
What happens when glycerol is heated ?
Answer
516.3k+ views
Hint: When, glycerol is a straightforward polyol compound. It is a dry, scentless, thick fluid that is sweet-tasting and non-harmful. The glycerol spine is found in those lipids known as glycerides. Due to having antimicrobial and antiviral properties it is generally utilized in FDA endorsed wound and consume medicines. It tends to be utilized as a successful marker to quantify liver infection.
Complete answer:
We have to know that, glycerol is seen in natural frameworks as a halfway in carb and lipid digestion since surplus sugar can be changed over into long chain unsaturated fats and esterified with the three-hydroxyl gatherings. Glycerol can impact invulnerable responses in the body through histamines, expanded counter acting agent creation and by improving resistant cell movement and is along these lines delegated an allergen. In the blood, glycerol can build circulatory strain by specially drawing in the water from tissues into plasma and lymph. In nephrons, glycerol can expand pee volume by forestalling water resorption.
The three hydroxyl gatherings of glycerol permit responses with numerous natural acids to frame esters. At the point when each of the three responsive gatherings are esterified with long chain natural unsaturated fats, a fatty substance is framed. Fatty substances are among the most widely recognized lipids in the human body.
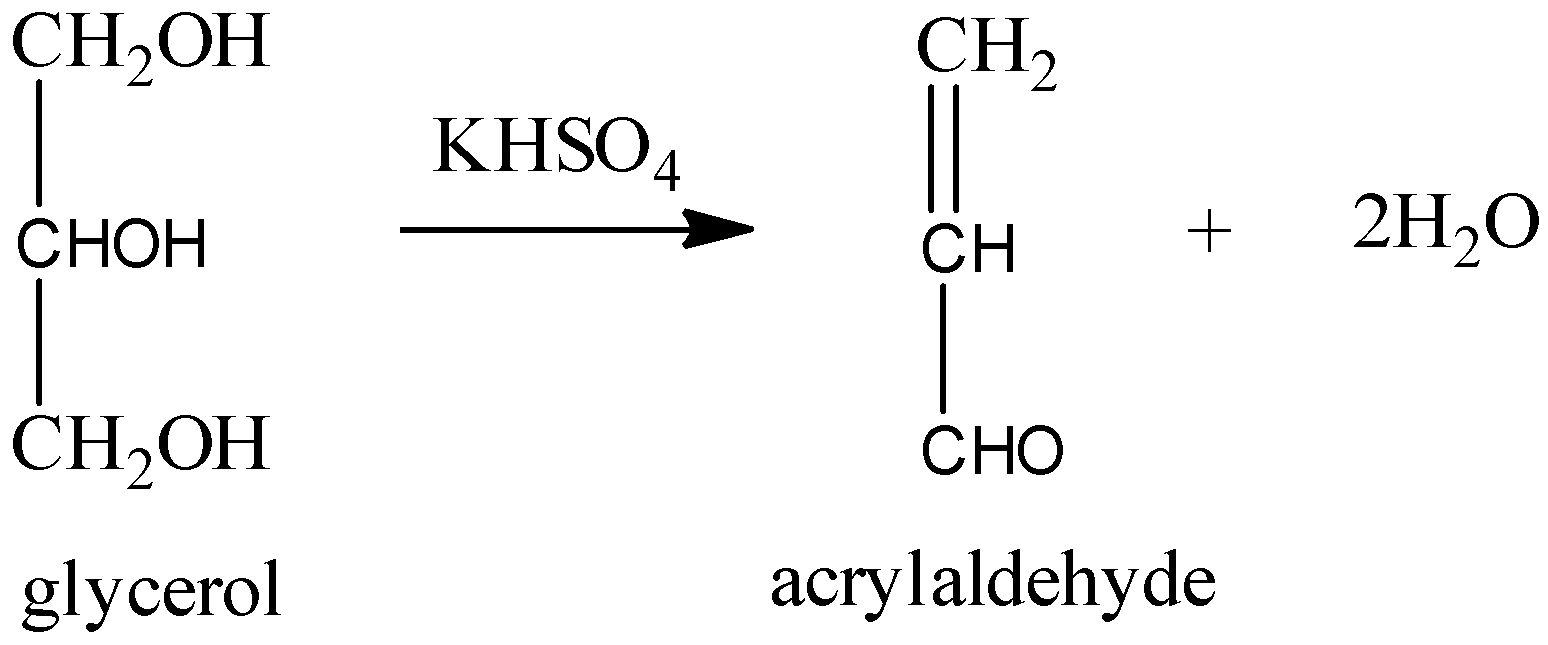
Glycerol on warming with potassium hydrogen sulfate, it goes through drying out with expulsion of two water particles from the glycerol atom. Hence, bringing about the arrangement of unsaturated aldehyde, that is acrylic aldehyde otherwise called acrolein.
Note:
We have to know that, lack of hydration is the deficiency of water and body salts through looseness of the bowels. The human body needs water to keep up sufficient blood and different liquids to work appropriately. In the event that your body loses significantly a bigger number of liquids than you are drinking, you become dried out.
Complete answer:
We have to know that, glycerol is seen in natural frameworks as a halfway in carb and lipid digestion since surplus sugar can be changed over into long chain unsaturated fats and esterified with the three-hydroxyl gatherings. Glycerol can impact invulnerable responses in the body through histamines, expanded counter acting agent creation and by improving resistant cell movement and is along these lines delegated an allergen. In the blood, glycerol can build circulatory strain by specially drawing in the water from tissues into plasma and lymph. In nephrons, glycerol can expand pee volume by forestalling water resorption.
The three hydroxyl gatherings of glycerol permit responses with numerous natural acids to frame esters. At the point when each of the three responsive gatherings are esterified with long chain natural unsaturated fats, a fatty substance is framed. Fatty substances are among the most widely recognized lipids in the human body.
Glycerol on warming with potassium hydrogen sulfate, it goes through drying out with expulsion of two water particles from the glycerol atom. Hence, bringing about the arrangement of unsaturated aldehyde, that is acrylic aldehyde otherwise called acrolein.

Note:
We have to know that, lack of hydration is the deficiency of water and body salts through looseness of the bowels. The human body needs water to keep up sufficient blood and different liquids to work appropriately. In the event that your body loses significantly a bigger number of liquids than you are drinking, you become dried out.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




