
Given,\[but - 2 - ene\] exhibits \[cis - trans\] isomerism due to:
A.Rotation around ${C_3} - {C_4}$ sigma bond
B.Restricted rotation around $C = C$ bond
C.Rotation around $C{}_1 - {C_2}$ bond
D.Rotation around ${C_2} - {C_3}$ double bond
Answer
563.7k+ views
Hint:We must remember that the similar molecular formula but different compounds are called isomers, similar molecular formula compounds behave as different compounds are called isomerism. The arrangement in the space is different for that compound; it is also known as stereoisomers. There are two types of stereoisomerism called cis-trans and optical isomerism.
Complete step by step answer:
We must remember that the \[cis - trans\] isomerism (also known as geometric isomerism), occurs in alkene, the carbon in the alkene is bonded two different groups.
\[but - 2 - ene\] structure is,
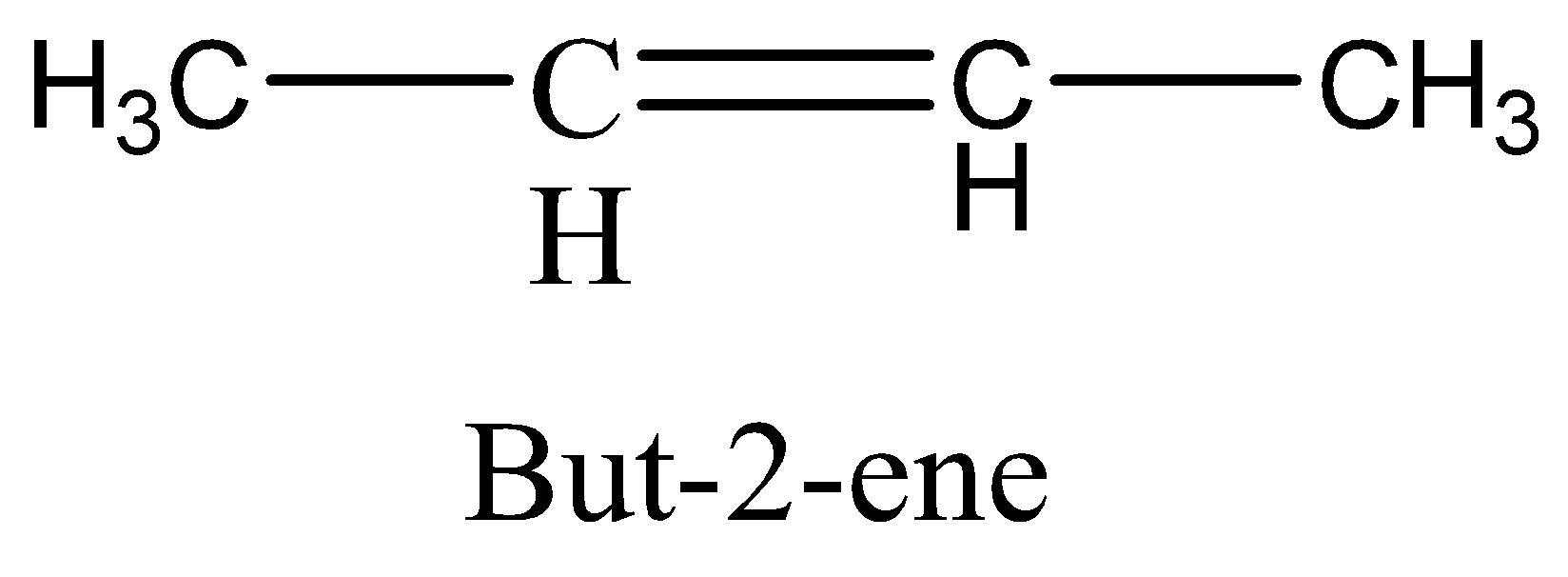
As see above, the \[methyl\] and hydrogen group is bonded to different carbon atoms, but this compound has two different structures as follows,
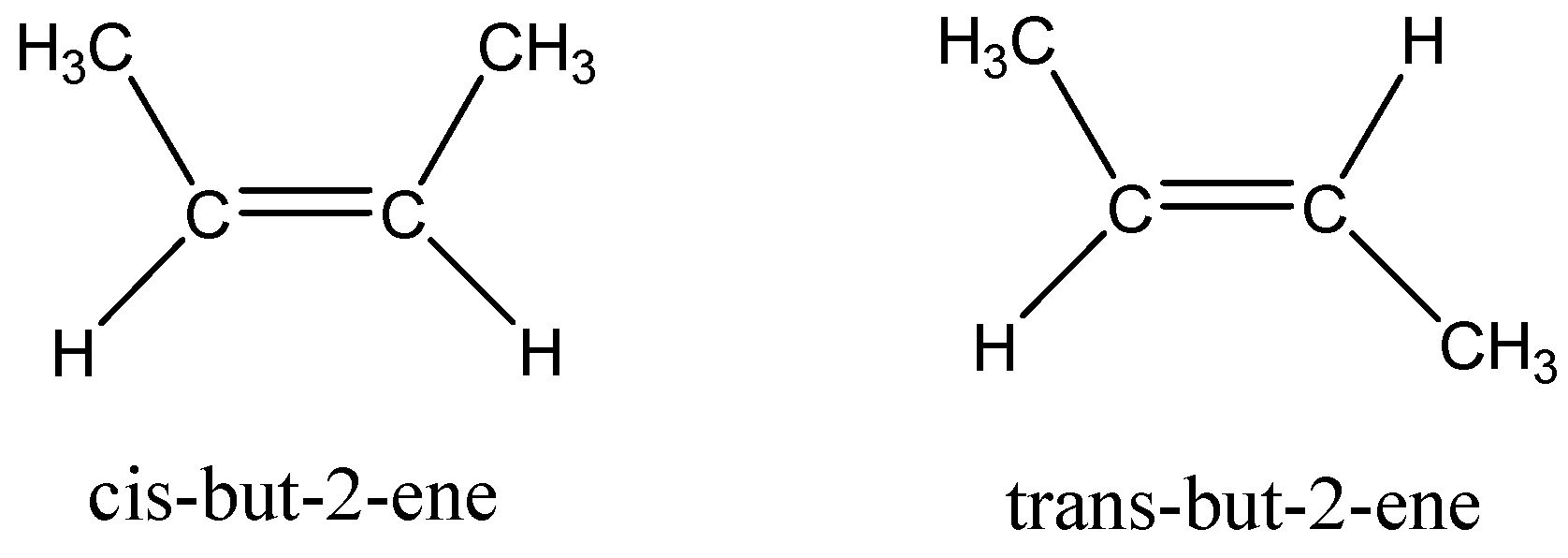
The two \[methyl\] groups on the same side in the molecule is cis isomer, called \[{\text{cis - but - 2 - ene}}\] and the two \[methyl\] groups on opposite side of the molecule is known as trans isomer, then the molecule is called \[{\text{trans - but - 2 - ene}}\] .
Let us see the options one by one to find the correct answer,
Option A. Rotation around ${C_3} - {C_4}$ sigma bond
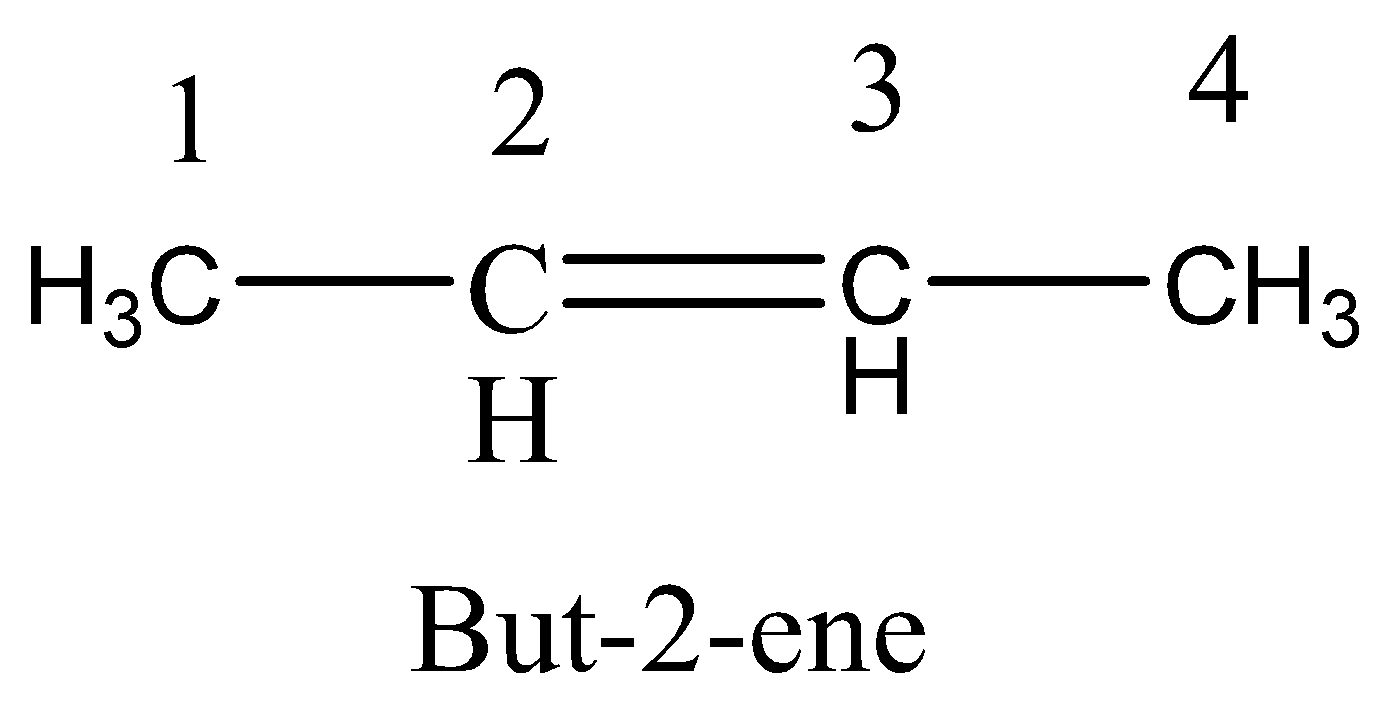
If the rotation around ${C_3} - {C_4}$ sigma bond, then there is no possible trans isomer. And so, there is no possible for \[cis - trans\] isomerism.
Option B. Restricted rotation around $C = C$ bond
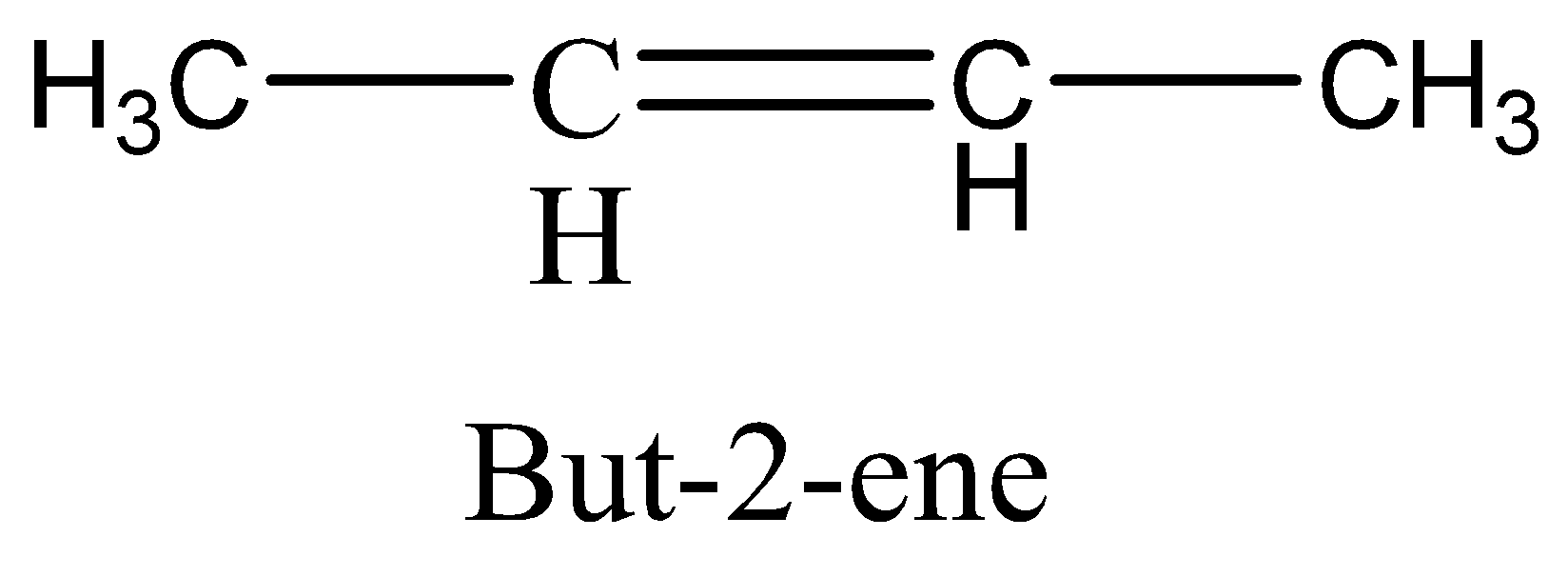
If the rotation is restricted on the molecule and there are two non-identical groups must be present on each doubly bonded carbon atom, then there should be \[cis - trans\] isomerism present. The molecule,
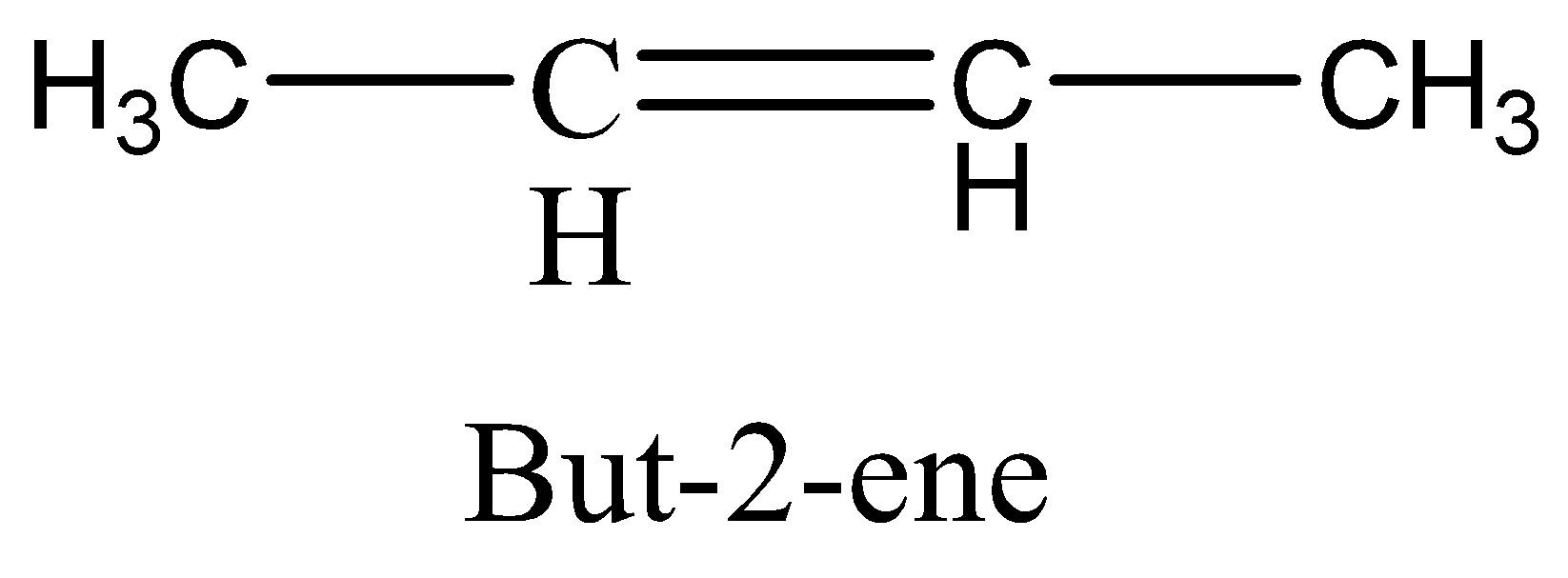
It has restricted rotation in the molecule and there are two non-identical groups present on each doubly bonded carbon atom ($C = C$ bond). So, this is correct option, but we will see the other two options to clarify,
Option C. Rotation around $C{}_1 - {C_2}$ bond
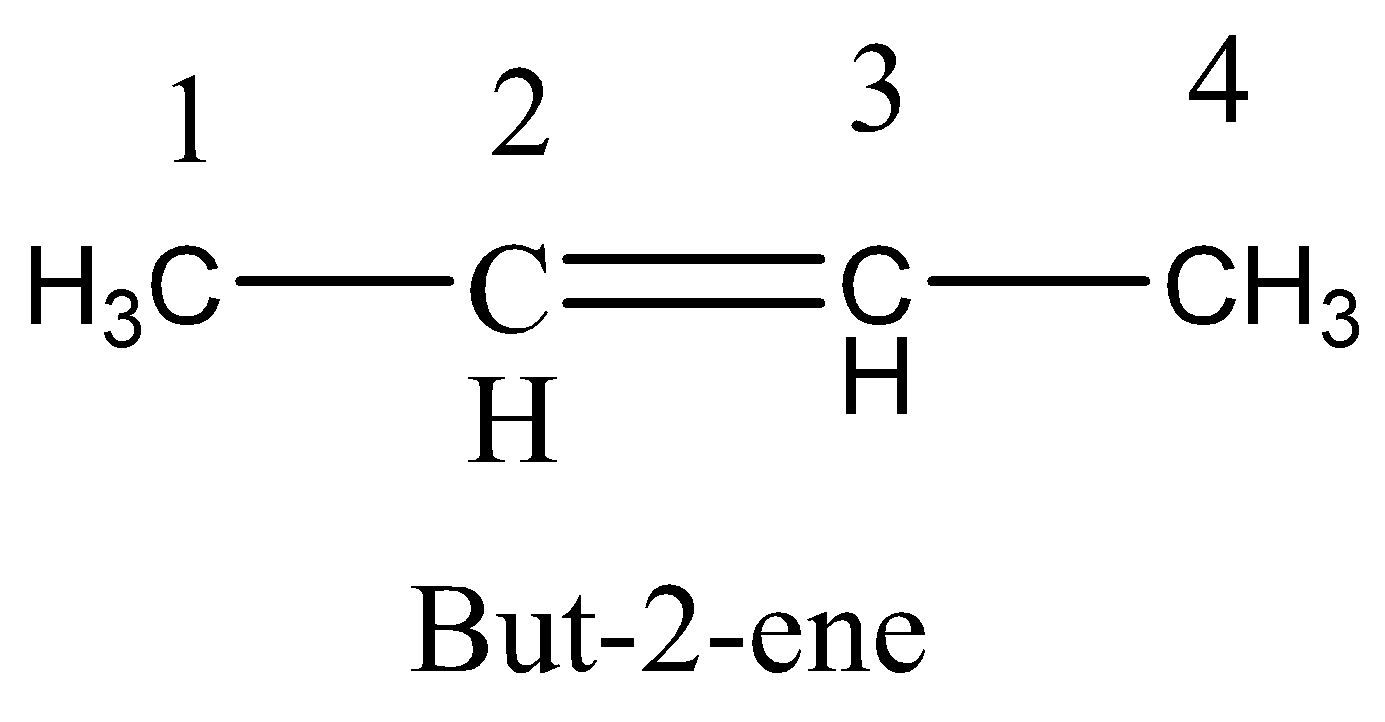
The rotation in the $C{}_1 - {C_2}$ bond does not lead to \[cis - trans\] isomerism because $C{}_1 - {C_2}$ bond contains sigma bond. So this is not the correct option.
Option D. Rotation around ${C_2} - {C_3}$ double bond
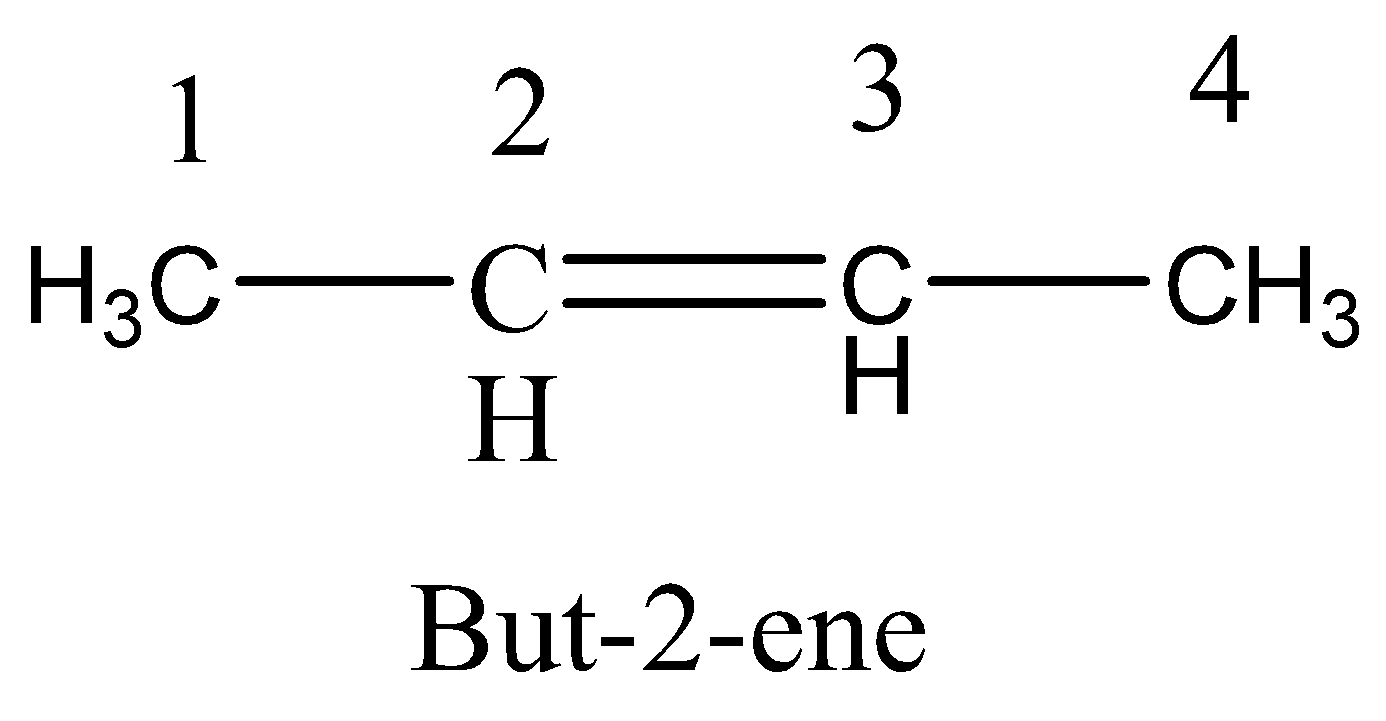
The hybridization in the carbon atom is $s{p^2}$ and two $p$ orbitals make sidewise overlap.
Two $p$ orbitals make ${90^0}$ overlap does not twisted, and does not lead to \[cis - trans\] isomerism.
From the above information, Option B. Restricted rotation around $C = C$ bond is the correct option.
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note:
We must have to remember that if an alkene contains \[C = C{H_2}\] , then there is no \[cis - trans\] isomerism.
In an alkene \[C = C{R_2}\] unit, the two $R$ groups are same then there is no \[cis - trans\] isomerism.
\[R-CH = CH-R\] , this type of alkene only exist \[cis - trans\] isomerism.
Complete step by step answer:
We must remember that the \[cis - trans\] isomerism (also known as geometric isomerism), occurs in alkene, the carbon in the alkene is bonded two different groups.
\[but - 2 - ene\] structure is,
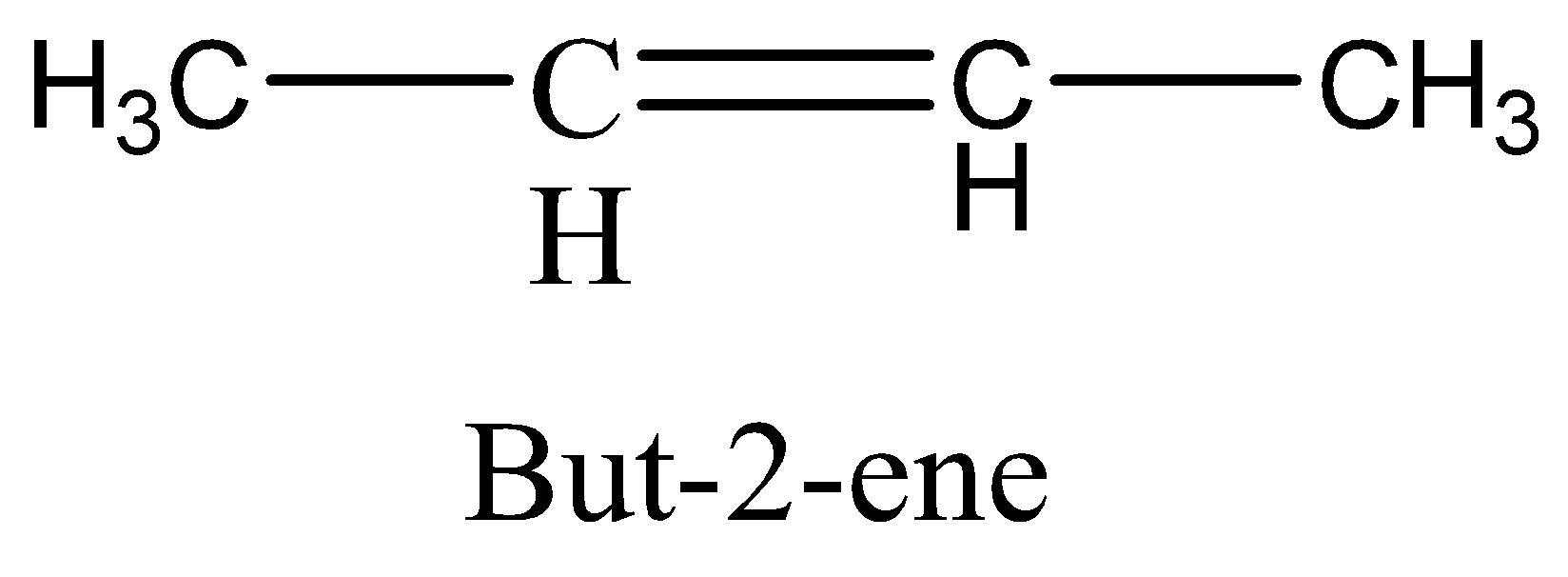
As see above, the \[methyl\] and hydrogen group is bonded to different carbon atoms, but this compound has two different structures as follows,

The two \[methyl\] groups on the same side in the molecule is cis isomer, called \[{\text{cis - but - 2 - ene}}\] and the two \[methyl\] groups on opposite side of the molecule is known as trans isomer, then the molecule is called \[{\text{trans - but - 2 - ene}}\] .
Let us see the options one by one to find the correct answer,
Option A. Rotation around ${C_3} - {C_4}$ sigma bond

If the rotation around ${C_3} - {C_4}$ sigma bond, then there is no possible trans isomer. And so, there is no possible for \[cis - trans\] isomerism.
Option B. Restricted rotation around $C = C$ bond
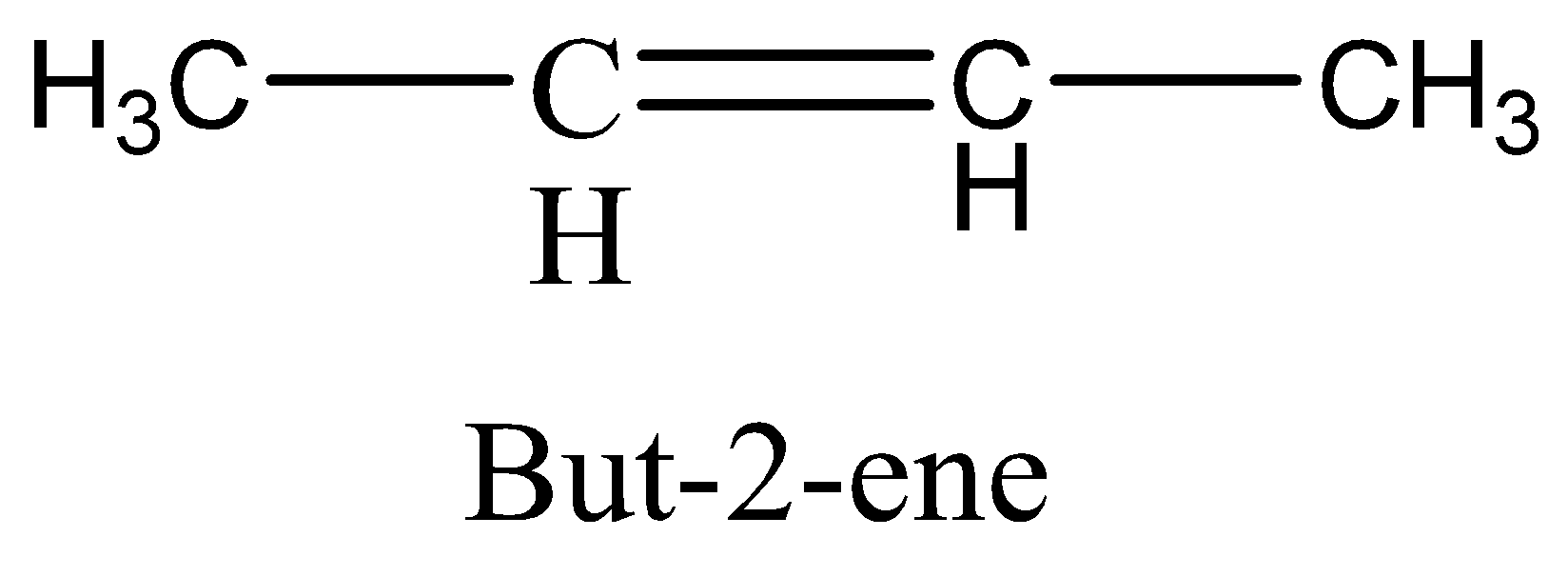
If the rotation is restricted on the molecule and there are two non-identical groups must be present on each doubly bonded carbon atom, then there should be \[cis - trans\] isomerism present. The molecule,
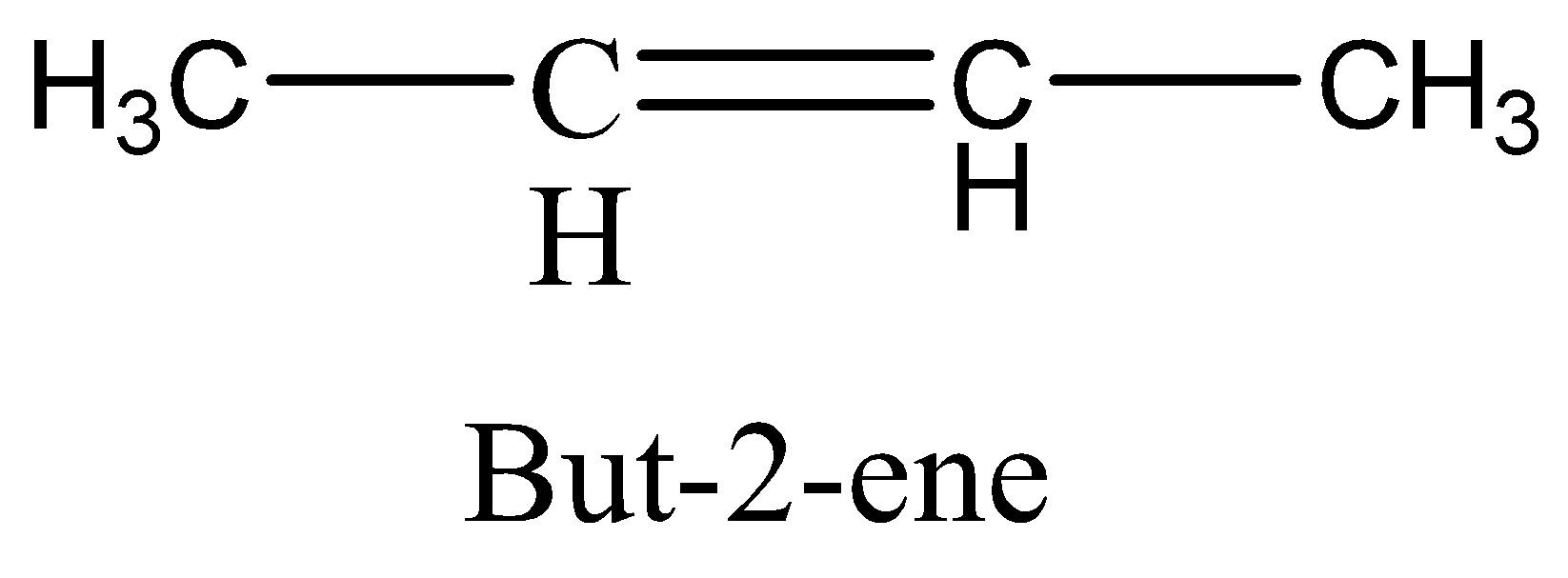
It has restricted rotation in the molecule and there are two non-identical groups present on each doubly bonded carbon atom ($C = C$ bond). So, this is correct option, but we will see the other two options to clarify,
Option C. Rotation around $C{}_1 - {C_2}$ bond

The rotation in the $C{}_1 - {C_2}$ bond does not lead to \[cis - trans\] isomerism because $C{}_1 - {C_2}$ bond contains sigma bond. So this is not the correct option.
Option D. Rotation around ${C_2} - {C_3}$ double bond

The hybridization in the carbon atom is $s{p^2}$ and two $p$ orbitals make sidewise overlap.
Two $p$ orbitals make ${90^0}$ overlap does not twisted, and does not lead to \[cis - trans\] isomerism.
From the above information, Option B. Restricted rotation around $C = C$ bond is the correct option.
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note:
We must have to remember that if an alkene contains \[C = C{H_2}\] , then there is no \[cis - trans\] isomerism.
In an alkene \[C = C{R_2}\] unit, the two $R$ groups are same then there is no \[cis - trans\] isomerism.
\[R-CH = CH-R\] , this type of alkene only exist \[cis - trans\] isomerism.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




