
What is the function of areolar tissue?
(a) Supports internal delicate organs
(b) Protects organs
(c) Storage of fluids
(d) All of the above
Answer
598.2k+ views
Hint: These tissues are strong enough to bind different types of tissues together, yet delicate enough to provide flexibility and to cushion to internal organs.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Areolar tissue is a widely distributed type of connective tissue in vertebrates and commonly known as “loose connective tissue.” They are made of cells and extracellular matrix and mainly found in the surrounding blood vessels, nerve fibers, muscles, and organs. The areolar tissue occupies the spaces between the various organs and associates the skin to the underlying muscles. The mesh structure of areolar tissue includes fibers like collagen fibers, elastic fibers, and reticular fibers, and different types of cells such as fibroblasts, plasma cells, mast cells, macrophages, and adipocytes. These fibers and cells are embedded in a semi-fluid ground substance that is similar to the ground substance in which the chondrocytes are situated in hyaline cartilage tissue.
Functions of areolar tissue:
1. Areolar tissue acts as a binding tissue to bind different tissue types together.
2. Areolar tissues permit the diffusion of oxygen/nutrients from small vessels to the cells and the diffusion of metabolites back to the vessels.
3. It surrounds the blood vessels and also supports the internal organs.
4. It holds the organs in place and attaches epithelial tissue to other underlying tissues.
5. It also helps as a reservoir of water and salts for surrounding tissues.
6. Areolar tissue is highly flexible in appearance.
So, the correct answer is ‘all of the above.’
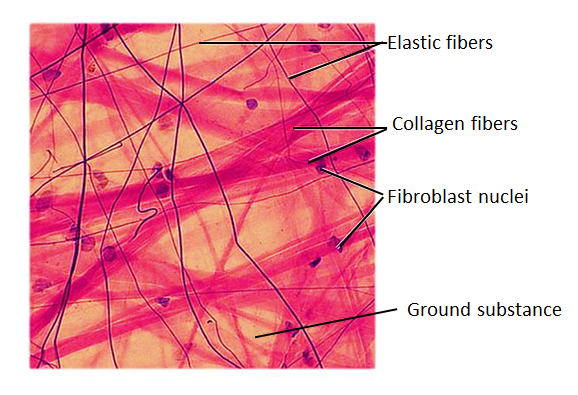
Figure: Structure of areolar tissues
Note: Fat cells are the usual constituents of loose connective tissue. When these cells are abundant and organized into large lobules, the tissue is called adipose tissue. Adipose tissue helps in the storage of energy in the form of fat.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Areolar tissue is a widely distributed type of connective tissue in vertebrates and commonly known as “loose connective tissue.” They are made of cells and extracellular matrix and mainly found in the surrounding blood vessels, nerve fibers, muscles, and organs. The areolar tissue occupies the spaces between the various organs and associates the skin to the underlying muscles. The mesh structure of areolar tissue includes fibers like collagen fibers, elastic fibers, and reticular fibers, and different types of cells such as fibroblasts, plasma cells, mast cells, macrophages, and adipocytes. These fibers and cells are embedded in a semi-fluid ground substance that is similar to the ground substance in which the chondrocytes are situated in hyaline cartilage tissue.
Functions of areolar tissue:
1. Areolar tissue acts as a binding tissue to bind different tissue types together.
2. Areolar tissues permit the diffusion of oxygen/nutrients from small vessels to the cells and the diffusion of metabolites back to the vessels.
3. It surrounds the blood vessels and also supports the internal organs.
4. It holds the organs in place and attaches epithelial tissue to other underlying tissues.
5. It also helps as a reservoir of water and salts for surrounding tissues.
6. Areolar tissue is highly flexible in appearance.
So, the correct answer is ‘all of the above.’

Figure: Structure of areolar tissues
Note: Fat cells are the usual constituents of loose connective tissue. When these cells are abundant and organized into large lobules, the tissue is called adipose tissue. Adipose tissue helps in the storage of energy in the form of fat.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




