
Give an example of the species that has a linear shape.
Answer
508.2k+ views
Hint: The shape of the molecules can be identified using VSEPR theory (Valence shell electron pair theory). VSEPR theory is based on the fact that there is a repulsion between the electron pairs of valence electrons in all atoms and hence, gives the geometry of the molecules by identifying their arrangement with minimum repulsion.
Complete answer:
VSEPR theory (Valence shell electron pair theory) helps to identify geometry and shape of the molecule. It is based on the fact that there is a repulsion between the electron pairs of valence electrons in all atoms and the atoms arrange themselves in such a way that this electron pair repulsion is minimum in the resultant geometry.
So, here is table based on VSEPR theory that shows the number of bond pairs and lone pairs in a molecule and the suitable geometry and shape:
Where, steric number is the number of bond pairs and lone pairs around the central atom.
So, now if we have to give an example of a molecule with linear shape, then it can have a steric number = $2$ and no lone pairs.
We consider $BeC{l_2}$ (Beryllium chloride) molecule:
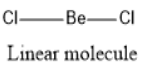
The valency of beryllium is two and there are two bond pairs in this molecule and hence, no lone pair is present.
Therefore, $BeC{l_2}$ is a linear molecule.
Note:
VSEPR theory has some disadvantages such as it cannot explain different shapes acquired by the isoelectronic species (species which have the same number of electrons) and also it does not give the geometry and shapes of the transition metal compounds which are coordination complexes.
Complete answer:
VSEPR theory (Valence shell electron pair theory) helps to identify geometry and shape of the molecule. It is based on the fact that there is a repulsion between the electron pairs of valence electrons in all atoms and the atoms arrange themselves in such a way that this electron pair repulsion is minimum in the resultant geometry.
So, here is table based on VSEPR theory that shows the number of bond pairs and lone pairs in a molecule and the suitable geometry and shape:
| Molecular shapes | ||||||
| Steric number | Geometry | No lone pairs | One lone pair | Two lone pairs | Three lone pairs | Four lone pairs |
| $2$ | Linear | Linear | ||||
| $3$ | Trigonal planar | Trigonal planar | Bent | |||
| $4$ | Tetrahedral | Tetrahedral | Trigonal pyramidal | Bent | ||
| $5$ | Trigonal bipyramidal | Trigonal bipyramidal | See-saw | T-shaped | Linear | |
| $6$ | octahedral | octahedral | Square pyramidal | Square planar | T-shaped | Linear |
Where, steric number is the number of bond pairs and lone pairs around the central atom.
So, now if we have to give an example of a molecule with linear shape, then it can have a steric number = $2$ and no lone pairs.
We consider $BeC{l_2}$ (Beryllium chloride) molecule:
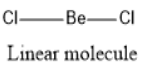
The valency of beryllium is two and there are two bond pairs in this molecule and hence, no lone pair is present.
Therefore, $BeC{l_2}$ is a linear molecule.
Note:
VSEPR theory has some disadvantages such as it cannot explain different shapes acquired by the isoelectronic species (species which have the same number of electrons) and also it does not give the geometry and shapes of the transition metal compounds which are coordination complexes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




