
Human blood type is determined by codominant alleles. There are three different alleles, known as \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{A}}}\], \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{B}}}\], and i. the \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{A}}}\] and \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{B}}}\], alleles are codominant, and the i allele is recessive.
The possible human phenotypes for blood group are type A, type B, type AB, and type O. type A and B individuals can be either homozygous (\[{{\text{I}}^{\text{A}}}\]\[{{\text{I}}^{\text{A}}}\]or \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{B}}}\]\[{{\text{I}}^{\text{B}}}\], respectively), or heterozygous (\[{{\text{I}}^{\text{A}}}\]i or \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{B}}}\]i, respectively).
A woman with type A blood and a man with type B blood could potentially have offspring with which of the following blood types?
A. Type A
B. Type B
C. Type AB
D. All of the above
Answer
548.1k+ views
Hint: The human blood grouping system, known as ABO blood grouping, is based upon the presence or absence of two antigens, namely A and B, which are present on the surface of RBCs. In response to these antigens, antibodies are also present in the plasma.
Complete answer:
There are four types of blood groups, A, B, AB, and O. Three major alleles for determining the blood groups are \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{A}}}\], \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{B}}}\], and i. The genotype of blood group A could be either \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{A}}}\]\[{{\text{I}}^{\text{A}}}\] or \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{A}}}\]i and similarly, blood group B could have genotype either of \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{B}}}\]\[{{\text{I}}^{\text{B}}}\] or \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{B}}}\]i. Blood group O is present if neither \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{A}}}\]nor \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{B}}}\]is present and in AB blood group both \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{A}}}\] and \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{B}}}\] are present. For blood group A, the antigen on the surface of RBC is A and the antibody would be anti-B. For blood group B, the antigen would be B and antibody, anti-A. For AB blood type, antigens on the surface of RBCs are both A and B and no antibody is present. For O blood type, there would be no antigen, but antibodies would be of both A and B types.
If a woman has a blood group of type A then it could be either in the form of homozygous alleles or heterozygous alleles, \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{A}}}\] or \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{A}}}\]i, respectively. Similarly, if the man has a blood type of B then the alleles could be homozygous or heterozygous.
In the homozygous condition, \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{A}}}\] from the female combines with \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{B}}}\] from the male to form AB blood type having genotype \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{A}}}\]\[{{\text{I}}^{\text{B}}}\]. But in the heterozygous condition, either \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{A}}}\] or i from the female could combine with either \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{B}}}\] or i from the male. Thus, the blood types that could be formed are A (\[{{\text{I}}^{\text{A}}}\]i), B (\[{{\text{I}}^{\text{B}}}\]i), AB (\[{{\text{I}}^{\text{A}}}\]\[{{\text{I}}^{\text{B}}}\]), or O (ii) as shown in the figure below.
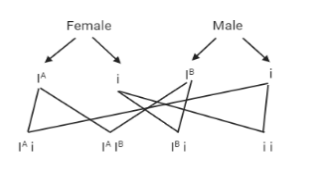
Hence, the correct answer is option (D)
Note: Apart from ABO blood grouping, Rh type of blood group determination is also very important. If the Rh antigen is present, then the individual is called Rh-positive, and if the antigen is absent, the individual is called Rh-negative.
Complete answer:
There are four types of blood groups, A, B, AB, and O. Three major alleles for determining the blood groups are \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{A}}}\], \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{B}}}\], and i. The genotype of blood group A could be either \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{A}}}\]\[{{\text{I}}^{\text{A}}}\] or \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{A}}}\]i and similarly, blood group B could have genotype either of \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{B}}}\]\[{{\text{I}}^{\text{B}}}\] or \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{B}}}\]i. Blood group O is present if neither \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{A}}}\]nor \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{B}}}\]is present and in AB blood group both \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{A}}}\] and \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{B}}}\] are present. For blood group A, the antigen on the surface of RBC is A and the antibody would be anti-B. For blood group B, the antigen would be B and antibody, anti-A. For AB blood type, antigens on the surface of RBCs are both A and B and no antibody is present. For O blood type, there would be no antigen, but antibodies would be of both A and B types.
If a woman has a blood group of type A then it could be either in the form of homozygous alleles or heterozygous alleles, \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{A}}}\] or \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{A}}}\]i, respectively. Similarly, if the man has a blood type of B then the alleles could be homozygous or heterozygous.
In the homozygous condition, \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{A}}}\] from the female combines with \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{B}}}\] from the male to form AB blood type having genotype \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{A}}}\]\[{{\text{I}}^{\text{B}}}\]. But in the heterozygous condition, either \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{A}}}\] or i from the female could combine with either \[{{\text{I}}^{\text{B}}}\] or i from the male. Thus, the blood types that could be formed are A (\[{{\text{I}}^{\text{A}}}\]i), B (\[{{\text{I}}^{\text{B}}}\]i), AB (\[{{\text{I}}^{\text{A}}}\]\[{{\text{I}}^{\text{B}}}\]), or O (ii) as shown in the figure below.

Hence, the correct answer is option (D)
Note: Apart from ABO blood grouping, Rh type of blood group determination is also very important. If the Rh antigen is present, then the individual is called Rh-positive, and if the antigen is absent, the individual is called Rh-negative.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




