
How are anhydrides formed?
Answer
532.8k+ views
Hint: We first need to know what are anhydrides. An anhydride is formed from an acid when a water molecule is removed. There are two types of anhydrides, organic acid anhydrides, and inorganic acid anhydrides.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us understand what are organic acid anhydrides.
It has two acyl groups (R-C=O) bonded to the same oxygen atom.
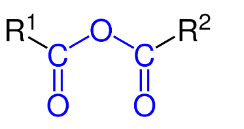
An organic acid anhydride can be prepared using the following methods:
- Carboxylic anhydride (${{(RC(O))}_{2}}O$) - These are acid anhydrides prepared from carboxylic acid.
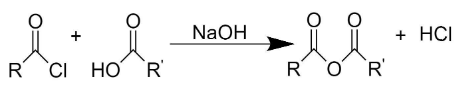
When a carboxylic acid is reacted with an acid chloride, in presence of a base, it forms carboxylic anhydride along with hydrochloric acid.
- Oxidation of butane in the presence of vanadium phosphate catalyst or oxidation of benzene in the presence of molybdenum trioxide and vanadium pentoxide can be used to prepare maleic anhydride.
\[{{C}_{4}}{{H}_{10}}+3.5{{O}_{2}}\xrightarrow{V{{O}_{x}}P{{O}_{4}}}{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{2}}{{(CO)}_{2}}O+4{{H}_{2}}O\]
- Dehydration of acid to produce corresponding acid anhydride in the presence of dehydrating agents like phosphorous pentoxide is a laboratory method to produce acid anhydride.
\[2C{{H}_{3}}COOH+{{P}_{4}}{{O}_{10}}\to C{{H}_{3}}C(O)OC(O)C{{H}_{3}}+{{P}_{4}}{{O}_{9}}{{(OH)}_{2}}\]
- Ketene can be used to prepare acetyl groups containing mixed anhydrides.
\[RC{{O}_{2}}H+{{H}_{2}}C=C=O\to RC{{O}_{2}}C(O)C{{H}_{3}}\]
Now let us understand what are inorganic acid anhydrides.
Oxides that react with a base to form a salt or with water to form an acid are known as acid anhydrides or acidic oxides.
When we remove water from oxygen-containing acid or oxoacids, the resultant compound is an acid anhydride.
For example, sulfuric acid ($S{{O}_{3}}$), sulfurous acid ($S{{O}_{2}}$), calcium oxide (CaO), carbonic acid ($C{{O}_{2}}$), etc.
Any acid anhydride which does not contain an organic component can be called an inorganic acid anhydride.
Note: It should be noted that simply renaming the word "acid" to "anhydride" of the parent carboxylic acid would suffice while naming a symmetrical organic acid anhydride. For example, acetic anhydride.
However, both of the carboxylic acids reacted must be named before adding "anhydride" while naming an unsymmetrical organic acid anhydride. For example, benzoic propanoic anhydride.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us understand what are organic acid anhydrides.
It has two acyl groups (R-C=O) bonded to the same oxygen atom.

An organic acid anhydride can be prepared using the following methods:
- Carboxylic anhydride (${{(RC(O))}_{2}}O$) - These are acid anhydrides prepared from carboxylic acid.
When a carboxylic acid is reacted with an acid chloride, in presence of a base, it forms carboxylic anhydride along with hydrochloric acid.

- Oxidation of butane in the presence of vanadium phosphate catalyst or oxidation of benzene in the presence of molybdenum trioxide and vanadium pentoxide can be used to prepare maleic anhydride.
\[{{C}_{4}}{{H}_{10}}+3.5{{O}_{2}}\xrightarrow{V{{O}_{x}}P{{O}_{4}}}{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{2}}{{(CO)}_{2}}O+4{{H}_{2}}O\]
- Dehydration of acid to produce corresponding acid anhydride in the presence of dehydrating agents like phosphorous pentoxide is a laboratory method to produce acid anhydride.
\[2C{{H}_{3}}COOH+{{P}_{4}}{{O}_{10}}\to C{{H}_{3}}C(O)OC(O)C{{H}_{3}}+{{P}_{4}}{{O}_{9}}{{(OH)}_{2}}\]
- Ketene can be used to prepare acetyl groups containing mixed anhydrides.
\[RC{{O}_{2}}H+{{H}_{2}}C=C=O\to RC{{O}_{2}}C(O)C{{H}_{3}}\]
Now let us understand what are inorganic acid anhydrides.
Oxides that react with a base to form a salt or with water to form an acid are known as acid anhydrides or acidic oxides.
When we remove water from oxygen-containing acid or oxoacids, the resultant compound is an acid anhydride.
For example, sulfuric acid ($S{{O}_{3}}$), sulfurous acid ($S{{O}_{2}}$), calcium oxide (CaO), carbonic acid ($C{{O}_{2}}$), etc.
Any acid anhydride which does not contain an organic component can be called an inorganic acid anhydride.
Note: It should be noted that simply renaming the word "acid" to "anhydride" of the parent carboxylic acid would suffice while naming a symmetrical organic acid anhydride. For example, acetic anhydride.
However, both of the carboxylic acids reacted must be named before adding "anhydride" while naming an unsymmetrical organic acid anhydride. For example, benzoic propanoic anhydride.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




