
Given, \[N,N - \]dimethylaniline is treated with aqueous $NaN{O_2}/HCl$, the product formed is:
A.$p - $($N,N - $Dimethylamino) benzenediazonium chloride.
B.$p - $($N,N - $Dimethylamino) phenol.
C.$p - $nitroso-$N,N - $dimethylaniline.
D.$p - $Nitro$N,N - $dimethylaniline.
Answer
510.6k+ views
Hint: The reaction between \[N,N - \] dimethylaniline and $NaN{O_2}/HCl$ is a sandmeyer reaction. The Sandmeyer reaction is a chemical reaction used to synthesize aryl halides from aryl diazonium salts using copper salts as reagents or catalysts. It is an example of a radical-nucleophilic aromatic substitution.
Complete answer:
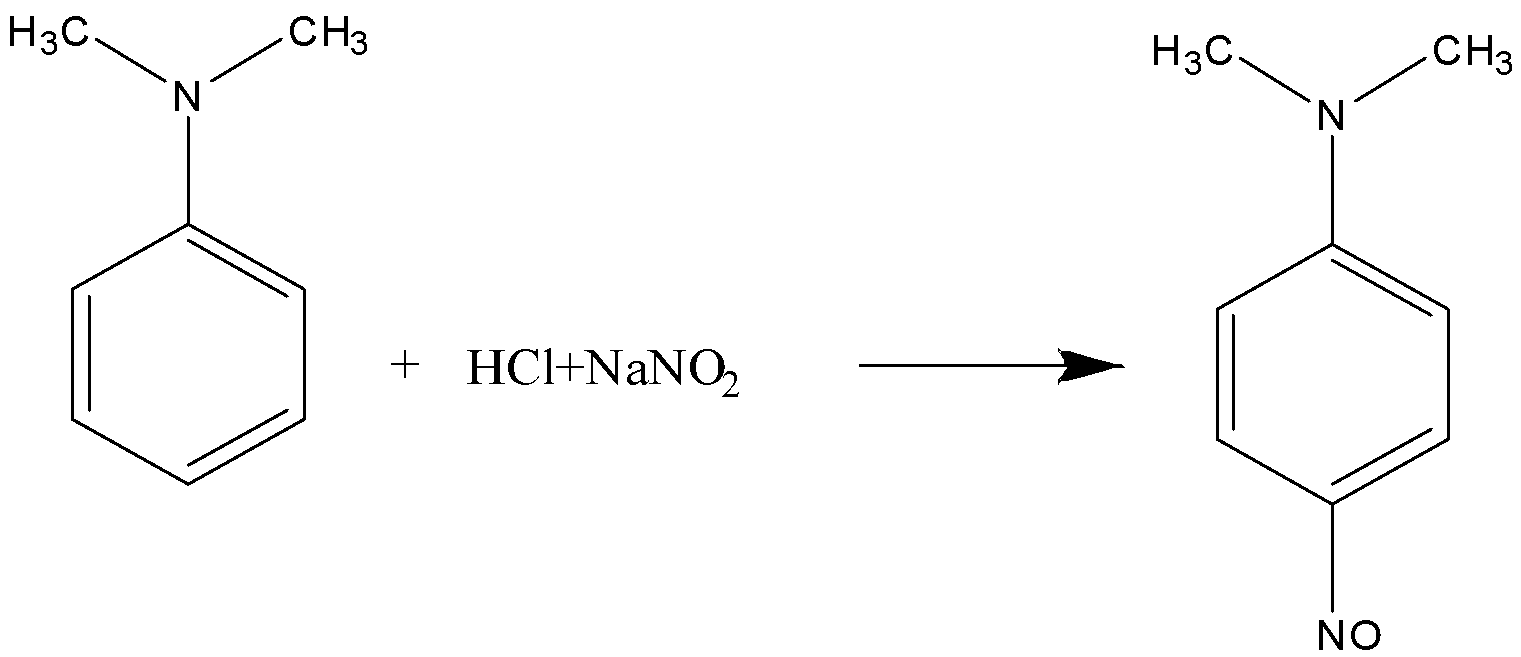
Sandmeyer reaction is a type of substitution reaction that is widely used in the production of aryl halides from aryl diazonium salts. Copper salts like chloride, bromide or iodide ions are used as catalysts in this reaction. Notably, the Sandmeyer reaction can be used to perform unique transformations on benzene.
Here, the \[N,N - \] dimethylaniline reacts with $NaN{O_2}/HCl$ and forms $p - $nitroso-$N,N - $dimethylaniline.
So, the correct answer is (C) $p - $nitroso-$N,N - $dimethylaniline
Additional information:
The most commonly employed Sandmeyer reactions are the chlorination, bromination, cyanation, and hydroxylation reactions using $CuCl,CuBr,CuCN$ and $Cu{O_2}$, respectively. Diazonium salts also react with boronates, iodide, thiols, water, hypophosphorous acid and others, and fluorination can be carried out using tetrafluoroborate anions. However, since these processes do not require a metal catalyst, they are not usually referred to as Sandmeyer reactions.
Note:
The nitrous acid is typically prepared in situ from sodium nitrite and acid. In two protonation steps, one equivalent of water is lost to form the nitrosonium ion. The nitrosonium ion then acts as an electrophile in a reaction with an aromatic amine, such as aniline, to form a diazonium salt, proceeding through a nitrosamine intermediate.
Complete answer:
Sandmeyer reaction is a type of substitution reaction that is widely used in the production of aryl halides from aryl diazonium salts. Copper salts like chloride, bromide or iodide ions are used as catalysts in this reaction. Notably, the Sandmeyer reaction can be used to perform unique transformations on benzene.
Here, the \[N,N - \] dimethylaniline reacts with $NaN{O_2}/HCl$ and forms $p - $nitroso-$N,N - $dimethylaniline.
So, the correct answer is (C) $p - $nitroso-$N,N - $dimethylaniline

Additional information:
The most commonly employed Sandmeyer reactions are the chlorination, bromination, cyanation, and hydroxylation reactions using $CuCl,CuBr,CuCN$ and $Cu{O_2}$, respectively. Diazonium salts also react with boronates, iodide, thiols, water, hypophosphorous acid and others, and fluorination can be carried out using tetrafluoroborate anions. However, since these processes do not require a metal catalyst, they are not usually referred to as Sandmeyer reactions.
Note:
The nitrous acid is typically prepared in situ from sodium nitrite and acid. In two protonation steps, one equivalent of water is lost to form the nitrosonium ion. The nitrosonium ion then acts as an electrophile in a reaction with an aromatic amine, such as aniline, to form a diazonium salt, proceeding through a nitrosamine intermediate.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE

Find the foot of the perpendicular from point232to class 12 maths CBSE




