
Four charges $2C$ , $ - 3C$ , $ - 4C$ and $5C$ respectively are placed at the four corners of a square. Which of the following statements is true for the point of intersection of the diagonals?
A. $E = 0,V = 0$
B. $E \ne 0,V = 0$
C. $E = 0,V \ne 0$
D. $E \ne 0,V \ne 0$
Answer
522.6k+ views
Hint: Electric potential due to a point charge is calculated as $V = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{Q}{r}$ which is a scalar quantity and net electric potential due to multiple charges can be added by using scalar addition. Electric field due to a point charge is $E = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{Q}{{{r^2}}}$ which a vector quantity is.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us draw the diagram of a given problem as, let $P$ be the point at the centre.
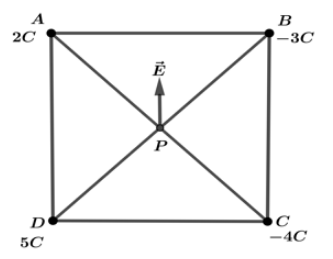
Intersection of diagonals of square and let $L$ be the distance from each charge to the point $P$ such that $AP = BP = CP = DP = L$. Now, we will find the electric potential at point $P$ due to each charge one by one. Electric potential due to $2C$ be given by
${V_A} = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{2}{L}$ Joules per coulomb
Electric potential due to $ - 3C$ be given by,
${V_B} = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{{ - 3}}{L}$ Joules per coulomb
Electric potential due to $ - 4C$ be given by,
${V_C} = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{{ - 4}}{L}$ Joules per coulomb
Electric potential due to $5C$ be given by,
${V_D} = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{5}{L}$ Joules per coulomb
Now, adding all four potentials, we will get net potential at point $P$
${V_P} = $$\dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{1}{L}(5 + 2 - 3 - 4)$
$\therefore {V_P} = $$0$
Hence potential at the point of intersection of diagonal is zero. As we know, an electric field is a vector quantity and their resultant is always added using vector algebra which shows at the point of intersection of diagonals the electric field cannot be zero. So, we get $E \ne 0,V = 0$
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note:Here, $\dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}$ is also denoted as $k$ which is a proportionality constant which has a numerical value of $9 \times {10^9}N{m^2}{C^{ - 2}}$ and the ${\varepsilon _0}$ is called the permittivity of free space. Electric field is a vector quantity whose direction due to positive charge is always away from the point charge and for negative charge it’s towards the point charge.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us draw the diagram of a given problem as, let $P$ be the point at the centre.

Intersection of diagonals of square and let $L$ be the distance from each charge to the point $P$ such that $AP = BP = CP = DP = L$. Now, we will find the electric potential at point $P$ due to each charge one by one. Electric potential due to $2C$ be given by
${V_A} = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{2}{L}$ Joules per coulomb
Electric potential due to $ - 3C$ be given by,
${V_B} = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{{ - 3}}{L}$ Joules per coulomb
Electric potential due to $ - 4C$ be given by,
${V_C} = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{{ - 4}}{L}$ Joules per coulomb
Electric potential due to $5C$ be given by,
${V_D} = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{5}{L}$ Joules per coulomb
Now, adding all four potentials, we will get net potential at point $P$
${V_P} = $$\dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{1}{L}(5 + 2 - 3 - 4)$
$\therefore {V_P} = $$0$
Hence potential at the point of intersection of diagonal is zero. As we know, an electric field is a vector quantity and their resultant is always added using vector algebra which shows at the point of intersection of diagonals the electric field cannot be zero. So, we get $E \ne 0,V = 0$
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note:Here, $\dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}$ is also denoted as $k$ which is a proportionality constant which has a numerical value of $9 \times {10^9}N{m^2}{C^{ - 2}}$ and the ${\varepsilon _0}$ is called the permittivity of free space. Electric field is a vector quantity whose direction due to positive charge is always away from the point charge and for negative charge it’s towards the point charge.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




