
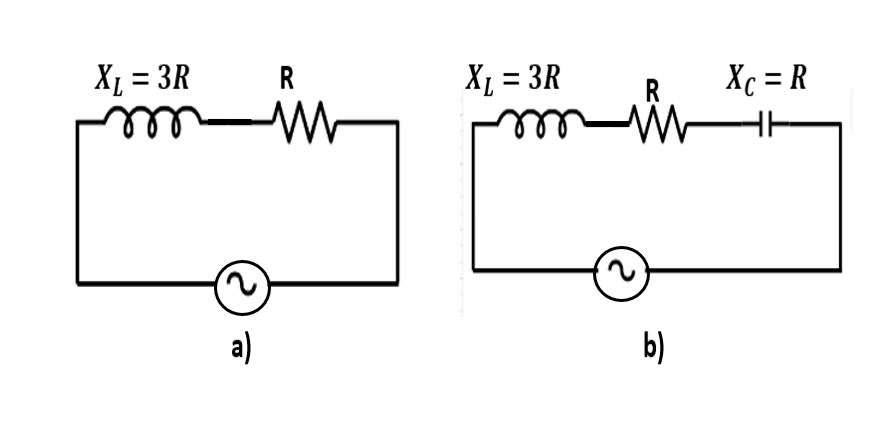
Given are two electricals’ circuits A and B. Calculate the ratio of power factor of circuit B to the power factor of circuit A.

Answer
508.5k+ views
Hint: In a circuit, when the voltage leads the current, then the power factor of the circuit is identified as a lagging power factor. Power factor is described as the cosine angle between current and voltage. Ideally, in AC circuits, the phase difference between current and voltage is zero. However, practically there is some phase difference between the two. The cosine angle of the phase difference between the two is represented as the power factor.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The power factor of a circuit is given by-
$cos \phi = \dfrac{R}{Z} = \dfrac{R}{\sqrt{ R^{2} + \left(X_{L} – X_{C} \right)^{2} }}$
For circuit A: $X_{L} = 3R$, $ X_{C} = 0$
The power factor of a circuit A is given by-
$cos \phi_{A} = \dfrac{R}{Z} = \dfrac{R}{\sqrt{ R^{2} + \left(3R – 0 \right)^{2} }}$
$cos \phi_{A} = \dfrac{R}{\sqrt{ R^{2} +9R^{2}} } = \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{10}}$
For circuit B: $X_{L} = 3R$, $ X_{C} = R$
The power factor of a circuit B is given by-
$cos \phi_{B} = \dfrac{R}{Z} = \dfrac{R}{\sqrt{ R^{2} + \left(3R – R \right)^{2} }}$
$cos \phi_{B} = \dfrac{R}{\sqrt{ R^{2} +4R^{2}} } = \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}}$
Ratio of power factor of both circuits:
$\dfrac{ cos \phi_{B} }{ cos \phi_{A}} = \dfrac{\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}}}{\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{10}}} =\sqrt{2} $
The ratio of power factor of circuit B to the power factor of circuit A is $\sqrt{2}$.
Note: The power factor is the estimation of how efficiently the incoming power is utilized in an electrical system. A high-power factor symbolizes that the power supplied to the electrical system is efficiently used. A low power factor does not effectively utilize the incoming electric supply and produces losses. There is no power factor included in DC circuits due to no frequency. However, in AC circuits, the value of the power factor lies between $0$ and $1$.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The power factor of a circuit is given by-
$cos \phi = \dfrac{R}{Z} = \dfrac{R}{\sqrt{ R^{2} + \left(X_{L} – X_{C} \right)^{2} }}$
For circuit A: $X_{L} = 3R$, $ X_{C} = 0$
The power factor of a circuit A is given by-
$cos \phi_{A} = \dfrac{R}{Z} = \dfrac{R}{\sqrt{ R^{2} + \left(3R – 0 \right)^{2} }}$
$cos \phi_{A} = \dfrac{R}{\sqrt{ R^{2} +9R^{2}} } = \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{10}}$
For circuit B: $X_{L} = 3R$, $ X_{C} = R$
The power factor of a circuit B is given by-
$cos \phi_{B} = \dfrac{R}{Z} = \dfrac{R}{\sqrt{ R^{2} + \left(3R – R \right)^{2} }}$
$cos \phi_{B} = \dfrac{R}{\sqrt{ R^{2} +4R^{2}} } = \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}}$
Ratio of power factor of both circuits:
$\dfrac{ cos \phi_{B} }{ cos \phi_{A}} = \dfrac{\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}}}{\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{10}}} =\sqrt{2} $
The ratio of power factor of circuit B to the power factor of circuit A is $\sqrt{2}$.
Note: The power factor is the estimation of how efficiently the incoming power is utilized in an electrical system. A high-power factor symbolizes that the power supplied to the electrical system is efficiently used. A low power factor does not effectively utilize the incoming electric supply and produces losses. There is no power factor included in DC circuits due to no frequency. However, in AC circuits, the value of the power factor lies between $0$ and $1$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




