
How do mosfets work?
Answer
540.3k+ views
Hint: A mosfet is a building block of most electronic devices. It is made of a semiconductor, usually silicon. It contains three terminals; source, gate, drain. It is used as switches or amplifiers. It also acts as a gate. It is a compact transistor which is being miniaturized.
Complete answer:
A MOSFET is a semiconductor device usually made of silicon. MOSFET is an acronym for metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor. It is the basic building block of all electronics.
MOSFET is a voltage controlled device.
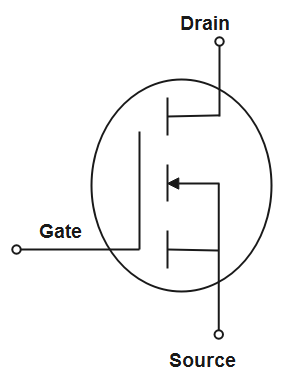
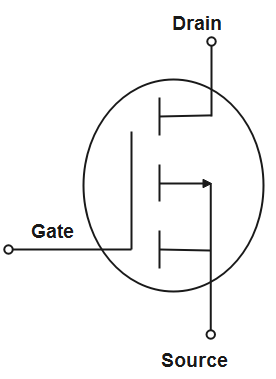
The above given figures depict n-channel mosfet and p-channel mosfet respectively. When a regulated voltage is applied to the gate pin, then the mosfet starts conducting through the drain and the source pin. Mosfet works as a switch as well as a n amplifier of electronic signals in electronic devices.
The main principle on which mosfet work is to control the voltage and current flow between the source and drain terminals. Its semiconductor surface is below the oxide layer and is located between the source and rain terminals. The semiconductor can be converted to t-type or n-type by applying positive voltage or negative voltage respectively.
The depletion region has abundant bounded negative electrons from the acceptor atoms. When a positive voltage is applied, it attracts all the electrons and drains the source and drain region into the channels. Now if voltage is applied between drain and source, the current flows freely between drain and source and the gate voltage controls the electrons.
Therefore, the Mosfet acts as a switch and controls voltage and current flow between the source and drain.
Note:
The depletion region is the region between the p-type and n-type semiconductors connected together. The functioning of the Mosfet is based on the MOS capacitor. It is used in both digital and analog circuits. A mosfet is a type of a transistor. Transistors are semiconductor devices used to amplifiers or switches.
Complete answer:
A MOSFET is a semiconductor device usually made of silicon. MOSFET is an acronym for metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor. It is the basic building block of all electronics.
MOSFET is a voltage controlled device.


The above given figures depict n-channel mosfet and p-channel mosfet respectively. When a regulated voltage is applied to the gate pin, then the mosfet starts conducting through the drain and the source pin. Mosfet works as a switch as well as a n amplifier of electronic signals in electronic devices.
The main principle on which mosfet work is to control the voltage and current flow between the source and drain terminals. Its semiconductor surface is below the oxide layer and is located between the source and rain terminals. The semiconductor can be converted to t-type or n-type by applying positive voltage or negative voltage respectively.
The depletion region has abundant bounded negative electrons from the acceptor atoms. When a positive voltage is applied, it attracts all the electrons and drains the source and drain region into the channels. Now if voltage is applied between drain and source, the current flows freely between drain and source and the gate voltage controls the electrons.
Therefore, the Mosfet acts as a switch and controls voltage and current flow between the source and drain.
Note:
The depletion region is the region between the p-type and n-type semiconductors connected together. The functioning of the Mosfet is based on the MOS capacitor. It is used in both digital and analog circuits. A mosfet is a type of a transistor. Transistors are semiconductor devices used to amplifiers or switches.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




