
Give a diagrammatic representation of energy flow through different trophic levels.
Answer
575.7k+ views
Hint: The movement of energy around the ecosystem through biotic and abiotic components is called energy flow. Energy passes through food chains. It primarily begins with the autotrophs. There are changes in energy amount when it goes through each trophic level.
Complete answer:
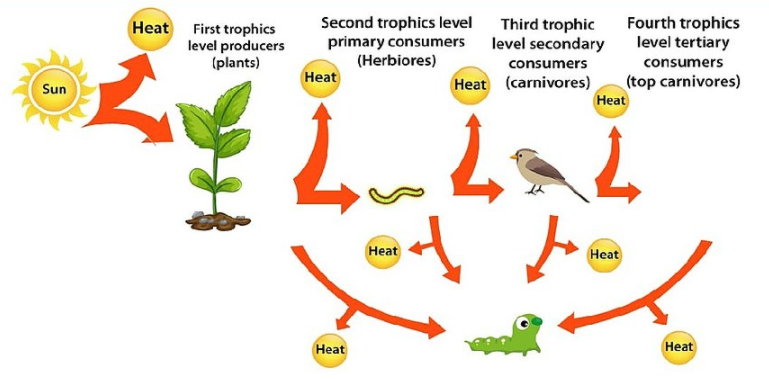
Energy can be passed on from one trophic level to the other when organic molecules from the organism’s body are consumed by another organism.
There are different trophic levels. They are:
> Producers- They are at the first level. They can prepare their own food in the presence of sunlight. Best examples are the plants.
> Primary consumers- They come at the second level. They are the ones that majorly eat the plants. Examples of which are the herbivores like cow, deer, sheep and others.
> Secondary Consumers- They constitute the third trophic level. They mainly feed on flesh. Hence they are called flesh eaters or carnivores. Such organisms are spiders, snakes, seals and some others.
> Tertiary Consumers- They form the fourth trophic level. They are the topmost carnivores that feed on the secondary consumers. Some examples are birds of prey, foxes and big cats.
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: There is deduction in the amount of energy as it moves up the trophic levels. The reason for it is that energy is lost as heat when one trophic level organisms are consumed by the other. One can measure the amount of energy transferred between trophic levels by TLTE which is also called Trophic level transfer efficiency. It is worth noting that food chains cannot sustain more than six energy transfers before all the energy exhausts. The Net production efficiency or NPE measures how each trophic level efficiently uses and incorporates energy from its food into biomass to fuel.
Complete answer:

Energy can be passed on from one trophic level to the other when organic molecules from the organism’s body are consumed by another organism.
There are different trophic levels. They are:
> Producers- They are at the first level. They can prepare their own food in the presence of sunlight. Best examples are the plants.
> Primary consumers- They come at the second level. They are the ones that majorly eat the plants. Examples of which are the herbivores like cow, deer, sheep and others.
> Secondary Consumers- They constitute the third trophic level. They mainly feed on flesh. Hence they are called flesh eaters or carnivores. Such organisms are spiders, snakes, seals and some others.
> Tertiary Consumers- They form the fourth trophic level. They are the topmost carnivores that feed on the secondary consumers. Some examples are birds of prey, foxes and big cats.
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: There is deduction in the amount of energy as it moves up the trophic levels. The reason for it is that energy is lost as heat when one trophic level organisms are consumed by the other. One can measure the amount of energy transferred between trophic levels by TLTE which is also called Trophic level transfer efficiency. It is worth noting that food chains cannot sustain more than six energy transfers before all the energy exhausts. The Net production efficiency or NPE measures how each trophic level efficiently uses and incorporates energy from its food into biomass to fuel.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




