
Give balanced equation for the preparation of salicylaldehyde from phenol.
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: Phenol can be converted to salicylaldehyde by Riemer Tiemann reaction. Salicylaldehyde is formed stepwise from phenol. It is not the direct product by phenol, intermediates are present.
Complete answer:
Let us study about Riemer Tiemann reaction at first,
Riemer Tiemann reaction-
It is a type of electrophilic substitution reaction where phenol goes o-formylation to give o-hydroxybenzaldehyde (salicylaldehyde).
Phenol is very reactive and thus, gives many reactions in nature. The presence of -OH group activates the benzene ring for ring wise substitution. The reaction of phenol to form salicylaldehyde requires chloroform along with NaOH (strong base) and light heating.
Mechanism-
1. NaOH takes away one proton from chloroform (deprotonation) to form carbanion.
2. The -Cl group is hence eliminated and we get electrophile dichlorocarbene.
3. The base deprotonates phenol as well to form phenoxide ion.
4. Dichlorocarbene is substituted at ortho position on the phenolic ring. Thus, we get dichloromethyl substituted phenol.
5. Rearrangement via aromatisation takes place and then chlorine atoms are taken away by sodium ions.
6. This is followed by the loss of water molecules and hence, aldehyde is formed.
Reaction-
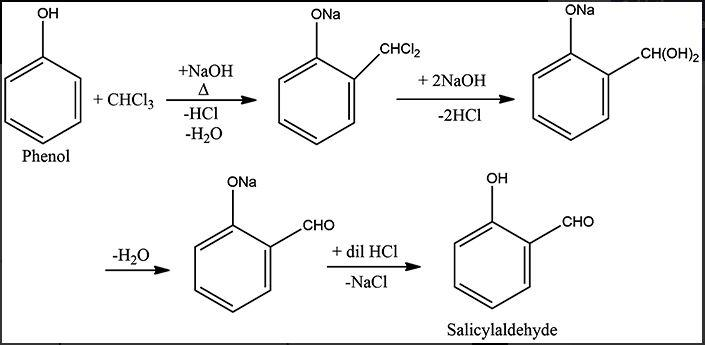
Note:
This reaction can be highly exothermic and can increase the rate of reaction when it proceeds. So, care must be taken.
This reaction can be altered to give phenolic acid i.e. salicylic acid by substituting chloroform with carbon tetrachloride.
Complete answer:
Let us study about Riemer Tiemann reaction at first,
Riemer Tiemann reaction-
It is a type of electrophilic substitution reaction where phenol goes o-formylation to give o-hydroxybenzaldehyde (salicylaldehyde).
Phenol is very reactive and thus, gives many reactions in nature. The presence of -OH group activates the benzene ring for ring wise substitution. The reaction of phenol to form salicylaldehyde requires chloroform along with NaOH (strong base) and light heating.
Mechanism-
1. NaOH takes away one proton from chloroform (deprotonation) to form carbanion.
2. The -Cl group is hence eliminated and we get electrophile dichlorocarbene.
3. The base deprotonates phenol as well to form phenoxide ion.
4. Dichlorocarbene is substituted at ortho position on the phenolic ring. Thus, we get dichloromethyl substituted phenol.
5. Rearrangement via aromatisation takes place and then chlorine atoms are taken away by sodium ions.
6. This is followed by the loss of water molecules and hence, aldehyde is formed.
Reaction-

Note:
This reaction can be highly exothermic and can increase the rate of reaction when it proceeds. So, care must be taken.
This reaction can be altered to give phenolic acid i.e. salicylic acid by substituting chloroform with carbon tetrachloride.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




