
How is forward biasing different from reverse biasing in a p-n junction diode?
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: We have to understand the mechanisms of working in a p-n junction diode to understand the different methods of connection it can be connected to. The forward and reverse bias are the two possible biases for the p-n junction diode systems.
Complete step by step answer:
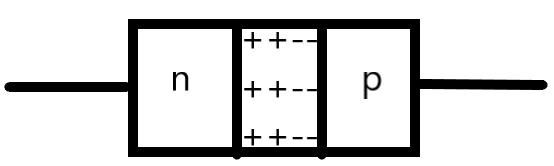
The p-n junction diodes can be connected to an external source in two different methods – the forward bias and the reverse bias. The p-n junction diodes are semiconductor devices which have a p-type and n-type semiconductor merged together. This merging results in the creation of a region in between the two types known as the depletion region, which has a collection of ionized atoms. This is due to the flow of excess charges from each side to the other.
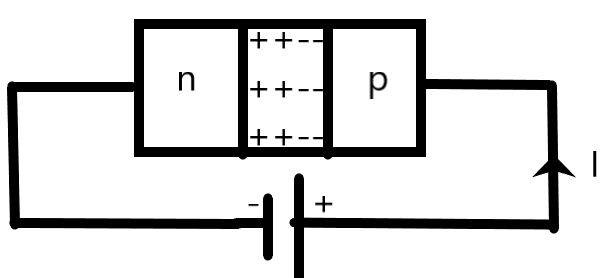
We need to apply the forward bias such that this inbuilt voltage is reduced. From the above figure, we can understand that when a positive terminal is attached to the p-side and the negative terminal to the n-side, this inbuilt voltage is reduced. This is the forward bias.
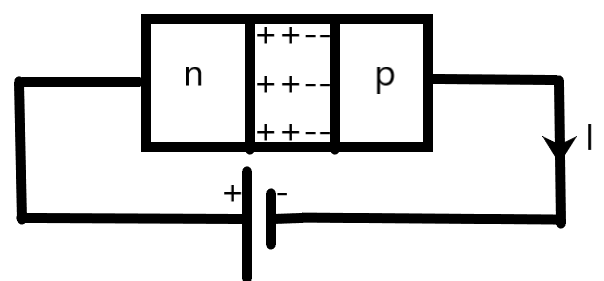
In a reverse bias the opposite configuration is applied. The n-side is connected to the positive terminal and the p-side is connected to the negative side. In this biasing, there will be no current flow as the barrier potential keeps on increasing leading the p-n junction diode to a breakdown.
The forward biasing allows current to pass whereas the reverse bias acts as a high-resistance without or nearly without conducting.
These are the major differences between the two types of biasing.
Note:
The p-n junction diode is designed to work in the forward biased condition, whereas there are other devices such as the Zener diode and avalanche diodes which function after the breakdown voltage is attained and act as voltage regulators in circuits.
Complete step by step answer:
The p-n junction diodes can be connected to an external source in two different methods – the forward bias and the reverse bias. The p-n junction diodes are semiconductor devices which have a p-type and n-type semiconductor merged together. This merging results in the creation of a region in between the two types known as the depletion region, which has a collection of ionized atoms. This is due to the flow of excess charges from each side to the other.

We need to apply the forward bias such that this inbuilt voltage is reduced. From the above figure, we can understand that when a positive terminal is attached to the p-side and the negative terminal to the n-side, this inbuilt voltage is reduced. This is the forward bias.

In a reverse bias the opposite configuration is applied. The n-side is connected to the positive terminal and the p-side is connected to the negative side. In this biasing, there will be no current flow as the barrier potential keeps on increasing leading the p-n junction diode to a breakdown.

The forward biasing allows current to pass whereas the reverse bias acts as a high-resistance without or nearly without conducting.
These are the major differences between the two types of biasing.
Note:
The p-n junction diode is designed to work in the forward biased condition, whereas there are other devices such as the Zener diode and avalanche diodes which function after the breakdown voltage is attained and act as voltage regulators in circuits.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




