
Given $P\left( x \right) = {x^4} + a{x^3} + b{x^2} + cx + d$ such that x = 0 is the only real root of $P'\left( x \right) = 0$. If P (-1) < P (1), then in the interval [-1, 1].
$\left( a \right)$ P (-1) is the minimum and P (1) is the maximum of P
$\left( b \right)$ P (-1) is not minimum but P (1) is the maximum of P
$\left( c \right)$ P (-1) is the minimum but P (1) is not the maximum of P
$\left( d \right)$ Neither P (-1) is the minimum nor P (1) is the maximum of P
Answer
591.6k+ views
Hint: In this particular question use the concept that after differentiating the equation equate the equation to zero and substitute x = 0 according to given condition and calculate the value of constant c, then use the concept that a quadratic equation has no real roots if the discriminant D of the quadratic equation is less than zero, so use these concepts to reach the solution of the question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given polynomial
$P\left( x \right) = {x^4} + a{x^3} + b{x^2} + cx + d$
Now differentiate this equation w.r.t x we have,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{d}{{dx}}P\left( x \right) = \dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {{x^4} + a{x^3} + b{x^2} + cx + d} \right)$
Now as we know that $\dfrac{d}{{dx}}{x^n} = n{x^{n - 1}}$ so use this property in the above equation we have,
$ \Rightarrow P'\left( x \right) = \left( {4{x^3} + 3a{x^2} + 2bx + c} \right)$........ (1)
Now it is given that x = 0 is the only real root of $P'\left( x \right) = 0$.
$ \Rightarrow P'\left( 0 \right) = \left( {4\left( 0 \right) + 3a\left( 0 \right) + 2b\left( 0 \right) + c} \right) = 0$
$ \Rightarrow c = 0$
Now from equation (1) we have,
$ \Rightarrow P'\left( x \right) = \left( {4{x^3} + 3a{x^2} + 2bx} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow P'\left( x \right) = x\left( {4{x^2} + 3ax + 2b} \right)$
Now the above equation has only one real root which is, x = 0, so the determinant of the above quadratic equation i.e. $4{x^2} + 3ax + 2b$ should be less than zero, otherwise it has more real roots.
So the determinant D, of the quadratic equation is,
$ \Rightarrow D = \sqrt {{B^2} - 4AC} $, Where, A = 4, B = 3a, C = 2b
$ \Rightarrow D = \sqrt {9{a^2} - 32b} < 0$
So, the quadratic equation, $4{x^2} + 3ax + 2b > 0,\left( {\forall x \in R} \right)$, if a > 0
So in the interval [-1, 0)
$ \Rightarrow P'\left( x \right) = x\left( {4{x^2} + 3ax + 2b} \right)$ < 0 i.e. in this interval P’(x) is a decreasing function.
And in the interval (0, 1]
$ \Rightarrow P'\left( x \right) = x\left( {4{x^2} + 3ax + 2b} \right)$ > 0 i.e. in this interval P’(x) is an increasing function.
The diagram of P (x) is shown below
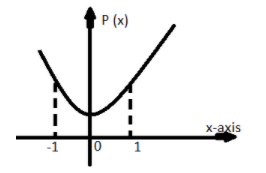
So we can say that the maximum of P (x) occurs at x = 1.
So, maximum of P (x) = P (1) in the interval [-1, 1]
But the minimum of P (x) does not occur at x = -1.
So, minimum of P (x) $ \ne $P (-1) in the interval [-1, 1].
So this is the required answer.
Hence option (a) is the correct answer.
Note: Whenever we face such types of questions the key concept we have to remember is that always recall the basic differentiation property which is stated above and always recall that if the differentiation of any function is less than zero then the function is strictly decreasing function and if greater than zero then the function is strictly increasing function.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given polynomial
$P\left( x \right) = {x^4} + a{x^3} + b{x^2} + cx + d$
Now differentiate this equation w.r.t x we have,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{d}{{dx}}P\left( x \right) = \dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {{x^4} + a{x^3} + b{x^2} + cx + d} \right)$
Now as we know that $\dfrac{d}{{dx}}{x^n} = n{x^{n - 1}}$ so use this property in the above equation we have,
$ \Rightarrow P'\left( x \right) = \left( {4{x^3} + 3a{x^2} + 2bx + c} \right)$........ (1)
Now it is given that x = 0 is the only real root of $P'\left( x \right) = 0$.
$ \Rightarrow P'\left( 0 \right) = \left( {4\left( 0 \right) + 3a\left( 0 \right) + 2b\left( 0 \right) + c} \right) = 0$
$ \Rightarrow c = 0$
Now from equation (1) we have,
$ \Rightarrow P'\left( x \right) = \left( {4{x^3} + 3a{x^2} + 2bx} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow P'\left( x \right) = x\left( {4{x^2} + 3ax + 2b} \right)$
Now the above equation has only one real root which is, x = 0, so the determinant of the above quadratic equation i.e. $4{x^2} + 3ax + 2b$ should be less than zero, otherwise it has more real roots.
So the determinant D, of the quadratic equation is,
$ \Rightarrow D = \sqrt {{B^2} - 4AC} $, Where, A = 4, B = 3a, C = 2b
$ \Rightarrow D = \sqrt {9{a^2} - 32b} < 0$
So, the quadratic equation, $4{x^2} + 3ax + 2b > 0,\left( {\forall x \in R} \right)$, if a > 0
So in the interval [-1, 0)
$ \Rightarrow P'\left( x \right) = x\left( {4{x^2} + 3ax + 2b} \right)$ < 0 i.e. in this interval P’(x) is a decreasing function.
And in the interval (0, 1]
$ \Rightarrow P'\left( x \right) = x\left( {4{x^2} + 3ax + 2b} \right)$ > 0 i.e. in this interval P’(x) is an increasing function.
The diagram of P (x) is shown below

So we can say that the maximum of P (x) occurs at x = 1.
So, maximum of P (x) = P (1) in the interval [-1, 1]
But the minimum of P (x) does not occur at x = -1.
So, minimum of P (x) $ \ne $P (-1) in the interval [-1, 1].
So this is the required answer.
Hence option (a) is the correct answer.
Note: Whenever we face such types of questions the key concept we have to remember is that always recall the basic differentiation property which is stated above and always recall that if the differentiation of any function is less than zero then the function is strictly decreasing function and if greater than zero then the function is strictly increasing function.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




