
Given in the figure is the chromosomal mutation.
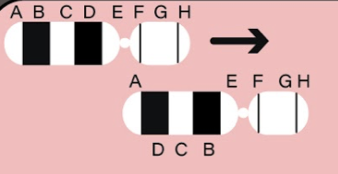
It is,
(a) Duplication
(b) Inversion
(c) Deletion
(d) Reciprocal Translocation

Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: This is a chromosome rearrangement in which a segment of a chromosome is reversed end to end. This process occurs when a single chromosome undergoes breakage and rearrangement within itself.
Complete step by step answer:
Inversion is a chromosomal mutation where a segment of a chromosome is reversed end to end. It occurs by the introduction of a break in a single chromosome, its rotation by l80o followed by its reinsertion in the same location. Loss of 1 or greater nucleotide bases to the DNA segment by removal of an intercalary DNA segment is known as deletion. Duplication is the presence of an extra- chromosomal segment that is attached to the normal homologous chromosome causing duplication of the set of genes in the same chromosome. The exchange of chromosomal segments between the 2 nonhomologous chromosomes is called reciprocal translocation. In the given image, A” BCD” EFGH is mutated to A” DCB” EFGH which means that segment “BCD” is inverted to “DCB”. There is no duplication, deletion, or exchange of segments but the intercalary segment “BCD” is rotated to 180o. The correct option is B. So, the correct answer is, ‘Inversion.’
Additional Information: The mutation is also seen in chromosomes where segments of genes are disturbed. These are called chromosomal aberrations or abnormalities and consist of the following types.
- Inversion: Part of the gene is inverted and attached again.
- Deletion: Part of the gene is deleted.
- Duplication: Part of the gene or the entire chromosome is duplicated.
- Translocation: Part of the gene from one chromosome is attached to a different chromosome.
Note: The mutation is referred to as the phenomenon which results in the alteration of the DNA sequence of the genome. This alteration happens in the sequence of nitrogenous bases present.
The mutation in the DNA is of two types:
- Point mutation: In point mutation, a single base pair is replaced by another which causes a change in the amino acids produced during translation. A classic example of this is Sickle cell anemia. A single base- pair change in the gene that codes for the beta- globin chain of hemoglobin results in the production of valine instead of glutamine. This causes the red blood cells to change into sickle- shaped cells.
- Frameshift mutation: In this mutation, a base pair is either added or removed from the gene which causes a complete alteration of the reading frame starting from the point of mutation. However, if base pairs in the multiple of three are added or removed, this won’t affect the reading frame but there will be a change in the number of amino acids produced.
Complete step by step answer:
Inversion is a chromosomal mutation where a segment of a chromosome is reversed end to end. It occurs by the introduction of a break in a single chromosome, its rotation by l80o followed by its reinsertion in the same location. Loss of 1 or greater nucleotide bases to the DNA segment by removal of an intercalary DNA segment is known as deletion. Duplication is the presence of an extra- chromosomal segment that is attached to the normal homologous chromosome causing duplication of the set of genes in the same chromosome. The exchange of chromosomal segments between the 2 nonhomologous chromosomes is called reciprocal translocation. In the given image, A” BCD” EFGH is mutated to A” DCB” EFGH which means that segment “BCD” is inverted to “DCB”. There is no duplication, deletion, or exchange of segments but the intercalary segment “BCD” is rotated to 180o. The correct option is B. So, the correct answer is, ‘Inversion.’
Additional Information: The mutation is also seen in chromosomes where segments of genes are disturbed. These are called chromosomal aberrations or abnormalities and consist of the following types.
- Inversion: Part of the gene is inverted and attached again.
- Deletion: Part of the gene is deleted.
- Duplication: Part of the gene or the entire chromosome is duplicated.
- Translocation: Part of the gene from one chromosome is attached to a different chromosome.
Note: The mutation is referred to as the phenomenon which results in the alteration of the DNA sequence of the genome. This alteration happens in the sequence of nitrogenous bases present.
The mutation in the DNA is of two types:
- Point mutation: In point mutation, a single base pair is replaced by another which causes a change in the amino acids produced during translation. A classic example of this is Sickle cell anemia. A single base- pair change in the gene that codes for the beta- globin chain of hemoglobin results in the production of valine instead of glutamine. This causes the red blood cells to change into sickle- shaped cells.
- Frameshift mutation: In this mutation, a base pair is either added or removed from the gene which causes a complete alteration of the reading frame starting from the point of mutation. However, if base pairs in the multiple of three are added or removed, this won’t affect the reading frame but there will be a change in the number of amino acids produced.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




