
How do traits get expressed?
Answer
508.5k+ views
Hint: The transmission of characters (or traits) from parents to their offspring is called heredity. The genetic material is present in the sex cells (or gametes) of the parents. Thus, gametes constitute the link between one generation and the next, and pass on the paternal and maternal traits to the offspring.
Complete Answer-
A recognizable feature of a human being like height, complexion, shape of hair, colour of eyes, and shape of nose and chin, etc. are called characters or traits.
The differences in the characters between the individuals of a species is termed as variation.
Cellular genetic material (DNA) is the information source for making proteins in the cell. A part of DNA that delivers information for one particular protein is termed as a gene for that protein.
For example- the tallness of a plant depends upon the growth hormone which is in turn controlled by the gene. If the gene is effective and more growth hormone is secreted the plant will grow high. If the genetic factor for that specific protein gets altered and fewer of it is secreted when the plant will remain short. Both the parents contribute equally to the DNA of succeeding generations during sexual reproduction. They actually contribute a copy of the identical gene.
For example- when a tall plant is crossed with a short plant the gametes will have only genes either for tallness or for shortness. The F1 generation will get one genetic factor for tallness and another for shortness also.
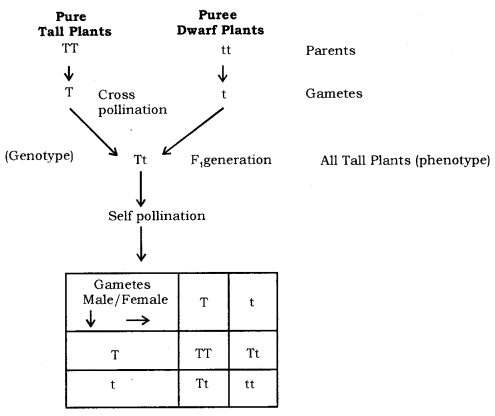
Note-
The traits which are transmitted by the parent to its offspring during the procedure of fertilization are inherited traits. The traits are of mainly two types- dominant and recessive.
The character which expresses itself in a F1 generation is a dominant trait and also the character which doesn’t express itself but is present in a generation is termed as a recessive trait.
Complete Answer-
A recognizable feature of a human being like height, complexion, shape of hair, colour of eyes, and shape of nose and chin, etc. are called characters or traits.
The differences in the characters between the individuals of a species is termed as variation.
Cellular genetic material (DNA) is the information source for making proteins in the cell. A part of DNA that delivers information for one particular protein is termed as a gene for that protein.
For example- the tallness of a plant depends upon the growth hormone which is in turn controlled by the gene. If the gene is effective and more growth hormone is secreted the plant will grow high. If the genetic factor for that specific protein gets altered and fewer of it is secreted when the plant will remain short. Both the parents contribute equally to the DNA of succeeding generations during sexual reproduction. They actually contribute a copy of the identical gene.
For example- when a tall plant is crossed with a short plant the gametes will have only genes either for tallness or for shortness. The F1 generation will get one genetic factor for tallness and another for shortness also.

Note-
The traits which are transmitted by the parent to its offspring during the procedure of fertilization are inherited traits. The traits are of mainly two types- dominant and recessive.
The character which expresses itself in a F1 generation is a dominant trait and also the character which doesn’t express itself but is present in a generation is termed as a recessive trait.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




