
Glass and glycerin have the same refractive index. How will you observe the
reflection and refraction phenomenon in a glass-glycerin interface?
Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint: Glass-glycerin has no interface as the refractive index of both is the same. Refraction is caused because the speed of light is different from one medium to another one. When there is no change in the direction of light, the light passes from glycerin to glass & goes out from glass to glycerin.
Complete answer:
The refractive record is identified with the quality of the association between the light and the dielectric, so if the refractive list is the equivalent either side of an interface that implies the cooperation of the light with the two materials is the equivalent.
Light cooperates with a dielectric on the grounds that the wavering electric field related to the light spell binds the electron thickness inside the dielectric, and this produces swaying electric dipoles. These swaying dipoles then reradiate light that meddles with the occurrence of light and changes its speed of engendering. It is the adjustment in the quality of this association that makes the light reflect at an interface.
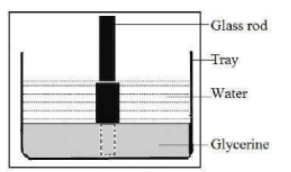
If the light collaborates similarly with the two materials, it is unaffected bypassing; however, a limit between them.
It may appear to be unusual that a strong like glass and fluid-like glycerin can cooperate with light similarly, however, recollect that the frequency of light is a lot more prominent than the measures of the atoms in the glass or glycerin. Undoubtedly both glass and glycerin are only a mass of electrons. On the off chance that the communication of the light with the electrons is the equivalent in both glass and glycerin, the light will engender at a similar speed in the two.
Note:
Refraction is the adjustment of course of a wave which is going to start with one medium then onto the next or from a steady change in the medium. Refraction of light is the most usual watched wonder, yet waves are different, for example, sound waves and water waves experience refraction.
Complete answer:
The refractive record is identified with the quality of the association between the light and the dielectric, so if the refractive list is the equivalent either side of an interface that implies the cooperation of the light with the two materials is the equivalent.
Light cooperates with a dielectric on the grounds that the wavering electric field related to the light spell binds the electron thickness inside the dielectric, and this produces swaying electric dipoles. These swaying dipoles then reradiate light that meddles with the occurrence of light and changes its speed of engendering. It is the adjustment in the quality of this association that makes the light reflect at an interface.

If the light collaborates similarly with the two materials, it is unaffected bypassing; however, a limit between them.
It may appear to be unusual that a strong like glass and fluid-like glycerin can cooperate with light similarly, however, recollect that the frequency of light is a lot more prominent than the measures of the atoms in the glass or glycerin. Undoubtedly both glass and glycerin are only a mass of electrons. On the off chance that the communication of the light with the electrons is the equivalent in both glass and glycerin, the light will engender at a similar speed in the two.
Note:
Refraction is the adjustment of course of a wave which is going to start with one medium then onto the next or from a steady change in the medium. Refraction of light is the most usual watched wonder, yet waves are different, for example, sound waves and water waves experience refraction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




