
Give an example of
1) Globular proteins.
2) Naturally occurring optically inactive amino acid.
Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint: As we know that Globular protein is a kind of protein, which is made of polypeptide or chain of amino acid. They are joined together by peptide bonds. An optically inactive compound has a plane of symmetry passing through it.
Complete step by step answer:
1) Globular protein: Globular proteins are spherical in shape and soluble in water, acids, bases, neutral salt solution or alcohol. Example is hemoglobin.
a) Hemoglobin: Hemoglobin is represented as Hb; it is a protein molecule which is present in (RBCs) red blood cells. This molecule is responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to the other tissues of the body, and collects the carbon dioxide from the tissues and returns it to the lungs from the tissues and returns it to the lungs. Hemoglobin is made up of four protein molecules, two alpha-globin chains and two beta-globin chains. This molecule is responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to other tissues of the body, and collects the carbon dioxide from the tissues and returns it to the lungs. Each of globulin chain contains an iron containing porphyrin compound called heme. Heme compound contains iron atom in it and is crucial for oxygen and carbon dioxide transportation in our blood.
2) Naturally occurring optically inactive amino acid.
(a) Glycine:
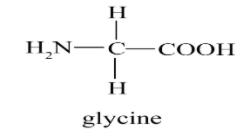
Glycine is the amino acid that is not optically inactive because it does not have a side chain when compared to other amino acids like Alanine, Leucine etc and also glycine can’t retain its optical state. So it’s a unique type of amino acid. To be an optically active molecule, it should contain asymmetric carbon. Glycine which is the simplest amino acid has not an asymmetric carbon atom, because of that it’s not optically active.
Note: There are several enzymes, which are present in globular proteins. The bonds between amino acids are peptide bonds, but hydrogen bonds, disulfide bonds and ionic bonds, they work together for making a secondary and tertiary structure.
Complete step by step answer:
1) Globular protein: Globular proteins are spherical in shape and soluble in water, acids, bases, neutral salt solution or alcohol. Example is hemoglobin.
a) Hemoglobin: Hemoglobin is represented as Hb; it is a protein molecule which is present in (RBCs) red blood cells. This molecule is responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to the other tissues of the body, and collects the carbon dioxide from the tissues and returns it to the lungs from the tissues and returns it to the lungs. Hemoglobin is made up of four protein molecules, two alpha-globin chains and two beta-globin chains. This molecule is responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to other tissues of the body, and collects the carbon dioxide from the tissues and returns it to the lungs. Each of globulin chain contains an iron containing porphyrin compound called heme. Heme compound contains iron atom in it and is crucial for oxygen and carbon dioxide transportation in our blood.
2) Naturally occurring optically inactive amino acid.
(a) Glycine:

Glycine is the amino acid that is not optically inactive because it does not have a side chain when compared to other amino acids like Alanine, Leucine etc and also glycine can’t retain its optical state. So it’s a unique type of amino acid. To be an optically active molecule, it should contain asymmetric carbon. Glycine which is the simplest amino acid has not an asymmetric carbon atom, because of that it’s not optically active.
Note: There are several enzymes, which are present in globular proteins. The bonds between amino acids are peptide bonds, but hydrogen bonds, disulfide bonds and ionic bonds, they work together for making a secondary and tertiary structure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




