
How will you graph \[f(x) = \dfrac{{{x^2} - 2x}}{{{x^2} - 4}}\] by the use of holes, vertical and horizontal asymptotes, \[x\] and \[y\] intercepts?
Answer
545.7k+ views
Hint:
The basic key that is helpful in solving the above problem is that we can list the basic information. Remember that x intercept occurs when \[y = 0\] and the equation can go to zero due to the numerator only while \[y\] intercept occurs when \[x = 0\]. Later on by picking some \[x\] values \[f(x)\] can be calculated in order to determine coordinates \[(x,f(x))\] though which graph can be passed.
Complete step by step solution:
Firstly we can factorize \[f(x)\]
\[
\Rightarrow f(x) = \dfrac{{x(x - 2)}}{{(x + 2)(x - 2)}} \\
\Rightarrow f(x) = \dfrac{x}{{x + 2}} \\
\]
As we know that we can find vertical asymptotes of a rational function by examining the factors of the denominator to the factors in the numerator that are not common.
So it means that there will be a hole at \[x = 2\] and at \[x = - 2\] there will be a vertical asymptote.
Therefore at \[y = \dfrac{1}{1} = 1\] there will be a horizontal asymptote.
In order to find x intercept, we need to substitute \[y = 0\]and solve for \[x\]and \[y\] intercept occurs when\[x = 0\]
So x intercept \[(0,0)\] and y intercept is \[(0,0)\]
Vertical asymptote will be \[x = - 2\] and Horizontal asymptote will be \[y = 1\]
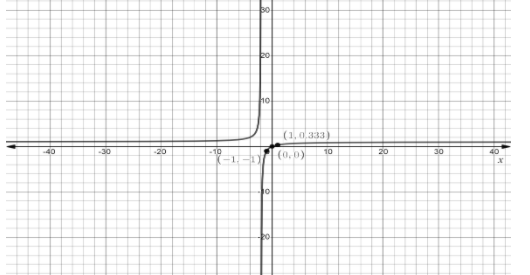
Hence the graph for \[\{ \left( {\dfrac{{{x^2} - 2x}}{{{x^2} - 4}}} \right)[ - 10,10, - 5,5]\} \] is as followed.
Formula:
In order to find horizontal asymptote let \[f(x) = \dfrac{{p(x)}}{{q(x)}}\]where \[p(x)\] stands for polynomial with degree m and leading coefficient. So if \[m\]is greater than \[n\] then \[f\] has no horizontal asymptote, if \[m\]is equal to \[n\]then \[y = \dfrac{a}{b}\]and lastly if \[m\]is smaller than \[n\]then \[y = 0\] is the horizontal asymptote.
Additional Information:
The lines that a particular function can get close to but do not intersect are referred to as asymptotes.
Note:
In the above equation remember the graph will pass through the origin as well ass \[x\] and \[y\] intercept will be served by origin. Lastly remember that only if the powers are equal then at the ratio between highest power in the numerator and denominator horizontal asymptote occurs and while solving vertical asymptote which is \[x\] find whether there are any common factors in numerator and denominator then cancel all term by setting denominator equal to zero.
The basic key that is helpful in solving the above problem is that we can list the basic information. Remember that x intercept occurs when \[y = 0\] and the equation can go to zero due to the numerator only while \[y\] intercept occurs when \[x = 0\]. Later on by picking some \[x\] values \[f(x)\] can be calculated in order to determine coordinates \[(x,f(x))\] though which graph can be passed.
Complete step by step solution:
Firstly we can factorize \[f(x)\]
\[
\Rightarrow f(x) = \dfrac{{x(x - 2)}}{{(x + 2)(x - 2)}} \\
\Rightarrow f(x) = \dfrac{x}{{x + 2}} \\
\]
As we know that we can find vertical asymptotes of a rational function by examining the factors of the denominator to the factors in the numerator that are not common.
So it means that there will be a hole at \[x = 2\] and at \[x = - 2\] there will be a vertical asymptote.
Therefore at \[y = \dfrac{1}{1} = 1\] there will be a horizontal asymptote.
In order to find x intercept, we need to substitute \[y = 0\]and solve for \[x\]and \[y\] intercept occurs when\[x = 0\]
So x intercept \[(0,0)\] and y intercept is \[(0,0)\]
Vertical asymptote will be \[x = - 2\] and Horizontal asymptote will be \[y = 1\]
Hence the graph for \[\{ \left( {\dfrac{{{x^2} - 2x}}{{{x^2} - 4}}} \right)[ - 10,10, - 5,5]\} \] is as followed.

Formula:
In order to find horizontal asymptote let \[f(x) = \dfrac{{p(x)}}{{q(x)}}\]where \[p(x)\] stands for polynomial with degree m and leading coefficient. So if \[m\]is greater than \[n\] then \[f\] has no horizontal asymptote, if \[m\]is equal to \[n\]then \[y = \dfrac{a}{b}\]and lastly if \[m\]is smaller than \[n\]then \[y = 0\] is the horizontal asymptote.
Additional Information:
The lines that a particular function can get close to but do not intersect are referred to as asymptotes.
Note:
In the above equation remember the graph will pass through the origin as well ass \[x\] and \[y\] intercept will be served by origin. Lastly remember that only if the powers are equal then at the ratio between highest power in the numerator and denominator horizontal asymptote occurs and while solving vertical asymptote which is \[x\] find whether there are any common factors in numerator and denominator then cancel all term by setting denominator equal to zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




