
Geometrical isomerism is possible in?
A. acetone-oxime
B. isobutene
C. acetophenone-oxime
D. benzophenone-oxime
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: To find the type of isomerism, first we need to see which type of compounds is given in the question. The types of isomerism are completely different in organic compounds. The geometrical isomerism is possible only along the double bond.
Complete step by step solution:
-The given options relate to the organic compounds. There are basically 2 types of isomerism in such compounds which are structural isomerism and stereoisomerism.
-Structural isomers are subdivided into functional isomers, position isomers, chain isomers and metamers. Stereoisomerism is subdivided into optical and geometrical isomerism.
-Now looking at the compounds given, we can ensure that the compounds do not have optical isomers as it is not chiral. We need to find which option has 2 different types of ligands and so can show geometrical isomers of two forms- cis and trans.
-First we need to discuss the ketone-oxime reactions. Ketones react with oximes showing elimination reaction. Water molecule is eliminated and the bond is formed between –C=N. N always has 2 different groups, 1 is the lone pair and other is the –OH group. So the geometrical isomer depends on the groups attached from the C atom.
-The reaction on ketones with oximes can be represented by the following diagram:
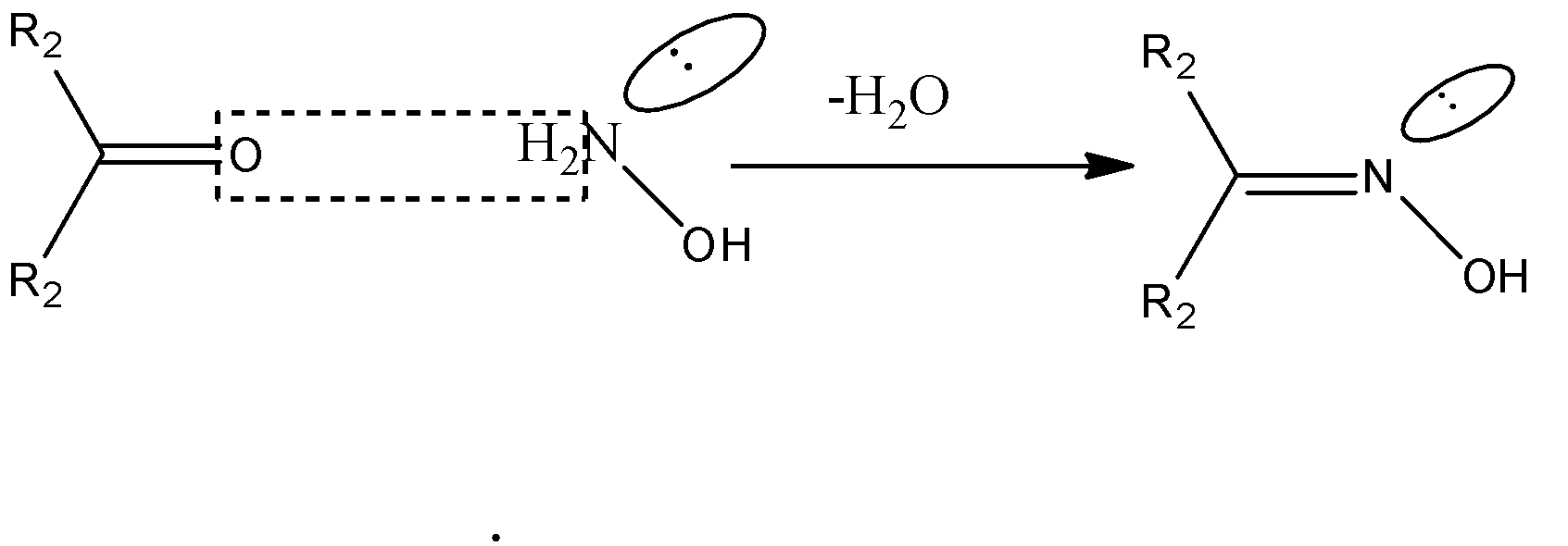
-Acetone contains both the methyl groups along –C=O bond which are the same and so it cannot show geometrical isomers along –C=N bond on reaction with oximes. Same is with benzophenone.
-There are 2 different groups along carbon in acetophenone. One is the acetate group and the other is phenone group. So it is capable of showing geometrical isomers. The isomers can be shown as
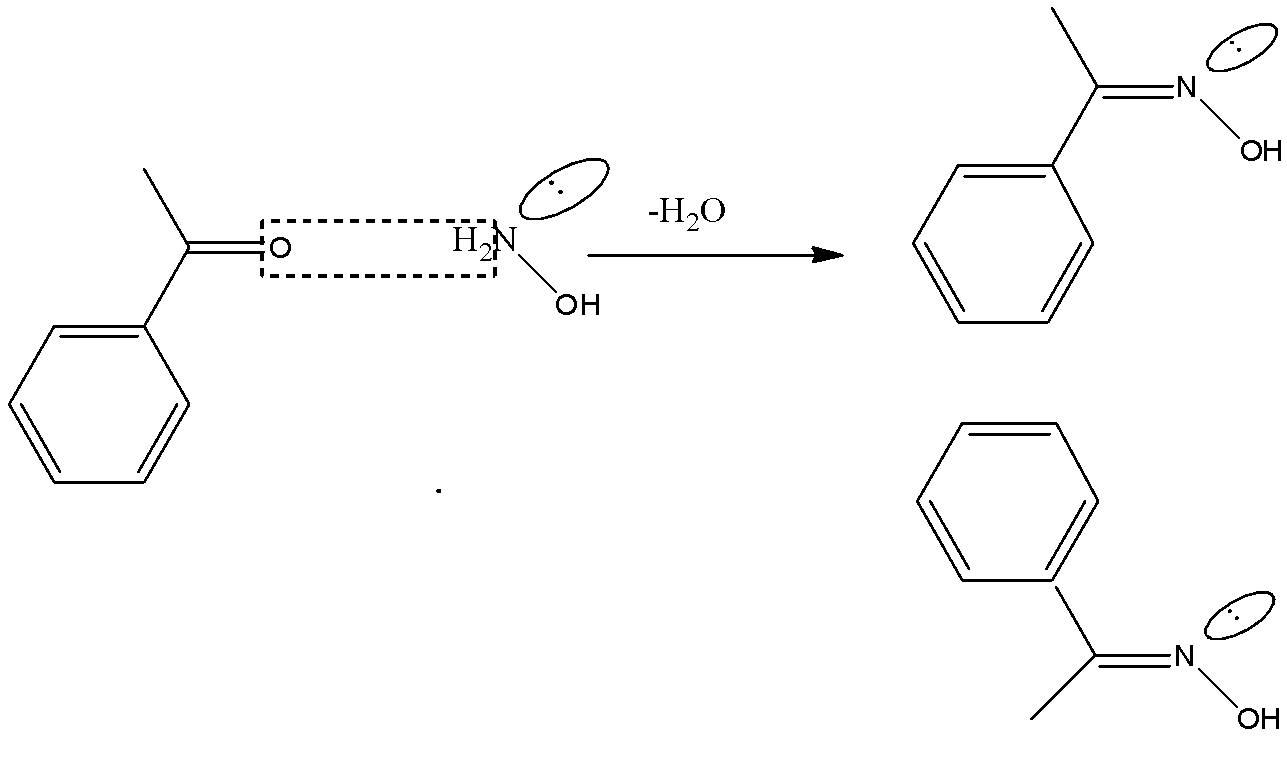
Therefore the correct option is C.
Note: The isomers in this question are not cis and trans as the groups are not same along carbon and nitrogen. They are E-Z isomers and they have certain rules called CIP rules that decide the numbering on the groups. If the numbering is the same along the atoms, it is Z else E isomer.
Complete step by step solution:
-The given options relate to the organic compounds. There are basically 2 types of isomerism in such compounds which are structural isomerism and stereoisomerism.
-Structural isomers are subdivided into functional isomers, position isomers, chain isomers and metamers. Stereoisomerism is subdivided into optical and geometrical isomerism.
-Now looking at the compounds given, we can ensure that the compounds do not have optical isomers as it is not chiral. We need to find which option has 2 different types of ligands and so can show geometrical isomers of two forms- cis and trans.
-First we need to discuss the ketone-oxime reactions. Ketones react with oximes showing elimination reaction. Water molecule is eliminated and the bond is formed between –C=N. N always has 2 different groups, 1 is the lone pair and other is the –OH group. So the geometrical isomer depends on the groups attached from the C atom.
-The reaction on ketones with oximes can be represented by the following diagram:

-Acetone contains both the methyl groups along –C=O bond which are the same and so it cannot show geometrical isomers along –C=N bond on reaction with oximes. Same is with benzophenone.
-There are 2 different groups along carbon in acetophenone. One is the acetate group and the other is phenone group. So it is capable of showing geometrical isomers. The isomers can be shown as

Therefore the correct option is C.
Note: The isomers in this question are not cis and trans as the groups are not same along carbon and nitrogen. They are E-Z isomers and they have certain rules called CIP rules that decide the numbering on the groups. If the numbering is the same along the atoms, it is Z else E isomer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




