
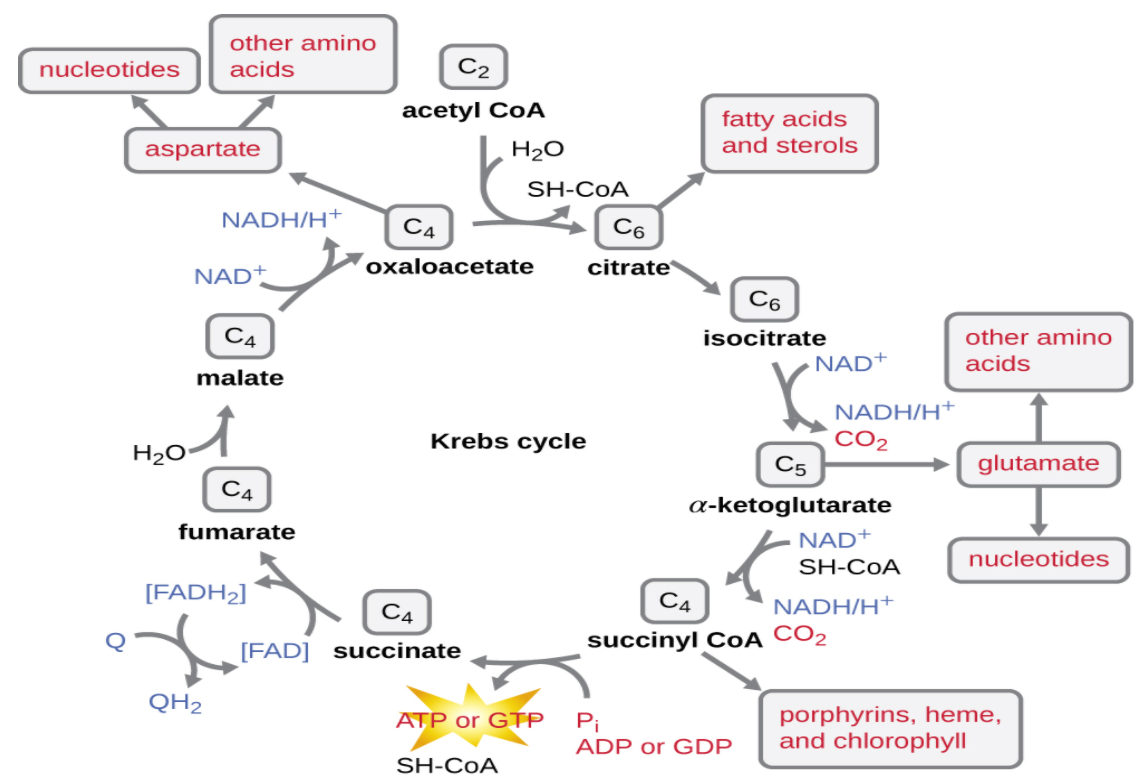
Give the schematic representation of an overall view of the Krebs cycles.
Answer
558.9k+ views
Hint: Krebs cycle is also known as citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle due to the main component of the cycle. It is the process which releases energy. This energy liberated enters the electron transport chain.
Complete answer:
TCA (tricarboxylic acid cycle) also known as Krebs cycle. It was discovered by Hans Adolf Kreb. In Krebs cycle CoA acetyl acts as a carrier of the acetyl group Acetyl CoA for the hydrolysis of the thioester which is 31.5 kJ/mol making it greater than the hydrolysis of ATP.
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex –
1. Multienzyme complex
2. 3 Enzyme – E1,E2,E3 and 5 coenzyme
(i) E1- pyruvate dehydrogenase
(ii) E2- dihydrolipoyl transacetylase
(iii) E3- dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase
Reaction mechanism: Pyruvate dehydrogenase – decarboxylase using a TPP cofactor froming hydroxyethyl- TPP.
- The hydro ethyl group A transfer to the lipoamide on E2 to form acetyl dihydrolipoamide E2. It catalysis the transfer of the acetyl group to CoA yielding Acetyl CoA and reduced dihydroxide E2
- Dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase E3 red oxidises Dihydrolipoamide – E2 and itself gets reduced as $FADH_2$ is formed.
- Reduced E3 is oxidized by $NAD^+$ to form SAD and NADH. The enzyme SH group are reoxidised by the FAD and electron are transfer to NADH
At each turn of cycle 3NADH, 1$FADH_2$, 1 GTP (or ATP), and 2 $CO_2$ is released.
Where- NADH and $FADH_2$ enter in the Electron Transport Chain, This oxidative phosphorylation produces ATP.
Note: The rate of conversion of Pyruvate to acetyl CoA.
- The Flux to citrate synthase, isocitrate dehydrogenase and alpha – ketoglutarate, dehydrogenase. The fluxes are largely determined by the concentration of substrate and products and : the end product ATP and NADH are inhibitory, and the substrate NAD and ADP are stimulating
- The production of AcetylCoA for Citric Acid cycle by the Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is inhibited allosterically by ATP, AcetylCoA, NAdh, and fatty acids and stimulated by AMP, NAD, CoA.
Complete answer:
TCA (tricarboxylic acid cycle) also known as Krebs cycle. It was discovered by Hans Adolf Kreb. In Krebs cycle CoA acetyl acts as a carrier of the acetyl group Acetyl CoA for the hydrolysis of the thioester which is 31.5 kJ/mol making it greater than the hydrolysis of ATP.
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex –
1. Multienzyme complex
2. 3 Enzyme – E1,E2,E3 and 5 coenzyme
(i) E1- pyruvate dehydrogenase
(ii) E2- dihydrolipoyl transacetylase
(iii) E3- dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase
Reaction mechanism: Pyruvate dehydrogenase – decarboxylase using a TPP cofactor froming hydroxyethyl- TPP.
- The hydro ethyl group A transfer to the lipoamide on E2 to form acetyl dihydrolipoamide E2. It catalysis the transfer of the acetyl group to CoA yielding Acetyl CoA and reduced dihydroxide E2
- Dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase E3 red oxidises Dihydrolipoamide – E2 and itself gets reduced as $FADH_2$ is formed.
- Reduced E3 is oxidized by $NAD^+$ to form SAD and NADH. The enzyme SH group are reoxidised by the FAD and electron are transfer to NADH
At each turn of cycle 3NADH, 1$FADH_2$, 1 GTP (or ATP), and 2 $CO_2$ is released.
Where- NADH and $FADH_2$ enter in the Electron Transport Chain, This oxidative phosphorylation produces ATP.

Note: The rate of conversion of Pyruvate to acetyl CoA.
- The Flux to citrate synthase, isocitrate dehydrogenase and alpha – ketoglutarate, dehydrogenase. The fluxes are largely determined by the concentration of substrate and products and : the end product ATP and NADH are inhibitory, and the substrate NAD and ADP are stimulating
- The production of AcetylCoA for Citric Acid cycle by the Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is inhibited allosterically by ATP, AcetylCoA, NAdh, and fatty acids and stimulated by AMP, NAD, CoA.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




