
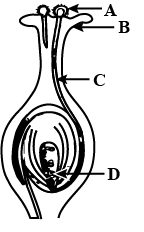
What happens to the part marked ‘D’ after the fertilization?

Answer
498k+ views
Hint: The ovule is the component in seed plants that gives rise to and contains female reproductive cells. It is made up of three layers: the integument on the outside, the nucellus (or megasporangium remnant), and the female gametophyte (produced from a haploid megaspore) in the middle. In angiosperms, the female gametophyte, also known as a megagametophyte, is also known as the embryo sac. For the goal of fertilisation, the megagametophyte creates an egg cell.
Complete answer:
The part D marked in the figure is an ovule or egg cell. The ovule is a flowering plant organ that produces seeds. It is produced in the flower’s ovary and consists of a nucellus protected by integuments, embryo/endosperm precursors, and seed coat, respectively. The nucellus is the core, micropylar-oriented tissue bordered by the integuments, which is where female meiosis and the production of female gametophytes (embryo sacs) take place.
In plants, fertilization occurs when the male and female gametes fuse to form a zygote. The zygote divides after fertilization to become an embryo. The fertilized ovule matures into a seed, which contains an embryo protected by a seed coat. The floral portions of the seed wither and fall off as it grows. In the meantime, the ovaries expand and develop into fruit.
When one of the sperm cells combines with the egg inside an ovule, fertilization occurs. After the process of fertilization, each ovule develops into a seed. Each seed contains an embryo, which is a tiny, undeveloped plant. Ovary which surrounds the ovules further matures into a fruit having one or more seeds.
Hence, the part D marked in the figure is an ovule or egg cell.
Note:
Embryonic development begins after fertilization. The zygote separates into two cells: the terminal cell (higher cell) and the lower cell (lower cell) (basal cell). The suspensor is formed as the basal cell divides, and it finally connects to the maternal tissue. The suspensor is a tube that transports nutrition from the mother plant to the growing embryo.
Complete answer:
The part D marked in the figure is an ovule or egg cell. The ovule is a flowering plant organ that produces seeds. It is produced in the flower’s ovary and consists of a nucellus protected by integuments, embryo/endosperm precursors, and seed coat, respectively. The nucellus is the core, micropylar-oriented tissue bordered by the integuments, which is where female meiosis and the production of female gametophytes (embryo sacs) take place.
In plants, fertilization occurs when the male and female gametes fuse to form a zygote. The zygote divides after fertilization to become an embryo. The fertilized ovule matures into a seed, which contains an embryo protected by a seed coat. The floral portions of the seed wither and fall off as it grows. In the meantime, the ovaries expand and develop into fruit.
When one of the sperm cells combines with the egg inside an ovule, fertilization occurs. After the process of fertilization, each ovule develops into a seed. Each seed contains an embryo, which is a tiny, undeveloped plant. Ovary which surrounds the ovules further matures into a fruit having one or more seeds.
Hence, the part D marked in the figure is an ovule or egg cell.
Note:
Embryonic development begins after fertilization. The zygote separates into two cells: the terminal cell (higher cell) and the lower cell (lower cell) (basal cell). The suspensor is formed as the basal cell divides, and it finally connects to the maternal tissue. The suspensor is a tube that transports nutrition from the mother plant to the growing embryo.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




