
Given that, x is a real number satisfying $\dfrac{{5{x^2} - 26x + 5}}{{3{x^2} - 10x + 3}} < 0$, then
$\left( a \right)x < \dfrac{1}{5}$
$\left( b \right)\dfrac{1}{5} < x < 3$
$\left( c \right)x > 5$
$\left( d \right)\dfrac{1}{5} < x < \dfrac{1}{3}{\text{ or }}3 < x < 5$
Answer
594.3k+ views
Hint: In this particular question use the concept that in order to get the solution less than zero, one of the factors from both of the equations is less than zero so that the complete solution is less than zero, so use this concept to reach the solution of the question.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given expression
$\dfrac{{5{x^2} - 26x + 5}}{{3{x^2} - 10x + 3}} < 0$
As we see that in numerator and denominator the highest power of x is 2 so both are the quadratic equation.
So factorize both of the equation we have,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{5{x^2} - 25x - x + 5}}{{3{x^2} - 9x - x + 3}} < 0$
Now take 5x common from first two terms of the numerator and 3x common from first two terms of the denominator we have,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{5x\left( {x - 5} \right) - 1\left( {x - 5} \right)}}{{3x\left( {x - 3} \right) - 1\left( {x - 3} \right)}} < 0$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\left( {x - 5} \right)\left( {5x - 1} \right)}}{{\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {3x - 1} \right)}} < 0$
Now as we see that the above function is less than zero, so in order to get the solution less than zero i.e. negative the required solution for x is
$ \Rightarrow x \in \left( {\dfrac{1}{5},\dfrac{1}{3}} \right){\text{ or }}x \in \left( {3,5} \right)$
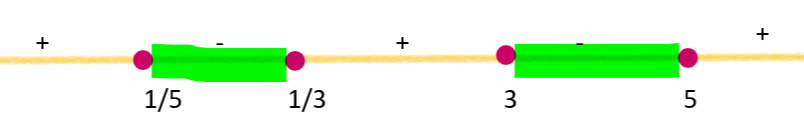
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{5} < x < \dfrac{1}{3}{\text{ or }}3 < x < 5$
So this is the required solution
Hence option (d) is the correct answer.
Note: Whenever we face such types of questions the key concept we have to remember is that always recall that the quadratic equation is solved using factorization method or we can use the quadratic formula for complex quadratic equation which is given as $x = \dfrac{{ - b \pm \sqrt {{b^2} - 4ac} }}{{2a}}$ where, a is the coefficient of ${x^2}$, b is the coefficient of x and c is the constant term.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given expression
$\dfrac{{5{x^2} - 26x + 5}}{{3{x^2} - 10x + 3}} < 0$
As we see that in numerator and denominator the highest power of x is 2 so both are the quadratic equation.
So factorize both of the equation we have,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{5{x^2} - 25x - x + 5}}{{3{x^2} - 9x - x + 3}} < 0$
Now take 5x common from first two terms of the numerator and 3x common from first two terms of the denominator we have,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{5x\left( {x - 5} \right) - 1\left( {x - 5} \right)}}{{3x\left( {x - 3} \right) - 1\left( {x - 3} \right)}} < 0$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\left( {x - 5} \right)\left( {5x - 1} \right)}}{{\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {3x - 1} \right)}} < 0$
Now as we see that the above function is less than zero, so in order to get the solution less than zero i.e. negative the required solution for x is
$ \Rightarrow x \in \left( {\dfrac{1}{5},\dfrac{1}{3}} \right){\text{ or }}x \in \left( {3,5} \right)$
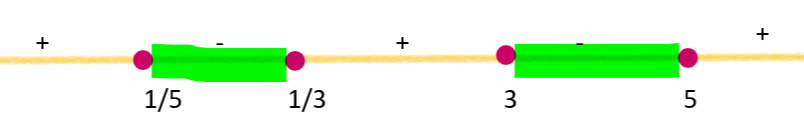
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{5} < x < \dfrac{1}{3}{\text{ or }}3 < x < 5$
So this is the required solution
Hence option (d) is the correct answer.
Note: Whenever we face such types of questions the key concept we have to remember is that always recall that the quadratic equation is solved using factorization method or we can use the quadratic formula for complex quadratic equation which is given as $x = \dfrac{{ - b \pm \sqrt {{b^2} - 4ac} }}{{2a}}$ where, a is the coefficient of ${x^2}$, b is the coefficient of x and c is the constant term.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

What is the difference between biodegradable and nonbiodegradable class 11 biology CBSE

Proton was discovered by A Thomson B Rutherford C Chadwick class 11 chemistry CBSE




