
What helps ovarian follicles grow?
Answer
479.1k+ views
Hint: The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries in the pelvic region, as well as oviducts, vagina, cervix, uterus, and external genitalia. These components, along with a pair of mammary glands that are functionally and structurally integrated, help with ovulation, fertilization, birth, and child care.
Complete answer:
There are several functions of the female reproductive system. The main function of this system is to give birth to a new organism by means of sexual reproduction. Ovaries in females produce egg cells which are female gametes. They are haploid in nature. Those egg cells are further transported to the fallopian tube which is the site of fertilisation. After fertilisation, the formed cell is diploid in nature and is known as zygote. This zygote moves further to the uterus for implantation in the uterine wall. After implantation, the zygote continues to develop further and forms a new organism.
If implantation has not taken place, the uterine wall is shed as menstrual flow. This process occurs in a regular period of time. The process of shedding of the uterine wall is known as menstruation.
In this whole process many hormones play a major role. Each hormone has its own function and every hormone is equally important. Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), which is secreted by the pituitary gland in females, is responsible for the growth and maturation of ovarian follicles. It also stimulates the production of estrogen and development of eggs.
Note:
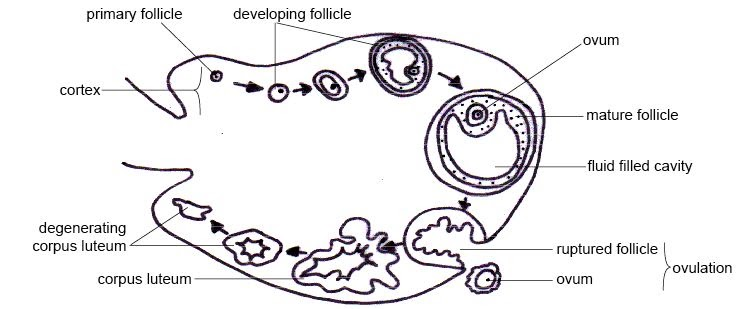
The cortex is made up of ovarian follicles at various stages of development. The basic unit of the female reproductive system is the ovarian follicle. The ampulla, isthmus, and infundibulum are the three anatomical regions that make up each oviduct.
Complete answer:
There are several functions of the female reproductive system. The main function of this system is to give birth to a new organism by means of sexual reproduction. Ovaries in females produce egg cells which are female gametes. They are haploid in nature. Those egg cells are further transported to the fallopian tube which is the site of fertilisation. After fertilisation, the formed cell is diploid in nature and is known as zygote. This zygote moves further to the uterus for implantation in the uterine wall. After implantation, the zygote continues to develop further and forms a new organism.
If implantation has not taken place, the uterine wall is shed as menstrual flow. This process occurs in a regular period of time. The process of shedding of the uterine wall is known as menstruation.
In this whole process many hormones play a major role. Each hormone has its own function and every hormone is equally important. Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), which is secreted by the pituitary gland in females, is responsible for the growth and maturation of ovarian follicles. It also stimulates the production of estrogen and development of eggs.

Note:
The cortex is made up of ovarian follicles at various stages of development. The basic unit of the female reproductive system is the ovarian follicle. The ampulla, isthmus, and infundibulum are the three anatomical regions that make up each oviduct.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




