
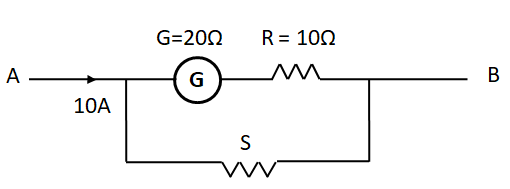
Full scale deflection for a galvanometer is $1{\text{mA}}$. The value of shunt resistance (approximately) so that galvanometer shows half scale deflection is
(A) $1.5{\text{m}}\Omega $
(B) ${\text{3m}}\Omega $
(C) $10{\text{m}}\Omega $
(D) $15{\text{m}}\Omega $

Answer
582k+ views
Hint
To solve this question, we have to find out the current through the galvanometer, which is equal to half of the full scale deflection current. Then, using KCL and KVL in the given circuit will give the required value of the shunt resistance.
Complete step by step answer
It is given that the full scale deflection current for the galvanometer is ${I_g} = 1{\text{mA}}$
Now, according to the question, the galvanometer should show half scale deflection, which means that the current which passes through the galvanometer in this case is
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{{I_g}}}{2}$
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{1{\text{mA}}}}{2} = 0.5{\text{mA}}$
Converting in amperes, we get
$\Rightarrow I = 0.5 \times {10^{ - 3}}{\text{A}}$
So, the current distribution in the circuit is as shown in the below diagram.
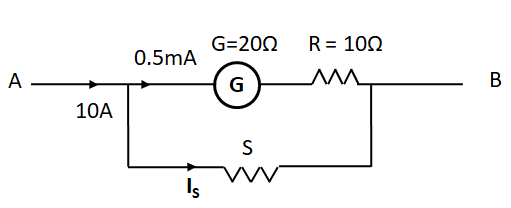
Here ${I_S}$ is the current flowing through the shunt resistance. Here the current of $10{\text{A}}$ is divided among the two branches, one branch containing the galvanometer and the series resistance, and the other containing the shunt resistance. Applying KCL at the point of division of current, we get
$\Rightarrow 10{\text{A}} = 0.5{\text{mA}} + {I_s}$
$\Rightarrow {I_s} = 10{\text{A}} - 0.5{\text{mA}}$
As $0.5{\text{mA}}$ current is negligibly small as compared to the current of $10{\text{A}}$, so we approximate the current through the shunt resistance as
$\Rightarrow {I_s} \approx 10{\text{A}}$
Now, as the shunt resistance is connected parallel to the serial combination of the galvanometer and the series resistance, so the potential difference across them will be equal. This gives
$\Rightarrow {I_S}\left( S \right) = I\left( {G + R} \right)$
$\Rightarrow 10\left( S \right) = 0.5 \times {10^{ - 3}}\left( {G + R} \right)$
According to the question, $G = 20\Omega $ and $R = 10\Omega $
$\Rightarrow 10\left( S \right) = 0.5 \times {10^{ - 3}}\left( {20 + 10} \right)$
On simplifying, we get
$\Rightarrow S = 1.5 \times {10^{ - 3}}\Omega $
$\Rightarrow S = 1.5{\text{m}}\Omega $
Thus, the shunt resistance is equal to $1.5{\text{m}}\Omega $.
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note
While approximating the current through the shunt resistance as the original current, do not take the current through the galvanometer equal to zero, although applying KCL will give it equal to zero. We have to take care of the fact that the galvanometer is a very much sensitive device. So it shows the deflection even for a negligibly small amount of current which flows through it. Hence, even the negligibly small value can’t be neglected for a galvanometer.
To solve this question, we have to find out the current through the galvanometer, which is equal to half of the full scale deflection current. Then, using KCL and KVL in the given circuit will give the required value of the shunt resistance.
Complete step by step answer
It is given that the full scale deflection current for the galvanometer is ${I_g} = 1{\text{mA}}$
Now, according to the question, the galvanometer should show half scale deflection, which means that the current which passes through the galvanometer in this case is
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{{I_g}}}{2}$
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{1{\text{mA}}}}{2} = 0.5{\text{mA}}$
Converting in amperes, we get
$\Rightarrow I = 0.5 \times {10^{ - 3}}{\text{A}}$
So, the current distribution in the circuit is as shown in the below diagram.

Here ${I_S}$ is the current flowing through the shunt resistance. Here the current of $10{\text{A}}$ is divided among the two branches, one branch containing the galvanometer and the series resistance, and the other containing the shunt resistance. Applying KCL at the point of division of current, we get
$\Rightarrow 10{\text{A}} = 0.5{\text{mA}} + {I_s}$
$\Rightarrow {I_s} = 10{\text{A}} - 0.5{\text{mA}}$
As $0.5{\text{mA}}$ current is negligibly small as compared to the current of $10{\text{A}}$, so we approximate the current through the shunt resistance as
$\Rightarrow {I_s} \approx 10{\text{A}}$
Now, as the shunt resistance is connected parallel to the serial combination of the galvanometer and the series resistance, so the potential difference across them will be equal. This gives
$\Rightarrow {I_S}\left( S \right) = I\left( {G + R} \right)$
$\Rightarrow 10\left( S \right) = 0.5 \times {10^{ - 3}}\left( {G + R} \right)$
According to the question, $G = 20\Omega $ and $R = 10\Omega $
$\Rightarrow 10\left( S \right) = 0.5 \times {10^{ - 3}}\left( {20 + 10} \right)$
On simplifying, we get
$\Rightarrow S = 1.5 \times {10^{ - 3}}\Omega $
$\Rightarrow S = 1.5{\text{m}}\Omega $
Thus, the shunt resistance is equal to $1.5{\text{m}}\Omega $.
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note
While approximating the current through the shunt resistance as the original current, do not take the current through the galvanometer equal to zero, although applying KCL will give it equal to zero. We have to take care of the fact that the galvanometer is a very much sensitive device. So it shows the deflection even for a negligibly small amount of current which flows through it. Hence, even the negligibly small value can’t be neglected for a galvanometer.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




