
Glucose when heated with \[C{H_3}OH\], in presence of dry \[HCl\] gas, \[\alpha \]-methyl glucosides and \[\beta \]-methyl glucosides are formed. This is because it contains:
A. an aldehyde group
B. $C{H_2}OH$
C. a ring structure
D. five hydroxyl groups
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint:Glucose is the most common monosaccharide. The six membered structure of glucose is called pyranose structure ($\alpha - $or$\beta - $) in analogy with pyran.
Complete answer:
Let us discuss glycosides briefly.
Hydroxyl group that is attached to the anomeric carbon (i.e. carbon containing the aldehyde or keto group) of carbohydrates in solution has unusual reactivity, and derivatives, called glycosides, can be formed; glycosides formed from glucose are called glucosides.
Glycosides are known reducing and will not show mutarotation because in neutral are basic condition glycosides are stable. The reaction by which a glycoside is formed involves the hydroxyl group (―OH) of the anomeric carbon atom of both α and β forms of D-glucose—α and β forms of D-glucose are shown in equilibrium in the reaction sequence—and the hydroxyl group of an alcohol); methyl α-D-glucosides and β-D-glucosides are formed as products, as is water.
In the formation of glycosides only one mole of alcohol is required so monosaccharide are already present in the hemiacetal form with one of the hydroxyl group and carbonyl group.
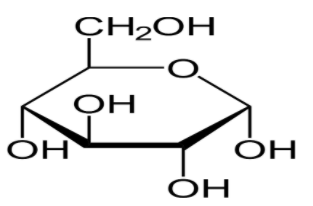
There are five hydroxyl groups on which glycoside formation occurs when glucose reacts with methyl alcohol in presence of dry HCl gas and \[\alpha \]-methyl glycosides, \[\beta \]-methyl glycosides are formed.
So our correct option is D. five hydroxyl groups
Note:
\[\alpha \]-methyl glucosides and \[\beta \]-methyl glucosides are acetals and these are non-reducing sugars. Also these shows mutarotation. Remember only methyl groups are attached in place of hydrogen in hydroxyl groups.
Complete answer:
Let us discuss glycosides briefly.
Hydroxyl group that is attached to the anomeric carbon (i.e. carbon containing the aldehyde or keto group) of carbohydrates in solution has unusual reactivity, and derivatives, called glycosides, can be formed; glycosides formed from glucose are called glucosides.
Glycosides are known reducing and will not show mutarotation because in neutral are basic condition glycosides are stable. The reaction by which a glycoside is formed involves the hydroxyl group (―OH) of the anomeric carbon atom of both α and β forms of D-glucose—α and β forms of D-glucose are shown in equilibrium in the reaction sequence—and the hydroxyl group of an alcohol); methyl α-D-glucosides and β-D-glucosides are formed as products, as is water.
In the formation of glycosides only one mole of alcohol is required so monosaccharide are already present in the hemiacetal form with one of the hydroxyl group and carbonyl group.

There are five hydroxyl groups on which glycoside formation occurs when glucose reacts with methyl alcohol in presence of dry HCl gas and \[\alpha \]-methyl glycosides, \[\beta \]-methyl glycosides are formed.
So our correct option is D. five hydroxyl groups
Note:
\[\alpha \]-methyl glucosides and \[\beta \]-methyl glucosides are acetals and these are non-reducing sugars. Also these shows mutarotation. Remember only methyl groups are attached in place of hydrogen in hydroxyl groups.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




