
Give the classification of fatty acids? Explain the function of EFA and their structures.
Answer
600.6k+ views
Hint: Fatty acids are important components of lipids (fat-soluble components of living cells) in plants, animals, and microorganisms. Try to recall their properties from biomolecules and then figure out what EFA is.
Complete step by step answer:
> In biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with a long aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28.
> Fatty acids are usually not found in organisms in their standalone form, but instead exist as three main classes of esters: triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesteryl esters.
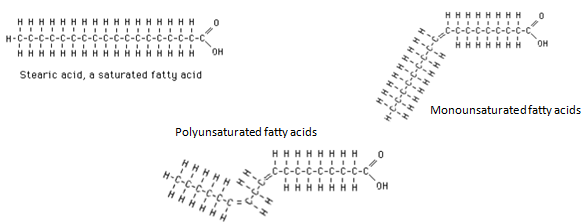
-Classification of fatty acids:
(1) Saturated fatty acid- these types of fatty acids are without double bonds.
Example-Stearic acid.
(2) Monounsaturated fatty acids:-these types of fatty acids are with one double bond.
Example- Oleic acid.
(3) Polyunsaturated fatty acids:- these types of fatty acids are with more than one double bond.
Example- Linoleic acid.
(4) Essential fatty acids, or EFAs, are fatty acids that humans and other animals must ingest because the body requires them for good health but cannot synthesize them.
Functions of EFA:
> It helps reduce fat production in the body.
> It increases fat burning and heat production in the body,
> It shifts the body from burning glucose to burning fats.
Structure of EFA:
Note: We should also know that EFAs are a special type of “good fat”. These are essential nutrients and sometimes we call them vitamin F. These EFAs are required for the proper function of every cell in the body.
Complete step by step answer:
> In biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with a long aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28.
> Fatty acids are usually not found in organisms in their standalone form, but instead exist as three main classes of esters: triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesteryl esters.
-Classification of fatty acids:
(1) Saturated fatty acid- these types of fatty acids are without double bonds.
Example-Stearic acid.
(2) Monounsaturated fatty acids:-these types of fatty acids are with one double bond.
Example- Oleic acid.
(3) Polyunsaturated fatty acids:- these types of fatty acids are with more than one double bond.
Example- Linoleic acid.
(4) Essential fatty acids, or EFAs, are fatty acids that humans and other animals must ingest because the body requires them for good health but cannot synthesize them.
Functions of EFA:
> It helps reduce fat production in the body.
> It increases fat burning and heat production in the body,
> It shifts the body from burning glucose to burning fats.
Structure of EFA:

Note: We should also know that EFAs are a special type of “good fat”. These are essential nutrients and sometimes we call them vitamin F. These EFAs are required for the proper function of every cell in the body.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




