
Given figures shows
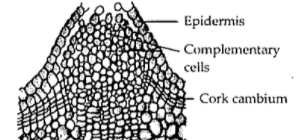
A. Structure of lenticel
B. Hydathode showing gaseous vapour exchange
C. Fungus reproducing by spore formation
D. Algae reproducing by spore formation

Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: It is usually found on woody plants which have vascular and cork cambium activity. In woody plants, they occur as rough, cor-like in young branches. It also has an important role in gas exchange.
Complete answer: The given figure shows the structure of a lenticel. A Lenticel is a porous tissue composed of cells having large intercellular spaces. It is usually found in the bark of woody stems, fruits of dicot flowering plants and on the surface of some fruits and tubers. It acts as a method of aeration in woody plants, in which the epidermis may be replaced by the suberized periderm or bark in which stomatal functions are replaced by lenticels. The formation of lenticels is linked to the growth and strength of the shoot and the internal moisture content of the tissue. Lenticels act as a medium for gaseous exchange and transpiration through loosely arranged thin-walled complementary cells. Complementary cells of lenticels are produced from phellogen. Phellogen is a ring of meristematic tissue formed from the outer parenchyma cells present in the cortex of dicot stems. Secondary cortex is known as phelloderm. These are thin-walled cells that arise from the inner side of the cork cambium. Phelloderm helps in the development of periderm. Cork cambium is a tissue found in the epidermis of many vascular plants. Its primary function is to produce cork which is a tough protective material found on the outer surfaces of the woody plants.
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note: Lenticels play an important role in gaseous exchange in plants. It promotes the exchange of carbon dioxide, oxygen and water vapour. They are found as raised circular, oval, or elongated areas on stems and roots.
Complete answer: The given figure shows the structure of a lenticel. A Lenticel is a porous tissue composed of cells having large intercellular spaces. It is usually found in the bark of woody stems, fruits of dicot flowering plants and on the surface of some fruits and tubers. It acts as a method of aeration in woody plants, in which the epidermis may be replaced by the suberized periderm or bark in which stomatal functions are replaced by lenticels. The formation of lenticels is linked to the growth and strength of the shoot and the internal moisture content of the tissue. Lenticels act as a medium for gaseous exchange and transpiration through loosely arranged thin-walled complementary cells. Complementary cells of lenticels are produced from phellogen. Phellogen is a ring of meristematic tissue formed from the outer parenchyma cells present in the cortex of dicot stems. Secondary cortex is known as phelloderm. These are thin-walled cells that arise from the inner side of the cork cambium. Phelloderm helps in the development of periderm. Cork cambium is a tissue found in the epidermis of many vascular plants. Its primary function is to produce cork which is a tough protective material found on the outer surfaces of the woody plants.
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note: Lenticels play an important role in gaseous exchange in plants. It promotes the exchange of carbon dioxide, oxygen and water vapour. They are found as raised circular, oval, or elongated areas on stems and roots.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




