
Given below are the different types of ovules. Identify A to F.
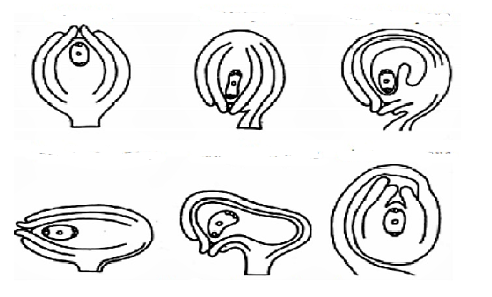
A. A-Circinotropous, B-Amphitropous, C-Campylotropous, D-Hemitropous, E-Anatropous, F-Orthotropous
B. A-Campylotropous, B-Anatropous, C-Hemitropous, D-Amphitropous, E-Circinotropous, F-Orthotropous
C. A-Orthotropous, B-Anatropous, C-Hemitropous, D-Campylotropous, E-Amphitropous, F-Circinotropous
D. A-Anatropous, B-Campylotropous, C-Hemitropous, D-Amphitropous, E-Circinotropous, F-Orthotropous

Answer
341.1k+ views
Hint: There are many things that go into fertilising a plant, but ovules may be the most important. Ovules are the female reproductive organs of flowering plants and are responsible for producing seeds. They contain everything that is needed to start a new plant - nutrients, water, and energy - which makes them an essential part of the agricultural process.
Step by step solution:
Orthotropous:
The micropyle, chalaza, and funicle are all in one straight line in an orthotropous ovule. For instance Polygonaceae, Piperaceae are ovules.
Anatropous: On bringing the micropyle and hilum very close together, the ovule's body is inverted wholly. This form of ovule is seen in 82% of angiosperm families. Plants are a gamopetalae subclass according to Bentham and Hooker classification.
Hemitropous ovule: When, the nucellus and integuments are at right angles to the funicle. Examples are the Ranunculaceae and Primulaceae families.
Campylotropous: When the ovule is crooked, the micropyle is aligned towards the chalaza. Chalaza is at right angles to the funicle. Members of the Cruciferae and Leguminosae families are two examples.
Amphitropous: The ovule curvature becomes more pronounced, and the embryo sac takes on a horseshoe form. Alismataceae and Butomaceae are two examples.
Circinotropous: Except for a small section at the end of the funicle, the funicle is extremely lengthy and forms a complete circle around the ovules.
Therefore, the correct arrangement from A to F is A-Orthotropous, B-Anatropous, C-Hemitropous, D-Campylotropous, E-Amphitropous, and F-Circinotropous
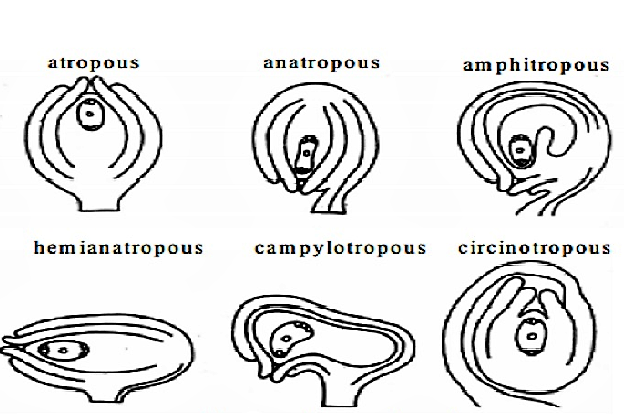
Fig: Different types of ovules.
Hence, the option C is correct
NOTE:
Angiosperms, or flowering plants, have their ovules covered. This stock, also known as the funicle or funiculus, joins the overview placenta to the placenta. The hilum is the place at which the funiculus attaches to the structure of the ovule.
Step by step solution:
Orthotropous:
The micropyle, chalaza, and funicle are all in one straight line in an orthotropous ovule. For instance Polygonaceae, Piperaceae are ovules.
Anatropous: On bringing the micropyle and hilum very close together, the ovule's body is inverted wholly. This form of ovule is seen in 82% of angiosperm families. Plants are a gamopetalae subclass according to Bentham and Hooker classification.
Hemitropous ovule: When, the nucellus and integuments are at right angles to the funicle. Examples are the Ranunculaceae and Primulaceae families.
Campylotropous: When the ovule is crooked, the micropyle is aligned towards the chalaza. Chalaza is at right angles to the funicle. Members of the Cruciferae and Leguminosae families are two examples.
Amphitropous: The ovule curvature becomes more pronounced, and the embryo sac takes on a horseshoe form. Alismataceae and Butomaceae are two examples.
Circinotropous: Except for a small section at the end of the funicle, the funicle is extremely lengthy and forms a complete circle around the ovules.
Therefore, the correct arrangement from A to F is A-Orthotropous, B-Anatropous, C-Hemitropous, D-Campylotropous, E-Amphitropous, and F-Circinotropous

Fig: Different types of ovules.
Hence, the option C is correct
NOTE:
Angiosperms, or flowering plants, have their ovules covered. This stock, also known as the funicle or funiculus, joins the overview placenta to the placenta. The hilum is the place at which the funiculus attaches to the structure of the ovule.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Hybrid seeds have to be produced every year because class 12 biology NEET_UG

Who is known as the "Little Master" in Indian cricket history?

What are gulf countries and why they are called Gulf class 8 social science CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Name the states through which the Tropic of Cancer class 8 social science CBSE




