
How do you get $(\cot )(\csc )(\sec )$ on my calculator?
Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint:
Here we need to know the properties and formula of the trigonometric function and we must know that $\cot = \dfrac{1}{{\tan }},\sec = \dfrac{1}{{\cos }},\csc = \dfrac{1}{{\sin }}$ and so we can use the calculator to solve for the value of trigonometric functions $\sin ,\cos ,\tan $ of any angle and then reciprocate them accordingly to get the value required.
Complete step by step solution:
Here we are given to find the way by which we can find $(\cot )(\csc )(\sec )$ of any angle on the calculator. We must know that we cannot find the value of $(\cot )(\csc )(\sec )$ to any angle directly on the calculator as it does not provide us with these functions. In the calculator we are displayed with the trigonometric functions $\sin ,\cos ,\tan $ of any angle and we need to use only these three trigonometric functions in order to find the value of $(\cot )(\csc )(\sec )$ to that angle.
Now we know that if we have the right angled triangle say $ABC$ right angled at $B$
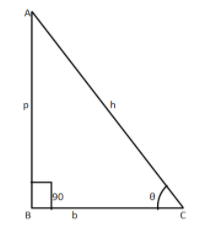
Let
$
AB = {\text{perpendicular}} = p \\
BC = {\text{base}} = b \\
AC = {\text{hypotenuse}} = h \\
$
Now we know that:
\[
\sin \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}} = \dfrac{p}{h} \\
\cos \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{base}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}} = \dfrac{b}{h} \\
\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{base}}}} = \dfrac{p}{b} \\
\cot \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{base}}}}{{{\text{perpendicular}}}} = \dfrac{b}{p} \\
\sec \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}{{{\text{base}}}} = \dfrac{h}{b} \\
\]
\[\csc \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}{{{\text{perpendicular}}}} = \dfrac{h}{p}\]
So we can see that $\cot = \dfrac{1}{{\tan }},\sec = \dfrac{1}{{\cos }},\csc = \dfrac{1}{{\sin }}$
Hence in the calculator as we know that we have $\sin ,\cos ,\tan $ as the trigonometric functions so we can reciprocate according to the trigonometric function we require and we can get the value of $\cot = \dfrac{1}{{\tan }},\sec = \dfrac{1}{{\cos }},\csc = \dfrac{1}{{\sin }}$
For example: If we want to find the value of $\sec 20^\circ $ so first we can see that in the calculator we can find the value of $\cos 20^\circ $ directly and after getting that value we can easily find the value of $\dfrac{1}{{\cos 20^\circ }}$ and we will get the value of $\sec 20^\circ $
Note:
Here the student must know the trigonometric formula and properties in order to solve such problems. This problem is very simple if the student knows the way by which we can find the value of $(\cot )(\csc )(\sec )$ from $\sin ,\cos ,\tan $
Here we need to know the properties and formula of the trigonometric function and we must know that $\cot = \dfrac{1}{{\tan }},\sec = \dfrac{1}{{\cos }},\csc = \dfrac{1}{{\sin }}$ and so we can use the calculator to solve for the value of trigonometric functions $\sin ,\cos ,\tan $ of any angle and then reciprocate them accordingly to get the value required.
Complete step by step solution:
Here we are given to find the way by which we can find $(\cot )(\csc )(\sec )$ of any angle on the calculator. We must know that we cannot find the value of $(\cot )(\csc )(\sec )$ to any angle directly on the calculator as it does not provide us with these functions. In the calculator we are displayed with the trigonometric functions $\sin ,\cos ,\tan $ of any angle and we need to use only these three trigonometric functions in order to find the value of $(\cot )(\csc )(\sec )$ to that angle.
Now we know that if we have the right angled triangle say $ABC$ right angled at $B$

Let
$
AB = {\text{perpendicular}} = p \\
BC = {\text{base}} = b \\
AC = {\text{hypotenuse}} = h \\
$
Now we know that:
\[
\sin \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}} = \dfrac{p}{h} \\
\cos \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{base}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}} = \dfrac{b}{h} \\
\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{base}}}} = \dfrac{p}{b} \\
\cot \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{base}}}}{{{\text{perpendicular}}}} = \dfrac{b}{p} \\
\sec \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}{{{\text{base}}}} = \dfrac{h}{b} \\
\]
\[\csc \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}{{{\text{perpendicular}}}} = \dfrac{h}{p}\]
So we can see that $\cot = \dfrac{1}{{\tan }},\sec = \dfrac{1}{{\cos }},\csc = \dfrac{1}{{\sin }}$
Hence in the calculator as we know that we have $\sin ,\cos ,\tan $ as the trigonometric functions so we can reciprocate according to the trigonometric function we require and we can get the value of $\cot = \dfrac{1}{{\tan }},\sec = \dfrac{1}{{\cos }},\csc = \dfrac{1}{{\sin }}$
For example: If we want to find the value of $\sec 20^\circ $ so first we can see that in the calculator we can find the value of $\cos 20^\circ $ directly and after getting that value we can easily find the value of $\dfrac{1}{{\cos 20^\circ }}$ and we will get the value of $\sec 20^\circ $
Note:
Here the student must know the trigonometric formula and properties in order to solve such problems. This problem is very simple if the student knows the way by which we can find the value of $(\cot )(\csc )(\sec )$ from $\sin ,\cos ,\tan $
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

Write a letter to the editor of a newspaper explaining class 10 english CBSE

What is a "free hit" awarded for in limited-overs cricket?

Write a letter to the newspaper editor highlighting class 10 english CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

PQ is a tangent to a circle with centre O at the point class 10 maths CBSE




