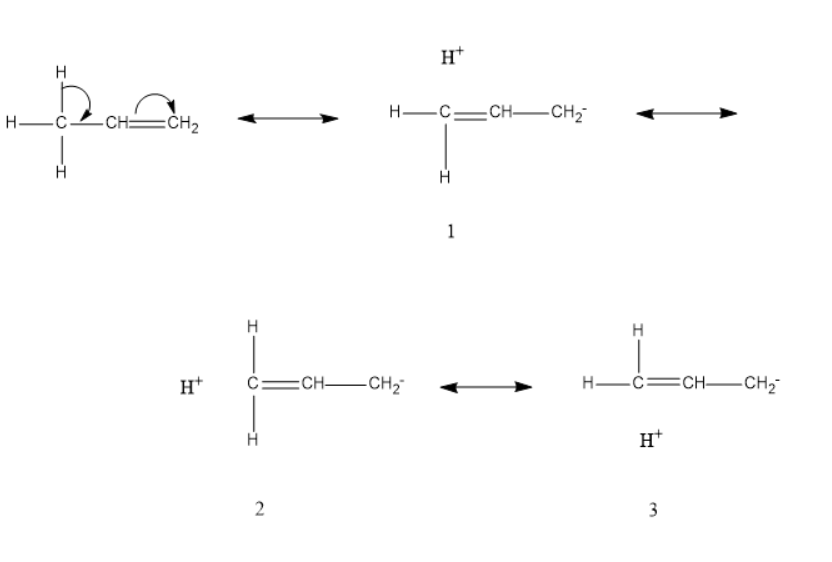
As we can see in hyperconjugative structure \[1,2,3\] that there is no bond between \[carbon\] and \[hydrogen\] atoms, hyperconjugation is called no bond resonance. As there is no bond between \[hydrogen\] and other atoms, therefore the bond broken is responsible for the possibility of the conjugation. There is no bond present from where the electrons are shifted. When the number of terminal \[hydrogen\] is more then the number of hyperconjugative structures are also more.
Note:
Hyperconjugation is an extension of resonance. Hyperconjugation involves delocalization of sigma bond electrons along with pi-bond electrons whereas resonance causes the delocalization through interaction between pi-bonds.
Complete answer:
Resonance is the delocalisation of electrons in a molecule from bond pairs to lone pair or vice-versa.
The delocalisation of \[\sigma \] -electrons or lone pairs of electrons into adjacent \[\pi \] -orbital or p-orbital is called hyperconjugation. It occurs due to overlapping of \[\sigma \] -bonding orbital or the orbital containing a lone pair with adjacent \[\pi \] -orbital or p-orbital. The displacement of \[\sigma \] –electrons towards the multiple bond occurs when there are \[hydrogens\] on the \[\alpha - carbon\] which is adjacent to the multiple bond. This results in polarisation of the multiple bond.
For a hyperconjugation there requires a condition which is, there must be an \[\alpha - CH\] group or a lone pair on atom adjacent to \[s{p^2}\] hybrid \[\;carbon\] or atoms like \[nitrogen\]
Let's understand why hyperconjugation is called no bond resonance with the help of \[propene\]

As we can see in hyperconjugative structure \[1,2,3\] that there is no bond between \[carbon\] and \[hydrogen\] atoms, hyperconjugation is called no bond resonance. As there is no bond between \[hydrogen\] and other atoms, therefore the bond broken is responsible for the possibility of the conjugation. There is no bond present from where the electrons are shifted. When the number of terminal \[hydrogen\] is more then the number of hyperconjugative structures are also more.
Note:
Hyperconjugation is an extension of resonance. Hyperconjugation involves delocalization of sigma bond electrons along with pi-bond electrons whereas resonance causes the delocalization through interaction between pi-bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




