
What will happen when D - (+) – glucose is treated with methanolic –HCl followed by Tollens’ reagent?
a.) – A black ppt. will be formed
b.) – A red ppt. will be formed
c.) – A green colour will appear
d.) – No characteristic colour or ppt. will be formed
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: This reaction is based on the biomolecules. Here, D - (+) - glucose will react with methanolic – HCl first, and then with the tollen’s reagent. First try to find out whether on reaction with HCl, the aldehyde group is free or not as Tollen’s reagent only responds when aldehyde group is free and oxidise it to carboxylate group and itself getting reduced to silver.
Complete Solution :
- First, we know that there will be the reaction of D – (+) – glucose with the methanolic – HCl.
- Now, here methanolic – HCl means the use of methanol, and HCl, and HCl is used in the form of hydrogen ions which acts as a catalyst in this reaction.
- So, D – (+) – glucose forms methyl glucoside by reacting with the methanolic HCl.
- As we know, methyl glucoside is a type of acetal. The reaction is given below for better understanding:
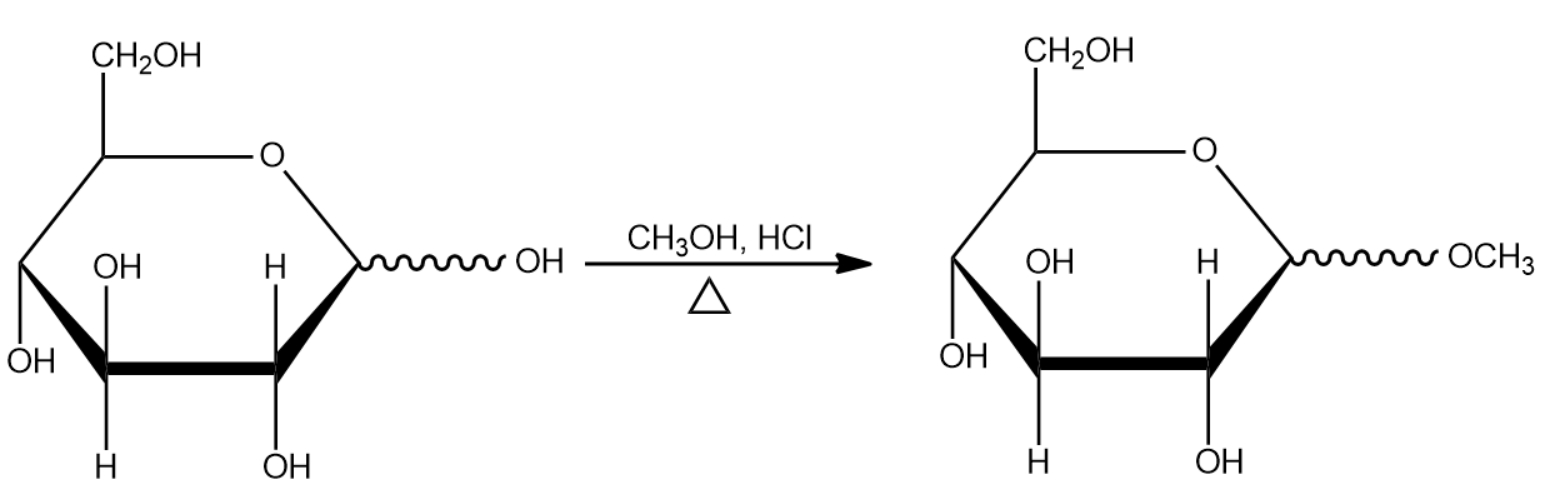
- Thus, no precipitates are formed in the first part of the reaction.
- Now, if we talk about the second part of the reaction, then the reaction will happen between the product formed methyl glucoside, and the Tollens’ reagent (ammoniacal silver nitrate).
- We know in consideration with the properties of Tollens’ reagent that it is a base.
- So, acetals do not get hydrolysed by a base. In other words; we can say that it doesn’t show any reaction with the Tollens’ reagent.
- In the last we can conclude that when D - (+) – glucose is treated with methanolic –HCl followed by Tollens’ reagent; then there are no characteristic colours or precipitates will be formed.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Don’t get confused between the reaction of glucose with Tollens reagent. As when there is no reaction with the methanolic –HCl, then the Tollens’ reagent is reduced to the metallic silver, and we can also say it forms the silver mirror.
Complete Solution :
- First, we know that there will be the reaction of D – (+) – glucose with the methanolic – HCl.
- Now, here methanolic – HCl means the use of methanol, and HCl, and HCl is used in the form of hydrogen ions which acts as a catalyst in this reaction.
- So, D – (+) – glucose forms methyl glucoside by reacting with the methanolic HCl.
- As we know, methyl glucoside is a type of acetal. The reaction is given below for better understanding:

- Thus, no precipitates are formed in the first part of the reaction.
- Now, if we talk about the second part of the reaction, then the reaction will happen between the product formed methyl glucoside, and the Tollens’ reagent (ammoniacal silver nitrate).
- We know in consideration with the properties of Tollens’ reagent that it is a base.
- So, acetals do not get hydrolysed by a base. In other words; we can say that it doesn’t show any reaction with the Tollens’ reagent.
- In the last we can conclude that when D - (+) – glucose is treated with methanolic –HCl followed by Tollens’ reagent; then there are no characteristic colours or precipitates will be formed.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Don’t get confused between the reaction of glucose with Tollens reagent. As when there is no reaction with the methanolic –HCl, then the Tollens’ reagent is reduced to the metallic silver, and we can also say it forms the silver mirror.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




