
Glucose does not react with:
A. ${Br}_2/H_2O$
B. $N{H_2}OH$
C. $NaHS{O_3}$
D. $HI$
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: We know that the chemical reactions of a compound can be used to deduce the structure of the compound and vice versa as both are interrelated. Glucose is one of the six carbon-containing hexopyranose. It is also known that there is no free $ - CHO$ group present in the cyclic structure of glucose.
Complete answer
Glucose is a very significant bio-molecule as it is a main constituent of sweet products such as fruits, honey or sugar. It also acts as a monomer for many other carbohydrates including starch and cellulose. It has a chemical formula \[{C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}\]. Now, let’s have a look at its structure which can be shown as below:
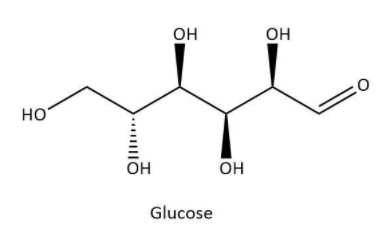
As we can see that it contains six carbons and an aldehyde group which gives it the name, aldohexose.
Now, we will discuss the reactions of glucose that results from its structure.
1. Reaction with $HI$: Glucose upon heating with $HI$ gives hexane. The reaction can be written as follows:
$HOC{H_2} - {\left( {CHOH} \right)_4} - CHO \overset{HI, Delta}{\longrightarrow} C{H_3}{\left( {C{H_2}} \right)_4}C{H_3}$
This reaction provides evidence of six carbons being in a straight chain as the product is n-hexane.
2. Reaction with $N{H_2}OH$: Glucose gives an oxime after reacting with $N{H_2}OH$. The reaction can be written as follows:
$HOC{H_2} - {\left( {CHOH} \right)_4} - CHO + N{H_2}OH \to HOC{H_2} - {\left( {CHOH} \right)_4} - HC = N - OH$
Formation of oxime is a characteristic reaction of the carbonyl group. So, we can say that this reaction can help us in confirming the presence of $ > C = O$ group in glucose.
3. Reaction with ${Br}_2/H_2O$: Glucose gives carboxylic acid after reacting with${Br}_2/H_2O$ as bromine water acts a mild oxidizing agent and the aldehyde group gets oxidized further to the carboxylic group. The reaction can be written as follows:
$HOC{H_2} - {\left( {CHOH} \right)_4} - CHO + {Br}_2/H_2O \longrightarrow HOC{H_2} - {\left( {CHOH} \right)_4} - COOH$
This reaction helps us to deduce that the carbonyl group present in glucose is aldehyde.
From the above discussion, we can see that glucose reacts with three of the given reagents, ${Br}_2/H_2O$, $N{H_2}OH$ and $HI$.
Hence, the reagent that it doesn’t react with is $NaHS{O_3}$ making option C to be the correct one.
Note:
We have to carefully choose the reagents because every compound shows characteristic reactions. Glucose consists of an aldehyde group. However, it does not undergo reaction with sodium hydrogen sulphite in order to form bisulphite addition products. This is due to the fact that this reaction occurs in the presence of a free aldehyde group, but there is no free $ - CHO$ group present in the structure of glucose. Therefore, we can say that sodium hydrogen sulphite is not able to cleave the cyclic ring $\left( {\delta {\rm{ - oxide}}\;{\rm{ring}}} \right)$ in glucose.
Complete answer
Glucose is a very significant bio-molecule as it is a main constituent of sweet products such as fruits, honey or sugar. It also acts as a monomer for many other carbohydrates including starch and cellulose. It has a chemical formula \[{C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}\]. Now, let’s have a look at its structure which can be shown as below:

As we can see that it contains six carbons and an aldehyde group which gives it the name, aldohexose.
Now, we will discuss the reactions of glucose that results from its structure.
1. Reaction with $HI$: Glucose upon heating with $HI$ gives hexane. The reaction can be written as follows:
$HOC{H_2} - {\left( {CHOH} \right)_4} - CHO \overset{HI, Delta}{\longrightarrow} C{H_3}{\left( {C{H_2}} \right)_4}C{H_3}$
This reaction provides evidence of six carbons being in a straight chain as the product is n-hexane.
2. Reaction with $N{H_2}OH$: Glucose gives an oxime after reacting with $N{H_2}OH$. The reaction can be written as follows:
$HOC{H_2} - {\left( {CHOH} \right)_4} - CHO + N{H_2}OH \to HOC{H_2} - {\left( {CHOH} \right)_4} - HC = N - OH$
Formation of oxime is a characteristic reaction of the carbonyl group. So, we can say that this reaction can help us in confirming the presence of $ > C = O$ group in glucose.
3. Reaction with ${Br}_2/H_2O$: Glucose gives carboxylic acid after reacting with${Br}_2/H_2O$ as bromine water acts a mild oxidizing agent and the aldehyde group gets oxidized further to the carboxylic group. The reaction can be written as follows:
$HOC{H_2} - {\left( {CHOH} \right)_4} - CHO + {Br}_2/H_2O \longrightarrow HOC{H_2} - {\left( {CHOH} \right)_4} - COOH$
This reaction helps us to deduce that the carbonyl group present in glucose is aldehyde.
From the above discussion, we can see that glucose reacts with three of the given reagents, ${Br}_2/H_2O$, $N{H_2}OH$ and $HI$.
Hence, the reagent that it doesn’t react with is $NaHS{O_3}$ making option C to be the correct one.
Note:
We have to carefully choose the reagents because every compound shows characteristic reactions. Glucose consists of an aldehyde group. However, it does not undergo reaction with sodium hydrogen sulphite in order to form bisulphite addition products. This is due to the fact that this reaction occurs in the presence of a free aldehyde group, but there is no free $ - CHO$ group present in the structure of glucose. Therefore, we can say that sodium hydrogen sulphite is not able to cleave the cyclic ring $\left( {\delta {\rm{ - oxide}}\;{\rm{ring}}} \right)$ in glucose.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




