
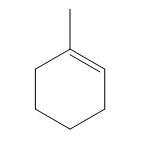
Hence (R) is
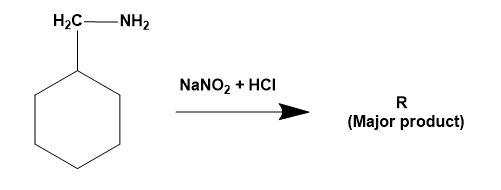
(A)
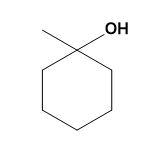
(B)
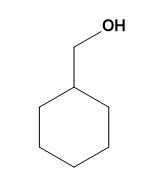
(C)
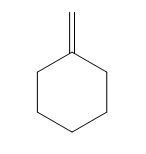
(D)





Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: Amines react with nitrous acid to form alcohols. So, among all the options mentioned above one would be our answer. Studying the mechanism of the reaction given we will reach the answer easily.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us first understand the concept of reactions based on primary amines. Reaction of primary amines with nitrous acid- Nitrous acid is a monobasic acid (weak) which is in the form of nitrite salt who is responsible to make azides from amines. The amine attacks on nitrite by nucleophilic substitution. Then this is deprotonated and double elimination of water takes place. In short, primary amines react with nitrous acid in cold conditions to form unstable diazonium salt which then decomposes to give alcohol and nitrogen gas. This technique was used in the past more efficiently to recognise the primary, secondary and tertiary amines. Secondary amines give a carcinogenic product, so this substitution is never practised. Nitrous acid is unstable so it is produced in situ by reacting a solution which consists of potassium or sodium nitrate with hydrochloric acid.
${{H}^{+}}+N{{O}^{-}}\rightleftarrows HN{{O}_{2}}$
Now when primary amines react with this nitrous acid, the reaction is recognised by the outburst of a colourless and odourless gas of nitrogen.
For example,
When 1-aminopropane reacts with nitrous acid, alcohol (propan 1 ol) is obtained along with a water molecule and nitrogen gas is evolved. $-N{{H}_{2}}$in the amine is replace by -OH during the reaction as,
$C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}N{{H}_{2}}+HN{{O}_{2}}\to C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}OH+{{H}_{2}}O+{{N}_{2}}$
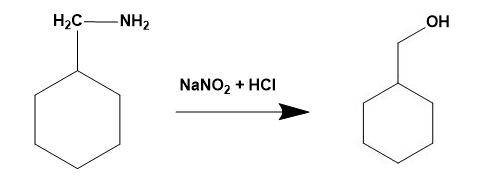
-Thus, for the given illustration: When cyclohexanemethylamine reacts with nitrous acid it gives cyclohexylmethanol.
Therefore option (B) is correct.
Note: Alternatively, if we want to know the amount of amine reacted, we simply can measure the amount of nitrogen involved which would directly give the required amounts of amine. Alkenes, alcohols and alkyl halides are produced simultaneously by the above reaction. But the major product is alcohol hence, the answer.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us first understand the concept of reactions based on primary amines. Reaction of primary amines with nitrous acid- Nitrous acid is a monobasic acid (weak) which is in the form of nitrite salt who is responsible to make azides from amines. The amine attacks on nitrite by nucleophilic substitution. Then this is deprotonated and double elimination of water takes place. In short, primary amines react with nitrous acid in cold conditions to form unstable diazonium salt which then decomposes to give alcohol and nitrogen gas. This technique was used in the past more efficiently to recognise the primary, secondary and tertiary amines. Secondary amines give a carcinogenic product, so this substitution is never practised. Nitrous acid is unstable so it is produced in situ by reacting a solution which consists of potassium or sodium nitrate with hydrochloric acid.
${{H}^{+}}+N{{O}^{-}}\rightleftarrows HN{{O}_{2}}$
Now when primary amines react with this nitrous acid, the reaction is recognised by the outburst of a colourless and odourless gas of nitrogen.
For example,
When 1-aminopropane reacts with nitrous acid, alcohol (propan 1 ol) is obtained along with a water molecule and nitrogen gas is evolved. $-N{{H}_{2}}$in the amine is replace by -OH during the reaction as,
$C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}N{{H}_{2}}+HN{{O}_{2}}\to C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}OH+{{H}_{2}}O+{{N}_{2}}$
-Thus, for the given illustration: When cyclohexanemethylamine reacts with nitrous acid it gives cyclohexylmethanol.

Therefore option (B) is correct.
Note: Alternatively, if we want to know the amount of amine reacted, we simply can measure the amount of nitrogen involved which would directly give the required amounts of amine. Alkenes, alcohols and alkyl halides are produced simultaneously by the above reaction. But the major product is alcohol hence, the answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




