
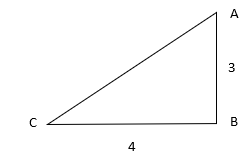
From the following figure find the value of $\sin C$?
${\text{(A) }}\dfrac{{\text{2}}}{{\text{3}}}$
${\text{(B) }}\dfrac{3}{5}$
${\text{(C) }}\dfrac{{\text{2}}}{7}$
${\text{(D) }}\dfrac{6}{5}$

Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint: Here we have to find the value of ${\text{sin C}}$. First we will first find the length of the hypotenuse of the triangle and then calculate the value of ${\text{sin C}}$ by using the formula. Finally we get the required answer.
Formula used: Pythagoras theorem: ${a^2} + {b^2} = {c^2}$, where $a,b$ and $c$ are lengths of the triangle $\vartriangle ABC$ respectively.
$\sin \theta = \dfrac{{opposite}}{{hypotenuse}}$
Complete step-by-step solution:
From the diagram we can see that $\vartriangle ABC$ is a right-angled triangle which has sides $AB,BC$ and $AC$.
The length of side $AB$ from the diagram is $3$ therefore:
$AB = 3$.
The length of side $BC$ from the diagram is $4$ therefore:
$BC = 4$.
Now we will find the length of the missing side using Pythagoras theorem.
Since$\vartriangle ABC$ is a right-angled triangle we know that:
${(AC)^2} = {(AB)^2} + {(BC)^2}$
On substituting the values, we get:
$\Rightarrow$${(AC)^2} = {(3)^2} + {(4)^2}$
This could be expanded as:
$\Rightarrow$${(AC)^2} = 9 + 16$
On further simplifying we get:
$\Rightarrow$${(AC)^2} = 25$
This could be also written as:
$\Rightarrow$${(AC)^2} = {(5)^2}$
Since there is a square on both sides, we take the square root of both sides.
$\Rightarrow$$AC = 5$
Now we have to find the value of $\sin C$,
${\text{sin C = }}\dfrac{{{\text{opposite}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}$
The side opposite to angle $C$ is the side $AB$
Therefore, $\sin C = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AC}}$
On substituting the values, we get:
$\Rightarrow$$\sin C = \dfrac{3}{5}$
Therefore, the correct option is $(B)$ which is $\dfrac{3}{5}$.
Note: It exists $\cos \theta = \dfrac{{adjacent}}{{hypotenuse}}$ where the adjacent side is the side which is next to the angle; it is also called the perpendicular side.
Example: $\cos C = \dfrac{{BC}}{{AC}}$
Also, there is $\tan \theta = \dfrac{{\sin \theta }}{{\cos \theta }} = \dfrac{{opposite}}{{adjacent}}$
Example: $\tan C = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BC}}$
There also exist other trigonometric relations which are $\sec \theta $ $\cos ec\theta $ and $\cot \theta $ which are the inverse of $\cos \theta ,\sin \theta $ and $\tan \theta $ respectively.
In this question, we had to find $\sin C$ therefore, the opposite side to the angle $C$ was side $AB$.
If it was asked to find out $\sin A$ then the opposite side to the angle $A$ is $BC$ which is the base of the triangle.
These $6$ are the trigonometric relations which are present in trigonometry.
Formula used: Pythagoras theorem: ${a^2} + {b^2} = {c^2}$, where $a,b$ and $c$ are lengths of the triangle $\vartriangle ABC$ respectively.
$\sin \theta = \dfrac{{opposite}}{{hypotenuse}}$
Complete step-by-step solution:
From the diagram we can see that $\vartriangle ABC$ is a right-angled triangle which has sides $AB,BC$ and $AC$.
The length of side $AB$ from the diagram is $3$ therefore:
$AB = 3$.
The length of side $BC$ from the diagram is $4$ therefore:
$BC = 4$.
Now we will find the length of the missing side using Pythagoras theorem.
Since$\vartriangle ABC$ is a right-angled triangle we know that:
${(AC)^2} = {(AB)^2} + {(BC)^2}$
On substituting the values, we get:
$\Rightarrow$${(AC)^2} = {(3)^2} + {(4)^2}$
This could be expanded as:
$\Rightarrow$${(AC)^2} = 9 + 16$
On further simplifying we get:
$\Rightarrow$${(AC)^2} = 25$
This could be also written as:
$\Rightarrow$${(AC)^2} = {(5)^2}$
Since there is a square on both sides, we take the square root of both sides.
$\Rightarrow$$AC = 5$
Now we have to find the value of $\sin C$,
${\text{sin C = }}\dfrac{{{\text{opposite}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}$
The side opposite to angle $C$ is the side $AB$
Therefore, $\sin C = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AC}}$
On substituting the values, we get:
$\Rightarrow$$\sin C = \dfrac{3}{5}$
Therefore, the correct option is $(B)$ which is $\dfrac{3}{5}$.
Note: It exists $\cos \theta = \dfrac{{adjacent}}{{hypotenuse}}$ where the adjacent side is the side which is next to the angle; it is also called the perpendicular side.
Example: $\cos C = \dfrac{{BC}}{{AC}}$
Also, there is $\tan \theta = \dfrac{{\sin \theta }}{{\cos \theta }} = \dfrac{{opposite}}{{adjacent}}$
Example: $\tan C = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BC}}$
There also exist other trigonometric relations which are $\sec \theta $ $\cos ec\theta $ and $\cot \theta $ which are the inverse of $\cos \theta ,\sin \theta $ and $\tan \theta $ respectively.
In this question, we had to find $\sin C$ therefore, the opposite side to the angle $C$ was side $AB$.
If it was asked to find out $\sin A$ then the opposite side to the angle $A$ is $BC$ which is the base of the triangle.
These $6$ are the trigonometric relations which are present in trigonometry.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




