
How do you find chirality centers?
Answer
563.1k+ views
Hint: The chirality center or chiral center is a tetrahedral atom with $s{p^3}$ hybridization which is usually a carbon atom. The carbon atom is attached to four different atoms or groups.
Complete step by step answer:The chiral centers are the tetrahedral atoms that are attached with four different atoms or substituent. Each chiral center in a molecule will be either R or S configuration as they are optically active. The optically active compounds are those which can rotate the plane polarized light either in clockwise or anticlockwise. R configuration means rotation towards clockwise and S configuration means rotation towards counterclockwise or anticlockwise.
The most common chiral atom is carbon as it is tetravalent in nature it can form four bonds and can attach four different atoms. It is $s{p^3}$ hybridized. The other atoms which are chiral in nature are quaternary nitrogen, tertiary nitrogen.
The chiral molecule contains one carbon atom attached to four non-identical atoms or groups. The carbon is considered as the chiral center. The chiral center is also known as stereogenic center. The chiral compounds are non-symmetric in nature thus they are non-superimposable mirror images.
Example of a chiral compound is shown below.
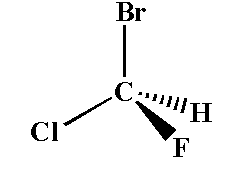
Here the carbon atom is attached to chlorine, fluorine, bromine and hydrogen. The carbon is the chiral center and the compound is the chiral compound.
Note:
Meso compounds are exceptions as they contain multiple chiral centres but are achiral in nature. The compound containing double bonds cannot have chiral centers as four double bonds cannot be bonded to one carbon atom.
Complete step by step answer:The chiral centers are the tetrahedral atoms that are attached with four different atoms or substituent. Each chiral center in a molecule will be either R or S configuration as they are optically active. The optically active compounds are those which can rotate the plane polarized light either in clockwise or anticlockwise. R configuration means rotation towards clockwise and S configuration means rotation towards counterclockwise or anticlockwise.
The most common chiral atom is carbon as it is tetravalent in nature it can form four bonds and can attach four different atoms. It is $s{p^3}$ hybridized. The other atoms which are chiral in nature are quaternary nitrogen, tertiary nitrogen.
The chiral molecule contains one carbon atom attached to four non-identical atoms or groups. The carbon is considered as the chiral center. The chiral center is also known as stereogenic center. The chiral compounds are non-symmetric in nature thus they are non-superimposable mirror images.
Example of a chiral compound is shown below.

Here the carbon atom is attached to chlorine, fluorine, bromine and hydrogen. The carbon is the chiral center and the compound is the chiral compound.
Note:
Meso compounds are exceptions as they contain multiple chiral centres but are achiral in nature. The compound containing double bonds cannot have chiral centers as four double bonds cannot be bonded to one carbon atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE

Find the foot of the perpendicular from point232to class 12 maths CBSE




