
Who gave the double strand helix structure for DNA?
Answer
496.8k+ views
Hint: A double-stranded DNA's molecular form is depicted by the double helix. Deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA, is the component that houses an individual's genetic makeup. Individuals share their DNA from their parents. Watson and Crick gave the double strand helix structure of DNA.
Complete answer:
Francis Crick and James Watson published the first description of DNA's chemical structure, which they named a "double helix," in the magazine Nature in \[1953\]. Watson, Crick, and their colleague Maurice Wilkins were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in \[1962\] for this scientific breakthrough.
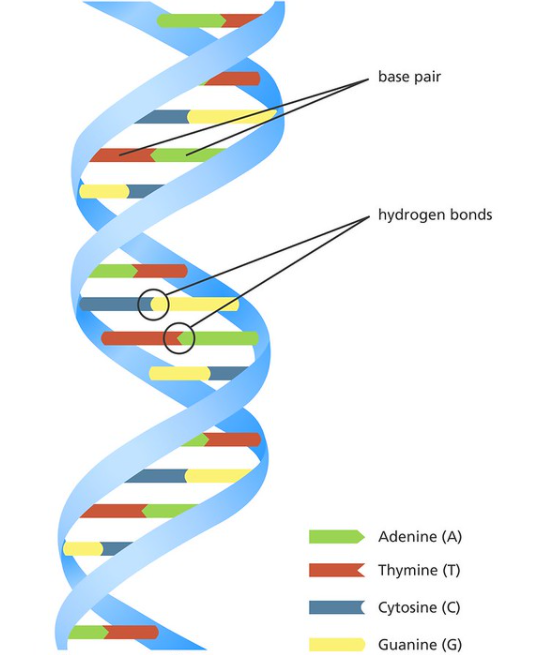
The aspect of double-stranded DNA is typified by the double helix, which is split into two linear strands that run in opposite directions, or anti-parallel, and coil intertwined. Within the double helix, each DNA is a lengthy, linear molecule composed of smaller units called nucleotides that link together to form a chain. Sugar and phosphate units are linked by chemical bonds to form the chemical backbones of the double helix, which are known as sugar-phosphate backbones.
Contacts between pairs of nucleotides, commonly known as base pairs, link the two helical strands. Base pairing happens in two ways: nucleotide A only combines with T, and nucleotide C combines only with G.
Note:
The double helix model is also known as the Watson and Crick model, named after the scientists who discovered them. Genetic data is stored via the nucleotide sequence in the chemical backbone. DNA holds all of an individual's blueprints for growth, survival, and procreation. DNA is required for heredity, protein translation, and imparting directions for life and its mechanisms in all living things.
Complete answer:
Francis Crick and James Watson published the first description of DNA's chemical structure, which they named a "double helix," in the magazine Nature in \[1953\]. Watson, Crick, and their colleague Maurice Wilkins were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in \[1962\] for this scientific breakthrough.

The aspect of double-stranded DNA is typified by the double helix, which is split into two linear strands that run in opposite directions, or anti-parallel, and coil intertwined. Within the double helix, each DNA is a lengthy, linear molecule composed of smaller units called nucleotides that link together to form a chain. Sugar and phosphate units are linked by chemical bonds to form the chemical backbones of the double helix, which are known as sugar-phosphate backbones.
Contacts between pairs of nucleotides, commonly known as base pairs, link the two helical strands. Base pairing happens in two ways: nucleotide A only combines with T, and nucleotide C combines only with G.
Note:
The double helix model is also known as the Watson and Crick model, named after the scientists who discovered them. Genetic data is stored via the nucleotide sequence in the chemical backbone. DNA holds all of an individual's blueprints for growth, survival, and procreation. DNA is required for heredity, protein translation, and imparting directions for life and its mechanisms in all living things.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




