
What is the functional group in Acetone?
Answer
510k+ views
Hint: Acetone or propanone is an organic compound with the formula $ {(C{H_3})_2}CO $ . It is the simplest and smallest ketone. It is a colorless, highly volatile and flammable liquid with a characteristic pungent odor. Acetone IUPAC name is propan- $ 2 $ -one
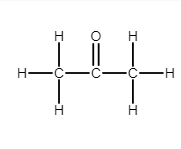
Complete answer:
Ketone is a functional group with the structure $ {R_2}C = O $ , where R can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketone only contains a carbonyl group. Acetone contains the functional group of ketone. It is described as $ s{p^2} $ hybridized. Ketones are trigonal planar around the carbon, with $ C - C - O $ and $ C - C - C $ bond angles of approximately $ 120^\circ $ .
Ketones are different from aldehydes in that they are carbonyl within a carbon skeleton. In aldehydes, the carbonyl is bonded to one carbon and one hydrogen and are located at the ends of carbon chains.
The carbonyl group is polar because the electronegativity of the oxygen is greater than that for carbon. Thus, ketones are nucleophile at oxygen and electrophile ate carbon. Ketones are soluble in water because the group interacts with water by hydrogen bonding.
Ketones do not have a hydrogen atom bonded to the carbonyl group, and are therefore more resistant to oxidation. They are oxidized only by powerful oxidizing agents which have the ability to cleave carbon-carbon bonds.
Acetone melting and boiling point is much lower than that of water because acetone does not have a strong intermolecular force as water does. Because of weaker forces of attraction between acetone molecules and the greater intermolecular forces between water due to its ability to hydrogen bond, less energy is needed to separate the acetone molecules and break them down.
Acetone production methods:
Acetone is produced directly or indirectly from propylene. In the cumene process, benzene is alkylated with propylene to produce cumene, which is oxidized by air to produce phenol and acetone. Previously acetone was produced by the dry distillation of acetates
Example- calcium acetate in ketonic decarboxylation $ Ca{(C{H_3}COO)_2} \to CaO(s) + C{O_2}(g) + {(C{H_3})_2}CO $
Acetone can be produced from an alkene, first the propene undergoes a reaction with water forming a propanol which gets oxidized to propanone in the presence of oxygen.
$ {C_3}{H_6} + {H_2}O \to {C_3}{H_7}OH $
$ {C_3}{H_7}OH\xrightarrow{{[O]}}{C_3}{H_7}O $ .
Note:
Acetone is a versatile compound, having the ability to undergo addition, oxidation, reduction and condensation reactions, it is also used as a raw material in chemical synthesis.
Aldol condensation- in the presence of suitable catalysts, two acetone molecules also combine to form the compound diacetone alcohol $ (C{H_3})C = O(CH) = C{(C{H_3})_2} $ , which on dehydration gives mesityl $ (C{H_3})C = O(CH) = C{(C{H_3})_2} $ oxide $ (C{H_3})C = O(CH) = C{(C{H_3})_2} $ . This product can further combine with another acetone molecule, with the loss of another molecule of water.

Complete answer:
Ketone is a functional group with the structure $ {R_2}C = O $ , where R can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketone only contains a carbonyl group. Acetone contains the functional group of ketone. It is described as $ s{p^2} $ hybridized. Ketones are trigonal planar around the carbon, with $ C - C - O $ and $ C - C - C $ bond angles of approximately $ 120^\circ $ .
Ketones are different from aldehydes in that they are carbonyl within a carbon skeleton. In aldehydes, the carbonyl is bonded to one carbon and one hydrogen and are located at the ends of carbon chains.
The carbonyl group is polar because the electronegativity of the oxygen is greater than that for carbon. Thus, ketones are nucleophile at oxygen and electrophile ate carbon. Ketones are soluble in water because the group interacts with water by hydrogen bonding.
Ketones do not have a hydrogen atom bonded to the carbonyl group, and are therefore more resistant to oxidation. They are oxidized only by powerful oxidizing agents which have the ability to cleave carbon-carbon bonds.
Acetone melting and boiling point is much lower than that of water because acetone does not have a strong intermolecular force as water does. Because of weaker forces of attraction between acetone molecules and the greater intermolecular forces between water due to its ability to hydrogen bond, less energy is needed to separate the acetone molecules and break them down.
Acetone production methods:
Acetone is produced directly or indirectly from propylene. In the cumene process, benzene is alkylated with propylene to produce cumene, which is oxidized by air to produce phenol and acetone. Previously acetone was produced by the dry distillation of acetates
Example- calcium acetate in ketonic decarboxylation $ Ca{(C{H_3}COO)_2} \to CaO(s) + C{O_2}(g) + {(C{H_3})_2}CO $
Acetone can be produced from an alkene, first the propene undergoes a reaction with water forming a propanol which gets oxidized to propanone in the presence of oxygen.
$ {C_3}{H_6} + {H_2}O \to {C_3}{H_7}OH $
$ {C_3}{H_7}OH\xrightarrow{{[O]}}{C_3}{H_7}O $ .
Note:
Acetone is a versatile compound, having the ability to undergo addition, oxidation, reduction and condensation reactions, it is also used as a raw material in chemical synthesis.
Aldol condensation- in the presence of suitable catalysts, two acetone molecules also combine to form the compound diacetone alcohol $ (C{H_3})C = O(CH) = C{(C{H_3})_2} $ , which on dehydration gives mesityl $ (C{H_3})C = O(CH) = C{(C{H_3})_2} $ oxide $ (C{H_3})C = O(CH) = C{(C{H_3})_2} $ . This product can further combine with another acetone molecule, with the loss of another molecule of water.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




