
Geometrical isomerism is possible in:
(A) Acetone oxime
(B) Isobutene
(C) acetophenone oxime
(D) benzophenone oxime
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: To identify the geometrical isomers we have to check the bond connectivity. The molecules having the same bonding connectivity can be geometrical isomers.
Complete step by step solution:
Before solving the question lets understand some basics terms:
Stereoisomers are defined as the molecules having the similar bond connectivity but different molecular configuration. Stereoisomers are of two types: optical and geometrical isomers. Geometrical isomers is the isomer where the groups differ in arrangements along the double bonds or the rings or the rigid structures. In the above given options acetophenone oxime shows geometrical isomerism in the syn form and anti-form. The syn and anti-form is used to describe the geometry around the double bond and it is identical to Z and E and are often used to describe the geometry around the carbon nitrogen double bond. The lone pair of electrons get the least priority and the sequence rule is applied as usual. The geometrical isomer of acetophenone oxime is shown below:
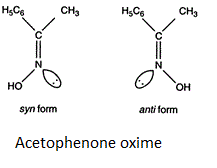
Additional information:
Acetophenone is used for the fragrance in soaps it is also used as a flavoring agent in foods. Acetophenone is used as a solvent for plastics and resins. Short term acetophenone vapor causes skin irritation and can cause corneal injury in the human body. Syn and anti-nomenclature is used to describe the isomerism between carbon and nitrogen double bonds. There is another type of isomerism i.e. E and Z which is used when all the four groups around the double bond are different and we need to give priority to the attached group to assign the E and Z configuration.
Note: To identify the geometrical isomerism we need to restrict the rotation of the carbon carbon double bond and if there is presence of carbon carbon double bond then we can check for the possibility of geometrical isomers. The main criteria of having geometrical isomers is to have different groups attached to it.
Complete step by step solution:
Before solving the question lets understand some basics terms:
Stereoisomers are defined as the molecules having the similar bond connectivity but different molecular configuration. Stereoisomers are of two types: optical and geometrical isomers. Geometrical isomers is the isomer where the groups differ in arrangements along the double bonds or the rings or the rigid structures. In the above given options acetophenone oxime shows geometrical isomerism in the syn form and anti-form. The syn and anti-form is used to describe the geometry around the double bond and it is identical to Z and E and are often used to describe the geometry around the carbon nitrogen double bond. The lone pair of electrons get the least priority and the sequence rule is applied as usual. The geometrical isomer of acetophenone oxime is shown below:

Additional information:
Acetophenone is used for the fragrance in soaps it is also used as a flavoring agent in foods. Acetophenone is used as a solvent for plastics and resins. Short term acetophenone vapor causes skin irritation and can cause corneal injury in the human body. Syn and anti-nomenclature is used to describe the isomerism between carbon and nitrogen double bonds. There is another type of isomerism i.e. E and Z which is used when all the four groups around the double bond are different and we need to give priority to the attached group to assign the E and Z configuration.
Note: To identify the geometrical isomerism we need to restrict the rotation of the carbon carbon double bond and if there is presence of carbon carbon double bond then we can check for the possibility of geometrical isomers. The main criteria of having geometrical isomers is to have different groups attached to it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




