
How many hydrogen atoms are in 5 molecules of isopropyl alcohol, $ {C_3}{H_7}O $ ?
Answer
533.1k+ views
Hint: The mole concept is very significant and useful in chemistry. It is actually the base of stoichiometry and it provides the best option to express the amounts of reactants as well as products that are consumed and formed during a chemical reaction.
Complete answer:
First of all the chemical formula given in question for isopropyl alcohol is wrong as the correct formula is $ {C_3}{H_7}OH $ not $ {C_3}{H_7}O $ . The structure for isopropyl alcohol is shown below:
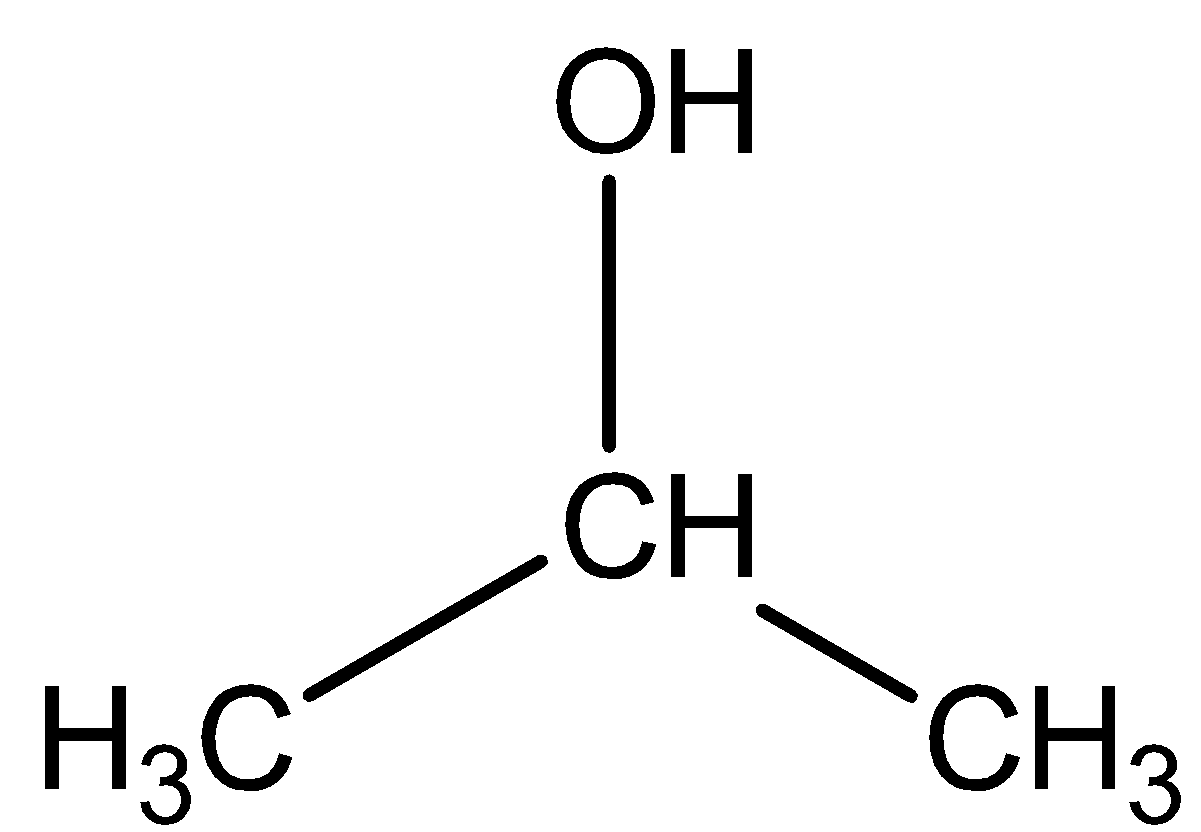
We know that $ {C_3}{H_7}OH $ actually represents one molecule of the compound i.e. isopropyl alcohol. It is clear from the chemical formula as well as from its chemical structure that one molecule of isopropyl alcohol comprises 8 Hydrogen atoms.
So applying the unitary method, 5 molecules of isopropyl alcohol will comprise Hydrogen atoms i.e. $ 8 \times 5 = 40 $ .
Hence, 40 hydrogen atoms are in 5 molecules of isopropyl alcohol, $ {C_3}{H_7}OH $ .
Additional information: Avogadro's number was actually obtained by dividing charge of one mole of electron by the charge of one single electron that equals $ 6.02214154 \times {10^{23}}\; $ particles per mole. 1 mole of any substance contains $ 6.023 \times {10^{23}}molecules $
Thus, the number of molecules of any substance can be identified by multiplying the number of moles with Avogadro's number i.e. $ 6.023 \times {10^{23}} $ . We can say:
$ Number{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}molecules = number{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}moles \times 6.023 \times {10^{23}} $
Note:
If we are provided with the given mass of the compound, we can calculate molecular mass of that compound by adding the relative atomic masses of each element present in that particular compound. Then using these two values, we can calculate the number of moles. Then from the number of moles, we can calculate the number of molecules.
Complete answer:
First of all the chemical formula given in question for isopropyl alcohol is wrong as the correct formula is $ {C_3}{H_7}OH $ not $ {C_3}{H_7}O $ . The structure for isopropyl alcohol is shown below:

We know that $ {C_3}{H_7}OH $ actually represents one molecule of the compound i.e. isopropyl alcohol. It is clear from the chemical formula as well as from its chemical structure that one molecule of isopropyl alcohol comprises 8 Hydrogen atoms.
So applying the unitary method, 5 molecules of isopropyl alcohol will comprise Hydrogen atoms i.e. $ 8 \times 5 = 40 $ .
Hence, 40 hydrogen atoms are in 5 molecules of isopropyl alcohol, $ {C_3}{H_7}OH $ .
Additional information: Avogadro's number was actually obtained by dividing charge of one mole of electron by the charge of one single electron that equals $ 6.02214154 \times {10^{23}}\; $ particles per mole. 1 mole of any substance contains $ 6.023 \times {10^{23}}molecules $
Thus, the number of molecules of any substance can be identified by multiplying the number of moles with Avogadro's number i.e. $ 6.023 \times {10^{23}} $ . We can say:
$ Number{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}molecules = number{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}moles \times 6.023 \times {10^{23}} $
Note:
If we are provided with the given mass of the compound, we can calculate molecular mass of that compound by adding the relative atomic masses of each element present in that particular compound. Then using these two values, we can calculate the number of moles. Then from the number of moles, we can calculate the number of molecules.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




