
Hinsberg’s reagent is
A) ${C_6}{H_5}S{O_2}Cl$
B) ${C_6}{H_5}COCl$
C) $SOC{l_2}$
D) ${\left( {COCl} \right)_2}$
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: This reagent is an organosulfur compound. Refer to the preparation reaction of Hinsberg reagent and then you will get to know the chemical formula of it. There are many methods of its preparation. One method is to by reacting benzene with chloro sulphuric acid.
Complete step by step solution:
Hinsberg’s reagent is used in the Hinsberg test for the detection and distinction of primary, secondary and tertiary amines in a given sample. Hinsberg’s reagent is an alternating name for Benzene sulphonyl chloride. Chemical formula of benzene sulphonyl chloride is: ${C_6}{H_5}S{O_2}Cl$. Thus, this reagent is an organosulfur compound.
Structure of Hinsberg’s reagent i.e, ${C_6}{H_5}S{O_2}Cl$ is as follows:
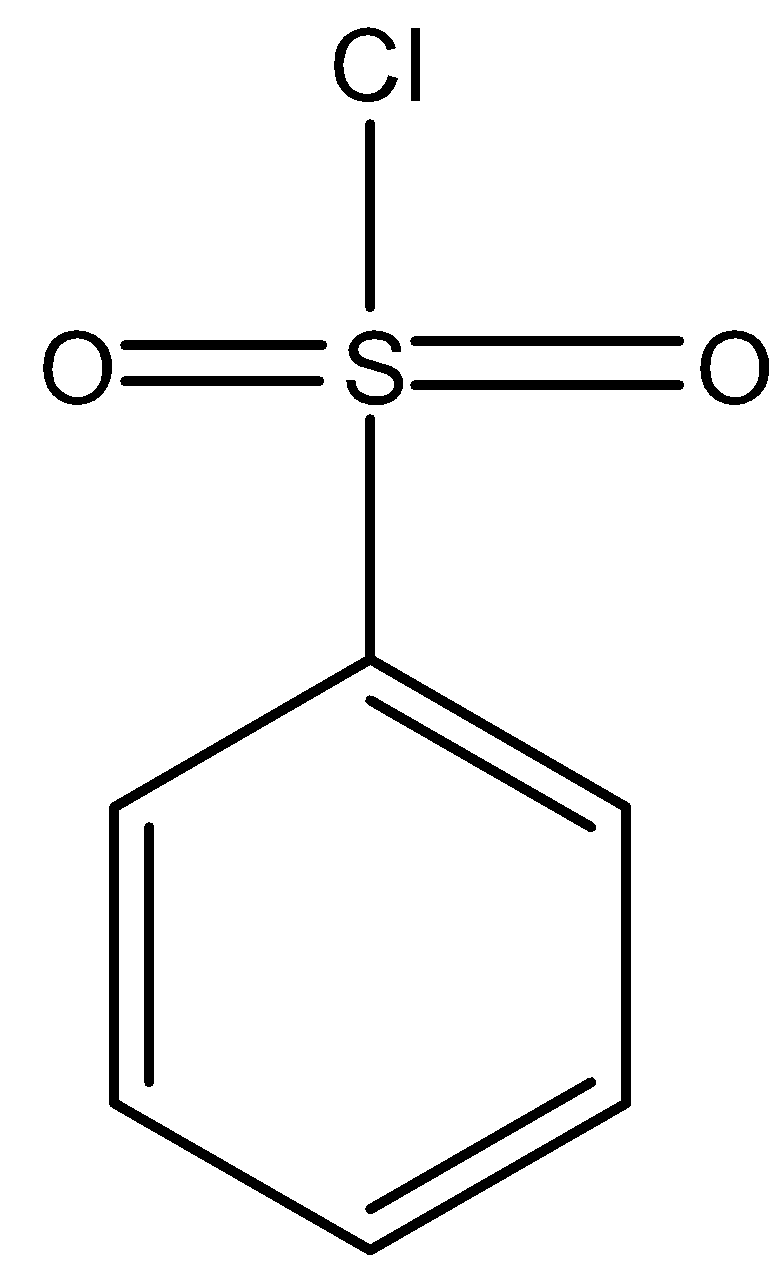
It is also used in the preparation of sulfonamides (via reaction with amines) and sulphonamide esters (via reaction with alcohol). Methods of preparation of Hinsberg’s reagent are as follows:
- The chlorination of benzene sulphonic acid or the salts of benzene sulphonic acid with phosphorus oxychloride ($POC{l_3}$) gives the required reagent. The preparation reaction can be represented as:
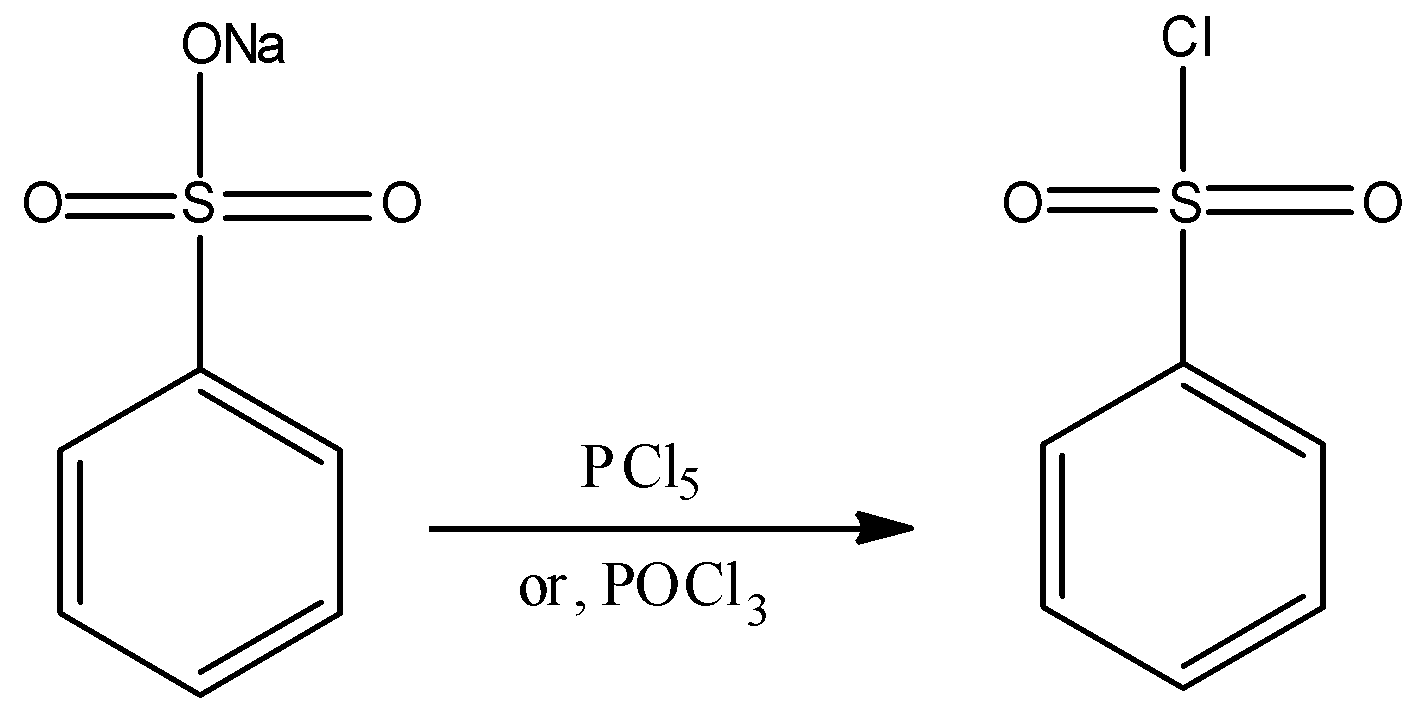
- Another method to prepare the required Hinsberg’s reagent by reacting benzene with chloro sulphuric acid. The reaction can be represented as:
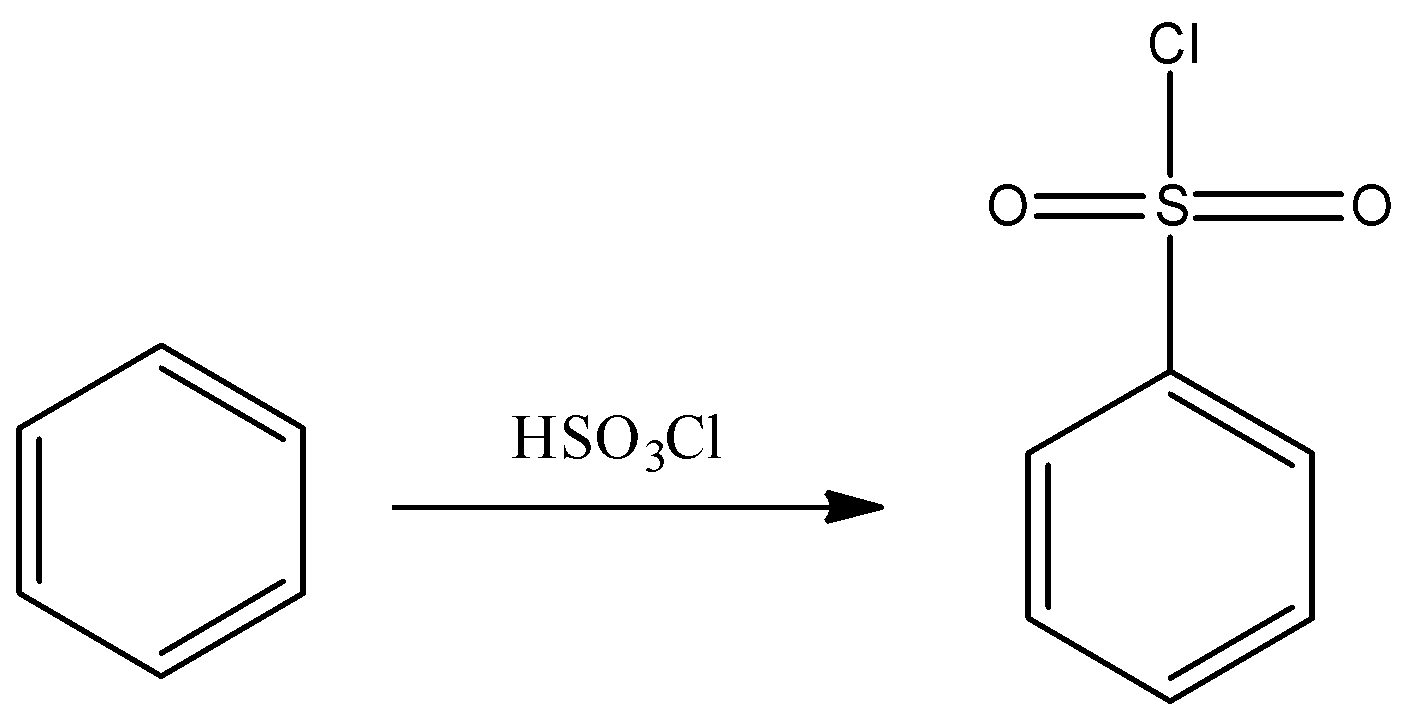
Hence, Hinsberg’s reagent is ${C_6}{H_5}S{O_2}Cl$ and thus, option A is correct.
Note: The reaction of Hinsberg’s reagent with primary amines gives a sulphonamide product that is soluble in an alkali. The reaction of Hinsberg’s reagent with secondary amines gives a sulphonamide product that is not soluble in an alkali. Tertiary amines do not undergo such a reaction but do the hydrolysis of sulfonyl chloride. This reaction of tertiary amines with Hinsberg’s reagent results in the formation of salts that are soluble in water.
Complete step by step solution:
Hinsberg’s reagent is used in the Hinsberg test for the detection and distinction of primary, secondary and tertiary amines in a given sample. Hinsberg’s reagent is an alternating name for Benzene sulphonyl chloride. Chemical formula of benzene sulphonyl chloride is: ${C_6}{H_5}S{O_2}Cl$. Thus, this reagent is an organosulfur compound.
Structure of Hinsberg’s reagent i.e, ${C_6}{H_5}S{O_2}Cl$ is as follows:

It is also used in the preparation of sulfonamides (via reaction with amines) and sulphonamide esters (via reaction with alcohol). Methods of preparation of Hinsberg’s reagent are as follows:
- The chlorination of benzene sulphonic acid or the salts of benzene sulphonic acid with phosphorus oxychloride ($POC{l_3}$) gives the required reagent. The preparation reaction can be represented as:

- Another method to prepare the required Hinsberg’s reagent by reacting benzene with chloro sulphuric acid. The reaction can be represented as:

Hence, Hinsberg’s reagent is ${C_6}{H_5}S{O_2}Cl$ and thus, option A is correct.
Note: The reaction of Hinsberg’s reagent with primary amines gives a sulphonamide product that is soluble in an alkali. The reaction of Hinsberg’s reagent with secondary amines gives a sulphonamide product that is not soluble in an alkali. Tertiary amines do not undergo such a reaction but do the hydrolysis of sulfonyl chloride. This reaction of tertiary amines with Hinsberg’s reagent results in the formation of salts that are soluble in water.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




