
Hardy Weinberg equation is
A. ${p^2} + 2pq + {q^2} = 1$
B. $p + 2pq + q = 1$
C. $p + q = 4$
D. $p + {q^2} + 2pq = 1$
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: For a populace in hereditary harmony: $p + q = 1.0$ (The amount of the frequencies of the two alleles is $100\% $). Here populace refers to "population". The alleles are in certain ratios with each other according to their chances of expression.
Complete answer:
Think about a populace of monoecious diploids, where every creature produces male and female gametes at equivalent recurrence and has two alleles at every quality locus. Living beings imitate the irregular association of gametes (the "genetic supply" populace model). A locus in this populace has two alleles, A and a, that happen with introductory frequencies ${f_0}(A) = p$ and ${f_0}(a) = q$ respectively. The allele frequencies at every age are acquired by pooling together the alleles from every genotype of a similar age as indicated by the normal commitment from the homozygote and heterozygote genotypes, which are 1 and a half, individually. The various approaches to frame genotypes for the cutting edge can appear in a Punnett square, where the extent of every genotype is equivalent to the result of the line and section allele frequencies from the current generation. The amount of the passages is ${p^2} + 2pq + {q^2} = 1$, as the genotype frequencies must total to one. Note again that as $p + q = 1$, the binomial development of ${(p + q)^2} = {p^2} + 2pq + {q^2} = 1$ gives similar relationships. Summing up the components of the Punnett square or the binomial extension, we acquire the normal genotype extents among the posterity after a solitary age
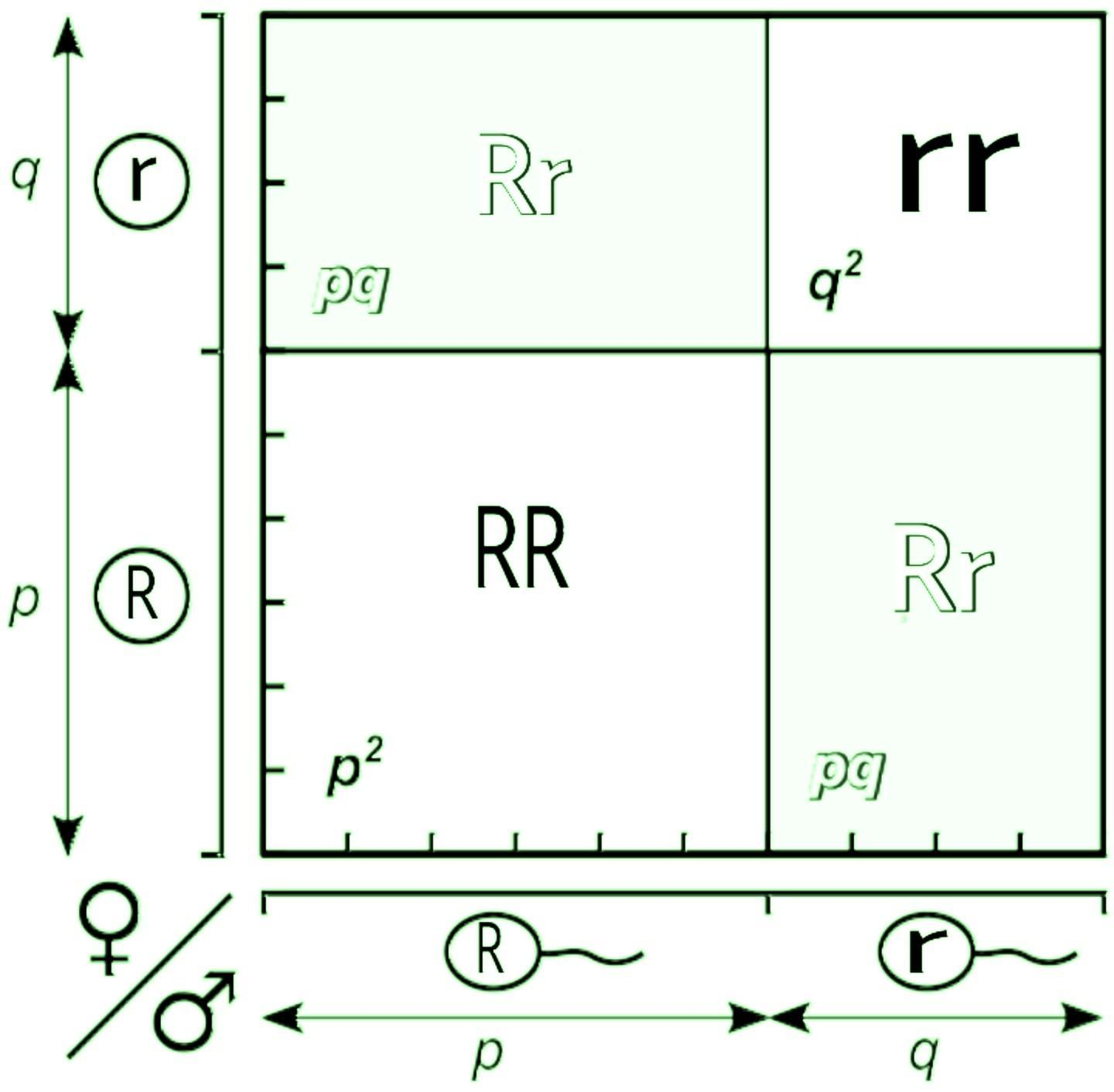
Length of p, q corresponds to allele frequencies (here $p = 0.6,q = 0.4$). Then the area of the rectangle represents genotype frequencies (thus $RR:Rr:rr = 0.36:0.48:0.16$).
So by calculating the area of this square we conclude that,
Area of first square is ${p^2}$
Area of second and third square is $2pq$
Area of fourth square is ${q^2}$
So, forming equation, we get: ${p^2} + 2pq + {q^2} = {(p + q)^2}$
From the above equations, we have: $p + q = 1$
That implies ${p^2} + 2pq + {q^2} = 1$
Hence, the correct answer is option "A".
Note: Population genetics, the Hardy–Weinberg principle, also known as the Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium, model, hypothesis, or law, expresses that in enormous irregular mating populace quality allele and genotype frequencies in a populace will stay steady from age to age without other transformative impacts.
Complete answer:
Think about a populace of monoecious diploids, where every creature produces male and female gametes at equivalent recurrence and has two alleles at every quality locus. Living beings imitate the irregular association of gametes (the "genetic supply" populace model). A locus in this populace has two alleles, A and a, that happen with introductory frequencies ${f_0}(A) = p$ and ${f_0}(a) = q$ respectively. The allele frequencies at every age are acquired by pooling together the alleles from every genotype of a similar age as indicated by the normal commitment from the homozygote and heterozygote genotypes, which are 1 and a half, individually. The various approaches to frame genotypes for the cutting edge can appear in a Punnett square, where the extent of every genotype is equivalent to the result of the line and section allele frequencies from the current generation. The amount of the passages is ${p^2} + 2pq + {q^2} = 1$, as the genotype frequencies must total to one. Note again that as $p + q = 1$, the binomial development of ${(p + q)^2} = {p^2} + 2pq + {q^2} = 1$ gives similar relationships. Summing up the components of the Punnett square or the binomial extension, we acquire the normal genotype extents among the posterity after a solitary age

Length of p, q corresponds to allele frequencies (here $p = 0.6,q = 0.4$). Then the area of the rectangle represents genotype frequencies (thus $RR:Rr:rr = 0.36:0.48:0.16$).
So by calculating the area of this square we conclude that,
Area of first square is ${p^2}$
Area of second and third square is $2pq$
Area of fourth square is ${q^2}$
So, forming equation, we get: ${p^2} + 2pq + {q^2} = {(p + q)^2}$
From the above equations, we have: $p + q = 1$
That implies ${p^2} + 2pq + {q^2} = 1$
Hence, the correct answer is option "A".
Note: Population genetics, the Hardy–Weinberg principle, also known as the Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium, model, hypothesis, or law, expresses that in enormous irregular mating populace quality allele and genotype frequencies in a populace will stay steady from age to age without other transformative impacts.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




